Biology grade -9 (New Course)
Biology /Grade -9 (New Course)
Unit -2 (Classification of Organisms)
Classification :The process of grouping of the living being into various groups and sub groups on the basis of similar and dissimilar characteristics is called classification .
Importance of classification :
i)It makes the study of plants and animals easier ,scientific and systematic .
ii)It help the understand the relation between various group of plants and animals .
iv)It gives the ideas about the evolution of plants and animals .
v)It help to brings uniformity in the study of living organism all over the world .
Nomenclature :The system of providing scientific name to all the living organism is called nomenclature .
Binomial system of nomenclature :The naming of each organism by two words a generic name and specific name is known as binomial system of nomenclature .For example :scientific name of human being is Homo sapiens ,where Home is the name of the genus and sapiens is the name of species .
Genus :A genus is the closely related species .For example :All true cats like lion ,tiger,and domestic cats are kept in the genus Panthera or Felis .
Species : The closely related organisms having almost similar characteristics ,and can interbreed freely and produce healthy offspring is called species. For example : All types of human being through out the world are kept in
same species i.e. sapiens
Scientific name of some common organism
Common name Scientific name
1.Pea plant Pisum satvum
2.Onion Alium cepia
3.Mango Mangifera indica
4.Wheat Triticum astivum
5.Mustard Brassica compestris
6.Sun flower Helianthus annus
7.Rice Oryza sativa
8.Orange Citrus sinensis
9.Maze Zea mays
10. Potato Solanum tuberosum
11. Tiger Panthera Tigris
12Horse Equus caballus
13. Buffalow Babalus bubalis
14. Cat Felis domesticus
15. Cobra Naja naja
16. Lion Panthera leo
17. Dog Canis lupus
18. Cow Bos taurus
Two system of classification of organism :Carolous Linnaeus divided living organism into two kingdom i.e. 1)Plant kingdom 2.)Animal kingdom .This is known as two system of classification of organism .It is also called oldest system of classification .
Drawbacks of two system of classification of organism :
i)Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are put together .
ii)Green and non green plant are put together .
iii) Bacteria could not be classified as plants or animals in two system of classification .
Five system of classification of organisms : American scientist Robert H. Whitaker divided living organism into five into five kingdom .This is known as five system of classification .It is also regarded as best and widely accepted classification of system .
Advantages of five system of classification of organisms :
i)Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are kept separately .
ii)The unicellular and multi cellular are kept separately .
iii) The green and non green plants are kept separately .
A.1) Kingdom Monera
B.2) Kingdom Protista
C.3) Kingdom Fungi
D.4) Kingdom animalia
E.5) Kingdom plantae
A.)Kingdom Monera :
Characteristics :
i)They are simple and primitive .
ii)They are prokaryotes because they do not have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
iii)They are unicellular and microscopic.
iv) They have naked D.N.A.
v)They are autotrophic or heterotrophic .
For example :Bacteria ,green algae,azobactor etc.
Fig. Bacteria Fig. Green algae
ff Kingdom Monerra is classified into three subdivision 1:Archaebacteria :
Characteristics: 1.They are most ancient bacteria found n the most extreme habitat i.e. salty area, hot spring, and marshy areas.
2.The structure of cell wall is different from that of the other bacteria which help them to survive in extreme condition.
3.The mode of nutrition is autotrophic .For example :Halobacterium, Pyrolobus
Fig. Halobacteria
2 .Eubacteria:
Characteristics :1.It is also called true bacteria .
2..The cell wall is rigid and made up peptidoglycans.
3.It move with helps of flagella .
4. A few bacteria contains short appendages on cell surface known as pili ,which help in sexual reproduction and attach to the host.
5.They are divided into two categories :i)Gram positive ii) Gram Negative depending upon the nature of cell. For example: Rhizobium ,Clastridium etc.
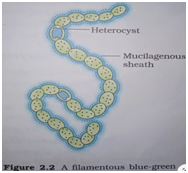
3.Cyanobacteria :
Characteristics :They are also known as blue green algae.
2.These bacteria are photosynthetic in nature .
3.The contains chlorophyll ,carotenoids, and phycobilines .
4.They are found in the aquatic region .For example :Nostoc, pirulina.
B.)Kingdom protista
Characteristics
i) They are eukaryotes because they have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
ii)They are unicellular and microscopic.
iii)They are autotrophic or heterotrophic .
For example :Amoeba, paramecium, euglena ,plasmodium etc.
The kingdom of protista is divided into 3 groups :
d
C.) kingdom Fungi
Characteristics
i.)They are eukaryotes because they have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
iii)They are heterotrophic .
For example :Yeast, mushroom ,mucor etc
The Kingdom fungi are divided on the basis of nutrition into 3 types : 1)Saprophytic :i)They obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substance .For example: Rhizopus, Penicillium, Aspergillus.

2.)Parasitic :i)They obtain their nutrition by feeding on other living organism i.e.plant or animals from their host. For example: Taphrina, Puccina
3.Symbiotic:i)They obtain their food by having an independent relationship association with other species in which both are mutually benefited. For example :Lichens :Lichens are the symbiotic association between algae and fungi .Here both algae and fungi are mutually benefited as fungi provide shelter for algae and in reserve algae synthesis carbohydrates for fungi.
D.) Kingdom plantae
E-Kingdom Animalia
Unit- 3 Life Cycle of Mushroom
1-Introduction
Classification:
Kingdom-Fungi
Example
:Mushroom

The plant body of mushroom consist of two parts:
i)Pileus: This is the part that
gives the fungi its umbrella shape. They are found in a variety of colours, i.e. white, brown, and yellow. It help to protect from the
heat of the sun, rain, and other weather conditions, and protects the
pores or gills where mushroom spores are produced
ii)Gills: Mushroom gills look like net. The gills are also called teeth or
pores. The gill is a structure that appears right under the mushroom cap and produces spores.
Structure of gills: Mature fruiting body is
called sporophore. It is present above the ground. Sporophore
is umbrella like, Sporophore is the reproductive structure. The gills of
sporophore have following structure.
i). Trama: The central part of gill is
called trama. The hyphae are compact
in the trama. ii)Hymenium: Basidia
are present on gills. Basidia are ‘ranged compactly to
form hymenium. Hymenium are present on both
surfaces of the gills The tips of this layer develop
basidia. Each basidium develops 2-4 sterigmata.
Basidiospores are borne on sterigmiata.
iii). Paraphysis: Gills have two types cells one
type of cells are sterile like basidia are called paraphyses.
iv)Basidia: : Gills have two types cells one
type of cells are sterile other cells are fertile
are called basidia .Each basidia of gills contains two nuclei of opposite
strain that help to produce basidiospore during
sexual reproduction.
iii)Annulus: An annulus
is the ring-like
or collar-like structure found on the stipe
of some species of mushrooms. The annulus represents the remaining part of the
partial veil, When the cap grows out and breaks through the
veil,
to expose the gills or other spore-producing surface.
iv)Stipe: The stipe is the long, vertical part of the mushroom that holds the cap above the
ground.
v) Mycelium. The mycelium is a collection of thin hair-like strands that grow outward and downward into the
soll in search of nutrients. The mycelium of mushrooms
acts like the roots in flowering plants and can produce new mushrooms when the conditions are suitable.
Reproduction :.In mushroom reproduction takes place by two ways :1.)Aaexual reproduction takes place by formation of resting spore are called thalmydospore .
2.Sexual
reproduction takes
place by fussion of 2 opposite strain of primary mycelia.
In mushroom sexual reproduction takes place by means of basidiospore
present in basidia of gills.Gills have two cells: Basidia and paraphysis. Basidia are fertile cell and paraphysis are sterile cell. The basidia contain
two nuclei of opposite strain. These nuclei fuse to form diploid nucleus which further undergoes
meiosis cell to produce four haploid nuclei.Four finger like
structure are developed on each basidium is called sterigmata then Each haploid nucleus goes to each sterigmata and surrounded by a small amount of cytoplasm
forming four haploid i.e.2 + basidiospores and 2-basidiospre.. When these spores are
released from the basidium, they germinate into mycelia with the own strain of nucleus.
When a basidiopores gets favourable conditions, it germinates
into a primary mycelium with one nuclues per cell. As each cell has only one type of
nucleus the primary hypha is monokaryotic (homokaryotic) in nature. Mushrooms then reproduce with the help of the two
monokaryotic primary mycelia of opposite strain. When two monokaryotic
primary mycelia come together, their cells fuse together to
form a dikaryotic secondary mycellium. This dikaryotic secondary mycelium grows to form a collection of mycelia that later form a button stage of mushroom which finally grows into a mushroom.
The advantages of mushroom :
1. Mushroom is taken as a nutritious food because it contains proteins, vitamins and minerals in a remarkable amount.
2. Mushroom helps to prevent high blood pressure, blood cholesterol, heart disease
diabetes, cancer etc.
4. Mushroom is the major source of protein. The protein of mushroom
contains the essential amino acid.
7. Mushroom is useful for the preparation of antibiotic medicines.
The disadvantages of mushroom are:
1. Some mushrooms are poisonous, may cause the death of person
taken.
2. Some mushrooms may
paralyse the central nervous system.
Mushroom Farming:
Mushroom farming has different techniques on the basis of species, Mushroom can be cultivated on the straw, log of wood etc.
a)Collect the straw from
the farm and cut into the small pieces of 1 to 2 inches
c) Dry the boiled straw and keep the straw in the small
polythene bags.
d) The straw should be managed in
layers and in every layer keep the spores of mushroom.
e) The plastic bags are kept on the dark place for about 7 days. We observe the small
f)Make
about 4 small holes on the plastic and pour water according to the necessity.
g)The mushroom will start to grow and will be
adult near about 25 days
Storage and Uses of Mushroom
The simple process of making sukuti from mushroom or to storage for long time as
given below:
a) Clean the mushroom properly.
b) Cut the mushroom into small pieces.
c)Keep it on the boiled water.
d) Dry up the mushroom with help of oven or dry air or sun.
e) Do the packaging in the air tight
plastic bag.
Non-edible mushroom :For example :
2.Death Cap mushroom
3.Autumn Skullcap mushroom
4.web cap mushroom
1.Enoki Mushroom
2.Button Mushroom
3.Shitake mushroom
All the mushrooms are not edible because ,some are also poisonous,so following points help to distinguish the poisonous and non- poisonous mushroom.
For poisonous
a)The mushroom with grey
colours are poisonous.
b) The mushroom with white gills are too poisonous
c)The red mushroom are poisonous
For edible mushroom
1.Choose mushrooms without white gills.
2.Select mushrooms without red
on the cap or stem.
3.Look
for mushrooms without scales on the cap.
4.Seek out mushrooms without a ring around the stem.
Evolution
:The process of origin of complex form of life from its simple form is called
evolution.It is slow ,continuous, and irreversible process .There are
some major of veiws
the origin of life or evolution:
a)Special
creation by god :According to
this view life was originated on the earth by super
natural power of god .He created all organisms and all life on the
earth.For example :According to Hindu Mythology
the whole universe was created by God Brahma
with his own desire .The first man was Manu and first
women was Sharadha.
2.Theory
of abiogenesis or spontaneous generation :
This theory was given by Plato, Thales, , Aristotle, and Von
Helmont. According to this theory living organisms were
originated from non living materials spontaneously (one that occurs on its own, without any
energy input from the outside.) This theory also states that life was originated from Nile
River like frog, toad, snake, fish and crocodile. For
example: Aristotle proposed that worms, insect, fish, frogs are
developed from soil. Van-Helmont stated that young mice could arise from wheat .This theory has no scientific evidence, therefore this theory was
rejected by scientist.
3. Theory of Biogenesis (Life from life) :According to this theory life forms produce life forms, but life were not originated from the non living substances. This theory has no scientific evidence, therefore this theory was rejected by scientist.
4. Organic evolution theory :According to this view 'gradual and orderly change of living beings from simple to complex form' .or first living creatures were unicellular, aquatic organism, then other different simpler organism were developed again from them complex organisms were developed ,due to variation in each and every generation there is appearance of new characters ,but it is slow and continuous process. Living organisms are made up of mainly the organic substances, hence their evolution is referred to as evolution.
Evidences of organic evolution :The following evidences
also support the theory of organic evolution :
2 Evidences from comparatively morphology and
anatomy.
3.Evidence from vestigial organs .
4. Evidences from embryology.
5. Evidences from distribution of organisms.
6. Evidences from connecting links (bridge animals).
1. Evidences from
paleontology.:
Paleontology is the study of fossils which are remains of dead animals or
plants in the
earth's crust of sedimentary rocks.
The
fossils of ancient organism's were found
in the deeper part of the earth's crust and
more and more developed organisms with
fossils were found in less depth from the earth's surface in crust. This shows that present
advanced formed of life was developed from ancient primitive form of life. This
provides evidence of organic evolution.
2. Evidences from comparatively
morphology and anatomy:
Anatomy studies the formation of the structures whereas morphology studies the physical forms of those structures. For example:
i)Homologous organs :Those
organs which have same fundamental structure but
perform different function
in different organisms are called homologous organs.i.e forelimbs of whale (flippers), bat
(wings), birds (wings), horse and man. They contain similar bones . This provides evidences
that they must have evolved from common
ancestors.
ii)Analogous organs: Those organs which have different fundamental structures but
perform the same function in different organisms are called analogous organs. For example the wings of an insect (dragonfly), bird (eagle),
mammal (bat) and reptiles (pterodactyl), perform the same function of assisting in flight but differ in the structure. This provides evidences that they must
have evolved from common ancestors.
Thus, comparative morphology and anatomical studies of homologous organs provide evidence for the organic evolution.
3.Evidence from vestigial organs: Organs that are poorly developed, non functional or useless to the process are called vestigial organs. For examples of vestigial organs in human beings are vermiform appendix, caudal vertebrae coccyx, vestigial wings of flightless birds such as ostriches.It is assumed that vestigial organs were fully developed and functional in their ancestors but due to change habitat these were no needed by the organisms and have gradually reduced to vestiges. This suggest that these organs evolved from same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus, vestigial organs provide evidence for the organic evolution.
4.Evidences from Embryology :The
embryo of some different animals usually resemble each other very closely i.e. embryo of fish, tortoise ,hen, rabbit, man, seem very similar in initial stage. This suggest that these organism evolved from same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus, embryo provide evidence for the organic evolution.
5. Evidences from distribution of organisms: Our earth has different geographical structure like high mountains, hills, plain lands, rivers, oceans, etc. If we observe the organisms of same species in these different geographical structure then we see variations among them in shape, size, colour and so on,due to different geographical structure. For example yak and cow, This suggest that these organism evolved from same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus, distribution of organisms provide evidence for the organic evolution.
6. Evidences from connecting links (bridge animals): The shape ,structure,and behaviour of some higher animals resembles with some lower animals i.e. cat and tiger, dog and fox. This similarities between these higher and lower animals suggest that these organism evolved from same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus, connecting links (bridge animals)provide evidence for the organic evolution.
7.Genetic evidence :A heredity materials an all organism is D.N.A. ,and D.N.A. controls heredity
characters in all organism ,Basic composition of D.N.A. in all organism is similar.This similarities in genetic structure suggest that these organism evolved from
same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus genetics materials provide evidence for the organic evolution.
8.Physiological evidence :The physiological life process i.e. digestion, respiration, nutrition, excretion and circulation etc in the most of organism seems similar. This similarities in physiological process suggest that these organism evolved from same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken place. Thus physiological process provide evidence for the organic evolution.
8.Bio-chemical evidences :The chemical present in organism body are called biochemical i.e. hormones, enzymes, and other chemical substances ,their
function structure are similar
in different organism .This similarities
in bio-chemical of different organism suggest
that these organism evolved from
same ancestors i.e. evolution has taken
place. Thus bio-chemicals provide evidence for the organic evolution.
Theories of organic evolution: The theories that proposed the mechanism of organism are called theories of organic evolution
.There are some major theories of organic evolution :
1. Direct environmental effect
and new needs
2.Use and disuse of organs
3. Inheritance of acquired
character
iv. Speciation
1. Direct environmental effect
and new needs :According to Lamark due to change in environmental condition the habit and habitat of living organisms are
also changed. This results in the new needs or requirement for an organism and development of new organs occur in organisms.
Weakness of organs ∝ disuse............ii
For example : The ancestors of giraffe were bearing small neck and
forelimbs and. were like horses.
But as they were living in places with no surface vegetation,
they had to stretch their neck and
forelimbs to take leaves for food, which resulted in the slight elongation of these parts from generation to generation as the result that a race of long necked and long fore limbed animals were developed
iv. Speciation: Formation of new species due to the modification and variation in species is termed as speciation. Due to environmental condition, new needs arises due to which some organs are more used and some are less used resulting in the strengthening, development, enlargement and change take . These changes are transferred from one generation to another making them different from which they are originated. After a long period of time, this results in the formation of new species and evolution occurs.
Criticism of Lamarckism
1..The change in the
structure of a body by use and disuse of
organs is not practically experienced .
iii. All the acquired characters are not inherited from one generation to another.
2. Theory of Natural selection (Darwinism) :Charles Robert Darwin
was a great philosopher and naturalist of
England. He explains theory of natural selection in his
book "the origin of species" .The evolution theory of Darwin is
based on following facts.
Facts of Darwinism
1. Over production (Rapid multiplication) or
Enormous fertility
2.The struggle for existence
3. Survival of the fittest
5. Variation and speciation
1. Over production or Enormous fertility: According to Darwin every organism have capacity to reproduce more and more so organism on the earth increase in geometrical ratio.If all the organism are survived then earth will be full of organism For example: A salmon produces 28000 eggs in a season. ,but due to environmental checks it is controlled.
2.. The struggle for existence: :
According to Darwin organism on
the earth increase in geometrical ratio but natural resources of earth cannot increase ,so there is always competition of struggle for better place and food . The one who can struggle with their own species is called intraspecific
struggle and with other species is called inter specific struggle
in the environment; so where they live, can struggle for survive
and have existence in the world. Otherwise they go extinct
and have no any future generation.
1. Darwin did not explain
the effect of use and disuse and
the presence of vestigial organs.
ii. Not only the useful variations are inheritated.
iii. Natural selection is not only the sole cause of speciation.
Mutation Theory of Hungo de
Vries
Hungo de Vries in his book 'Die mutations theorie' (1901) proposed the mutation theory. Mutation
is the sudden change in chromosomal
structure. Organisms that effected
by mutation or on which mutation occurs are called mutants and the and factors that brings out mutation
are called mutagene .Example of mutation
are six fingered limbs,
disability of person by birth, cut on the lip, etc.
Theory of Mutation
Mutation is the sudden change seen in the offspring due to the genetic change in the organisms. Double headed snake, six fingered persons are the examples of mutation.
2.Mutation is base of evolution.
3.The new characters is
seen suddenly in organism and the characters is functional.
4) Mutations is inherited to the another generation.
Criticism
of mutation theory
a) The theory of mutation does not give any direction of theory of evolution.
b) He did not explain the role of nature in the field of mutation.
c) Generally the mutation is recessive.
Effects of mutation on
evolution :The main
base of evolution is mutation. But some mutation brings positive and some brings negative effect in the process of evolution.
a)Neutral
Mutation: Some mutation does not
being any positive and negative
effect in the organism is called neutral mutation

Unit -5A Body structure and Life process A- Tissue
Cell :-The structural and functional unit of
life is called cell. Or Basic
unit of living being is called cell .
Tissues
:-A group of cell which is similar in structure and function is called
tissue .for example :Bone
,blood , muscle, etc are the animal tissues ,and xylem and phloem etc. are the example
of plant tissues .They
are two types : A)Animal tissues
B)
Plant tissues
On the basis of
division the plants tissue are classified into two types :
2.)Permanent
tissue
A)Meristematic
tissue :The tissue which is made up of from meristematic cells is called
meristematic tissue :
i)It has capacity of cell division .
ii)It has thin wall .
iii)Cytoplasm is dense .
iv)Intercellular space is absent .
Types
of meristematic tissue :On the basis of occurrence and position
in the plant ,meristematic tissues are divided into 3 types :
1)Apical
meristem: The meristematic tissues which are at the tip of stem ,root and
their branch is called apical meristem .It help to increase the length
root and stem .
2.)Lateral
meristem :The meristematic tissue which occurs on the side of root and shoot is
called lateral meristem .It help to increase the thickness of root and
shoot .
3.)Intercalary
meristem :The meristematic tissue which are present at he base of leaf ,base of
inner node, or at the base of leaf is called intercalary meristem .It help
for elongation
of organs .
B.)Permanent
of tissue :A group of cell that do not have power of cell division but have
permanent shape for special function is called permanent tissue .The major
function of permanent tissue are to conduct food, and water to different
parts of plants ,to provide mechanical support and secrete substance i.e. oil,
resin, latex etc.
1)Simple
Permanent Tissues :
The permanent tissue that consist of only one type of cell and are similar in
origin ,structure and function is called simple permanent . These are of three types –
i)Parenchyma
ii)Collenchyma
iii)Sclerenchyma
i)Parenchyma
tissue :The simple permanent tissue in all the soft parts of the
plant body is called parenchyma tissue .They are found in soft parts of the plant
body i.e. cortex (Outer region ) and pith (central region )of root and
stem .
Features
:
I)They have inter cellular spaces between them.
ii)The cells of this tissue are thin walled and polyhedral in shape
Functions
:
They act as storage for food and water.
They provides temporary support to the plants .
Types
of Parenchyma :They are also 2 types :
a)Aerenchyma :When
parenchymatous tissue having large air spaces is called
Aerenchyma.These help in gaseous exchange and provide buoyancy to plant. Or to float the
plants .
Features
:
i)They cell of this tissue are thick walled and longer than that of
parenchyma.
ii)They have no
inter cellular space between them.
Functions
:
i)They provide mechanical support to the growing plants i.e. youn stem,
petiole of leaf .
iii).
Sclerenchyma :The simple permanent tissue in which cells are thick walled and dead is called
sclerenchyma tissue .They are found in stem ,root, veins of
leaves and hard covering of seed .
Features
.
i)The cells of this tissue are dead and thick walled .
ii)They have no inter cellular spaces .
Functions
:
i)They provides mechanical support to the plants organs .
2)Complex
permanent tissues :The Permanent tissue which are made from xylem and phloem tissue
i.e.living and dead cells is called complex permanent tissue .
Complex
tissues are of following two types.:
1.)Xylem
tissue:The complex permanent tissue in which cells are thick, tubular, and
often dead and responsible for conduction of water from root to leaves is
called xylem.
i.)Xylem
Tracheids :
They help in conduction
of water in pteridophytes and gymnosperms and provide mechanical support
plants.
The cross wall (end wall) at both the ends dissolves and form a pipe like channel.
iii)Xylem
Fibers :
It provides tensile
strength and mechanical strength.
They store food materials.
2.)Phloem
tissue: The complex permanent tissue in which cells are tubular and living
and responsible for conduction of food from leaves to different parts of the
plants body is called Phloem tissue .
They help in conduction of food material.
ii)Companion
Cells :
They support the sieve tube in transport of food.
They are absent all monocots and some dicots.
iii)Phloem
Fibers (bast fibers) :
They provide mechanical support to the plant.
iv)Phloem
Parenchyma
The chief function of parenchyma is to store food material and other
substances like mucilage, tanins and resins.
3.)Special
Tissue :The special plant tissue which is formed by glandular and
lactiferous tissues to perform a particular function is called special tissue .Glandular
tissue produce resin
,oil gum etc. and lactiferous tissue produce milky or yellow watery
juice called latex .
A)
Animal tissue :A group
cell animal cells having the same origin ,structure and function is called
animal tissue .
Types
of Animal Tissue :-They are 4 types
1.)Epithelial
Tissue
The animal tissue
which cover and inner lining of the body surface, organs ,duct,
blood vessels is known as epithelial tissue.
Characteristics
of Epithelial Tissue
Following are the important characteristics of epithelial tissues:
1. The of cell of these tissue are
a single-layered
or multi-layered.
2. The tissues have the power to regenerate.
3. The cell are arranged on a basement membrane .
4. The tissues form the covering of organs and inner
lining of cavities .
Functions
of epithelial tissues :They have following functions :
i)Protection
ii) Secretion
iii)Sensation iv)Absorption v)
Excretion vi)Diffusion vii)Cleaning
Types
of epithelial tissues :On basis of structure and functions they are
following types :
i)Pavement
epithelial or squamous epithelial
ii)Cubical
epithelial tissue
iii)Columnar
epithelial
iv)Glandular
epithelial
i)Pavement epithelial :The epithelial tissue having plate like flat
hexagonal cell arranged without inter cellular space is called pavement
epithelial .
Location
:They are found in outer layer lungs ,kidney, heart, blood vessel
etc.
Functions .The major
functions of this tissues are covering ,protection ,filtration etc.
ii)Cubical
epithelial :The epithelial tissue made of single layered cubical cells is called
cubical epithelial .
Location
:They are found in the duct ,inside kidney, thyroid gland excretory
organs inner parts of uterus etc.
Functions
:The major functions of these tissues are covering ,protection, and secretion etc.
iii)Columnar epithelial :The epithelial tissue
of single layered longated column like is called columnar epithelial .
Location
:They are found in large duct of kidney, inner part of stomach, inner
parts of respiratory and reproductive system .
Functions :The major
functions of these tissues are secretion and absorption .
iv)Glandular
epithelial :The tissue which is found in various glands of the body is called
glandular epithelial .
Functions
: The major functions of this tissues are secretion of
hormones enzyme, mucus, saliva digestive juice etc.
2.)Muscular
tissues : The tissues which form muscles of the body is called muscular
tissue .It is responsible for the movement of the body .
3.)Connective
tissue :The tissues which help to connect or bind one tissue to another tissues
or support them to keep in proper place is called connective tissue .It
is to
bind help to bind ,support ,and pack together different organs the body .
4.)Nervous
tissue :The tissue which contains densely packed nerve cell or neuron is called
Nervous tissue .It help to receive massage impulses from different part of
body and conduct impulses to the brain and spinal cord .
Unit:(5) - Body structure and Life
process
B-Nervous & Glandular system
Nervous system: The group of organs working together to conduction of massage from one
part of body to another part and co-ordinates the all activities of body is
called the nervous system .
iii)It regulate involuntary activities of smooth organ i.e. lungs
,kidney heart ,alimentary canal.

1.)Central nervous system(CNS) : It consist of mainly
two parts :ie A)Brain B) Spinal cord
The biggest and upper most part of central nervous system is called brain. It is situated in cranial cavity or cranium and surrounded by 3 layers is called meninges ie Duramater ,Piamater and Arachnoidmater .The space between inner two layers is filled with a fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid .It protects brain from injuries and absorb shocks .The brain is also divided into mainly 3 parts :

Note :Damage to the
cerebrum causes of coma .
iii)It maintenance the muscles tones .
Note
: Small injury in cerebellum causes of dizziness that disturb the
body balance .
iii)Medulla oblongata : The lower most and small part of
brain is called medulla oblongata .The lower portion of it has many nerve
tracts that connect with spinal cord .
Functions i)It controls the
system ie respiratory ,heart beat ,blood pressure ,breathing etc .
iii)It controls the contractions and expansion of blood vessels .
Note
:- injury in medulla oblongata causes of instant death .
B)Spinal cord : A long soft and
white rod like structure present inner part of back bone is called spinal cord
.It is also surrounded with 3 layers meninges .
Note
: Any injury or shocks to the spinal cord due to disease or accident
,causes of paralysis of the body below the point of injury .
2.)Peripheral nervous system(PNS) :-It consist of mainly
following parts i.e.)Cranial nerves or fibers B) Spinal nerves or
fibers
i)Sympathetic nervous system :The autonomic nervous
system that
increase the working rate of smooth organs i.e. respiration , heart beat
stomach , intestine ,urinary bladder etc. and decrease the secretion
of glands is called sympathetic nervous system.
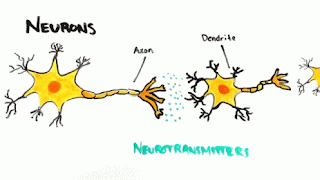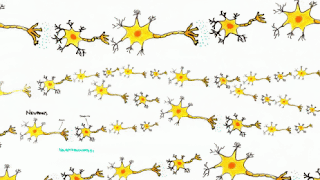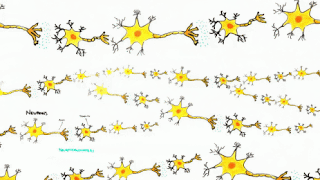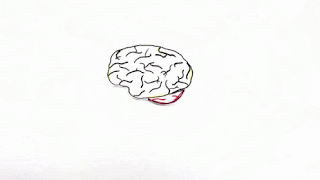
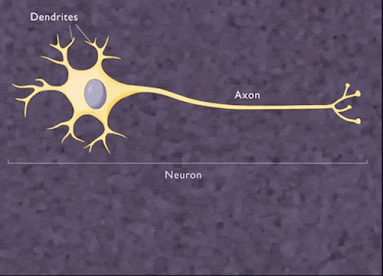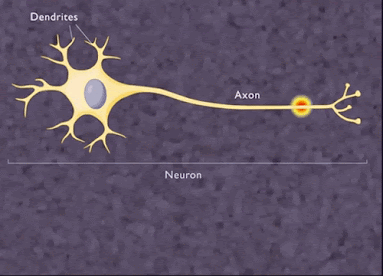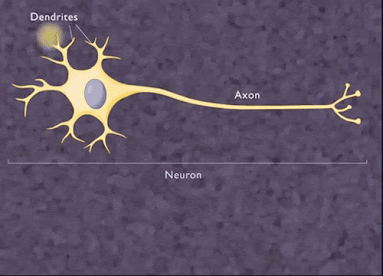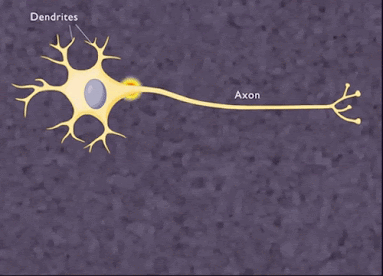
Neuron or nerve cell :
The structural and functional unit of nervous system is called neuron
.It is also called largest cell present in the human body .It consist of
following parts :
i)Cell body or cyton : It consist of a
nucleus and surrounded by a granular cytoplasm (Nissl’s
granules).It produce
cytoplasm and controls metabolism in the axon and dendrite .
iv)Connector neurons or mixed
neuron(relaying) : A group of nerves
which are made up from combination of sensory nerves and motor nerves is called
connector nerve .It act as links between sensory nerve and motor nerve for
distant transmission of nerve impulses and located in the brain and spinal cord
.
Unit:(5) - Body structure and Life process
B-Nervous & Glandular system
Glandular system
Gland :A group of cell that help in secretion is
called gland .They
are two types :
i)Exocrine gland :The gland that have
duct are called exocrine gland .They secrete enzyme .The secretion
of this gland is carried by the duct to the organs .They lie closely to the
target organs. For example :Saliva from salivary gland, tear from tear gland
,sweat from sweat gland etc.
ii)Endocrine gland
The ductless gland are called endocrine gland. They secrete hormone .The secretion
of these glands is directly poured into the blood stream. They may lie far
from the target organs .For example :Pituitary gland,
thyroid gland etc.
Major endocrine glands in human body :
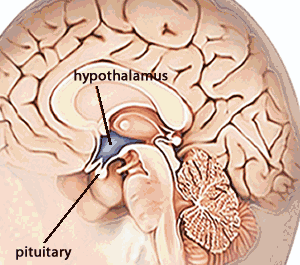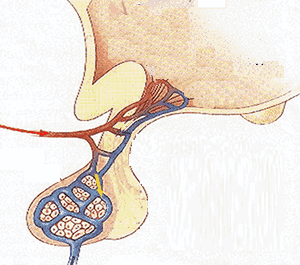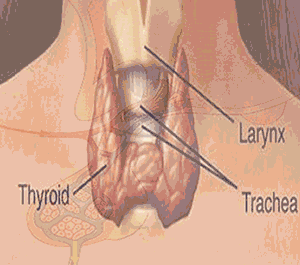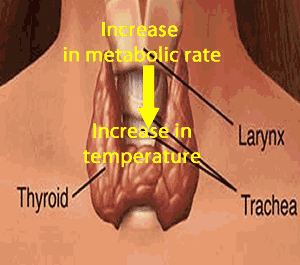
1.)Gland : Pituitary
gland
Location :Below the brain
Functions :i)It control physical and mental growth of the body .
Location : In the
neck or throat
Hormones : i)
Thyroxin hormone
Function
: i)It control the rate of metabolism by which body
burn calories into energy for mental and physical growth .
Note
: Over
secretion(hyper secretion):increase rate of metabolism ,increase pulse rate
,sweating, weight loss, under secretion(hypo section): lack of iodine and
causes of enlargement of thyroid gland is known as goiter.
ii)Calcitonin
hormone
Functions :i)It regulate
the calcium level in blood .
3.)Gland : Para
thyroid gland
Location :
In backside of thyroid gland in 2 parts 4 in number.
Hormones: i)
Parathyroid or parathormone hormone
Function
: i)It controls the calcium and phosphate level in the
blood .
iii)It controls the proper development of the bone .
Note : Over secretion (hyper
secretion):causes of tumour and stone in kidney and gallbladder , under
secretion(hyposecretion): decrease calcium level in blood and twitching of
muscles is known as
tetany .
4.Adrenal
gland : It consist of Two parts:
A)Outer
is cortex B)Inner
is medulla
Location
: In the anterior part of each kidney 2 in number.
Hormones : i)Cortisone
or corticoids hormone
Function :i)It regulates
the metabolism of carbohydrates ,fat and protein.
iii)It help to adopt the body in extreme condition i.e.
extreme heat ,cold, burn, infection etc-sex
iv)It also produce sex hormone in small amount for later year when
sex gland decrease their secretion.
Note
:over
secretion(hyper secretion) causes of abnormal sexual maturity in
early age, under
secretion(Hyposecretion) causes of addison’s disease .
Hormone
:
i)Adrenalin hormone
Functions: i)It help to
prepare the body to face for emergency situation by increasing
blood pressure, heart beat and glucose level in blood ,so it is also
known as
emergency gland.
Note: Over secretion (hyper
secretion) cause of high blood pressure ,hyper tension. Under secretion
(hyposecretion ) causes of weakness ,low blood pressure, unconsciousness.
Location
: In the abdominal cavity behind stomach and the top of abdomen.
Hormone
: i)
Insulin hormone
Functions
: i) It help to balance or remove excess
sugar from the blood by converting sugar into glycogen and stored in the liver
.
Functions :i)It increase
sugar level in blood if sugar level become low by converting glycogen into
sugar from liver .
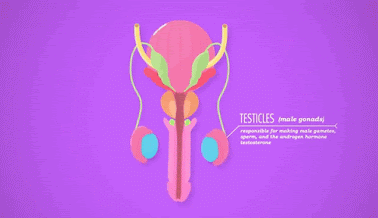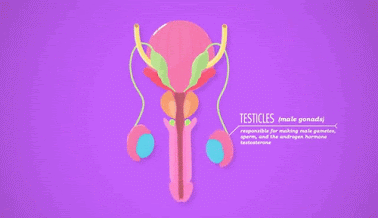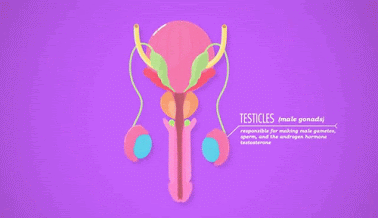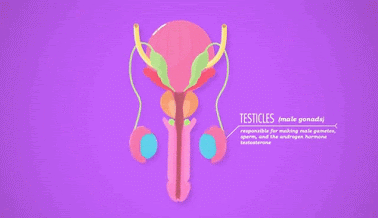
A)Testes
:
Location : In male
reproductive organ.
Hormones :Testosteron
hormone
Functions : i)It regulate the
development of secondary sexual characters i.e.Voice, beard etc.
B)Ovary
:
Location: In male
reproductive organ.
Functions: i)It stimulate
female sex organs i.e. uterus and ovaries.
Plant Hormones: The chemicals which are produced by plants that regulate their growth, development, reproductive processes,
longevity, and even death,are called plant
hormones or "Phytohormones" For example : indole (auxins), terpenes (Gibberellins),
adenine (Cytokinins), carotenoids (Abscisic acid) and gases (Ethylene).
i)Plants growth promoters
ii)Growth inhibitors
iii)Growth inhibitors and
promoters.
Use of plant hormones in agriculture:There are many types of plant hormones.
They are used in agriculture and horticulture for specific effect.
2.Cytokinins: In
the roots, cytokinin is produced. Cell division in roots and the shoots of plant and
enlargements are promoted by cytokinins. Lateral
bud growth is signaled by the movements of cytokinins from roots into
shoots. In fruits and roots, in the embryo of seeds and
endosperm cytokinins are found. Lateral bud
growth is promoted by cytokinins.
If the concentration of auxin is higher then roots will form and if the auxin is less, shoots will form.
4.)Tissue culture: A modern
technique of producing new plants from isolated plant cells or small pieces of
plant tissues in culture solution under controlled condition is called tissue
culture . In tissue culture after days small tissue grow into an
undifferentiated mass is called callus ,then
callus is transferred into culture solution i.e.
mixture of auxin hormone that help to
growth roots and cytokinin that
help to growth of shoots It is widely used to produce orchids,
carnations, chrysanthemums asparagus .
Steps in tissue culture
i. A
piece of tissue (generally from shoot
portion) is taken which is called explant
ii. An explant is introduced in an artificial culture solution containing minerals, vitamins, nutrients and growth
hormones like auxin and cytokinin under sterile condition and the vessel is left at room
temperature.
iii. With days, explant starts to divide and develops into an
unorganized an undifferentiated
mass called callus.
iv. Now, small portion of callus is transferred to another cultural solution containing different plant hormones responsible for
differentiation of parts
v. After some days, cells differentiated to roots and shoots and
plants are formed.
Advantages of tissue culture
i. Indefinite number of genetically identical plants can be produced in a short time
iii. Disease resistant plants can be growth by tissue culture
technique.
i. It is a tedious (boring)process which should be done in sterile
condition.
ii. It is expensive method of vegetative propagation.
iv. There is a high chance of contamination (Pollution)in tissue culture.
Unit- 6 Nature and Environment
Ecology :The branch of biology that consisting study of the interrelation between the living and nonliving, organism or biotic and abiotic factors of the environment is known as ecology
Factors influencing the
ecosystem/components of ecosystem:
A. Abiotic Components:
The non-living or physical factors of the ecosystem are
called abiotic component. They are also known as the climatic factors. For example: air, sunlight,
soll, wir etc.
i.Air. Air is the mixture of gases in the atmosphere. It consists of
Nitrogens(78%) Oxygen (21%), Carbondioxide (0.03%) and other gases (0.97%). The
gases play a functioning for the survival of living organisms. For example: Oxygen is require by all the living
organisms for
respiration ,Carbondioxide is required by plants for photosynthesis.
ii. Sunlight/solar energy: The heat and light energy
that is provided by the sun is known solar energy. Sunlight is trapped by chlorophyll present in plants is used for photosynthesis. Heat and light is also
necessary for
survival of living organisms. It is also responsible for climate change.
iii. Soil: Soil is composed of minerals, microorganism organic
matter, air, water, etc. It is a major source of food for living organisms
iv. Water: It the basic requirement of
life. All the plants and animals require water for their day to day functioning.
B. Biotic Components:
The living organisms of the ecosystem are known as biotic components. They are grouped into three classes:
1.)Producers: The organisms which can prepare their own food are known as producers. They are also known as autotrophs .For example : green plants like: phytoplankton i.e. Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Cladophora, Diatoms, Volvox.,
trees shrubs, etc. or chemosynthetic bacteria. Producers are the primary basis of life.
2.)Consumers: The organisms that consume the food prepared by the producers are called consumers. They are also known as heterotrophs Consumers can further be divided 3 types..
i).Primary consumer :Those consumers that directly depends on green plants for their food are known as primary consumers or herbivores. Zooplanktons ,Tadpoles, protozoans, molluses, etc. are the examples of
primary consumers of aquatic ecosystem. Similarly Rabbit, Grasshopper , goats,
beetles, etc
are the examples of herbivores terrestrial ecosystem.
ii.)Secondary consumer: The consumers that depends
on primary consumer and green plants for their food are known
as secondary consumer or omnivorous.
For example: small fish, Frog
etc,are example of secondary consumers of
aquatic ecosystem similarly cats, dogs, foxes, wolves (Buaso),
etc are the example of secondary consumer of terrestrial ecosystem.
iii.)Tertiary consumer :The consumer that depends on secondary consumers and
primary consumer for their food are known as tertiary consumers or carnivores or top level
consumers.
For example:Large
fish is example of tertiary consumer of aquatic ecosystem similarly tiger,
lion, eagle, vulture, etc are the example of tertiary consumer of terrestrial
ecosystem .
3). Decomposers: Those microorganisms that decompose the dead bodies of plants and
animals are called decomposers.
They are saprophytic
organisms.
Decomposers break
down the complex organic
compound of plants and animals into simpler substance.
For example: bacteria, fungi,
etc.
Interrelation between abiotic and biotic components
The producer prepare food by using the abiotic components of the
ecosystem like sunlight, soil, air, water, etc. The food produced is consumed by the consumers like herbivores and herbivores are further consumed by carnivores. When the living organisms die, their complex organic
structure is broken down into simpler substance by the decomposers and get mixed up with the soil. The producers as such again
produce food with the materials present in the soil. Thus, there is a direct relation established between
abiotic and biotic components of the ecosystem.
Interrelationship between plants and animals
The green plants (producers) produce food by converting simple inorganic matter(sunlight,CO,H,O) into complex organic matter(food). On the basis of production and consumption of such food, living organisms are divided into two major categories of autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Autotrophs
The organisms which produce their own food by using the abiotic
components of the ecosystem are
called autotrophs. The process by which producer convert the inorganic compound into organic compounds is known as autotrop For example : Green plants, phytoplanktons etc. are the examples of autotrop organisms
When sunlight and chlorolhyll is required for the preparation of food then it is know as photoautotrophic nutrition. But when sunlight and chlorophyll is not required for the preparation of food then it is known as autochemotrophic nutrition. For example :bacteria..
Heterotrophs
The organisms that cannot produce their own food and are dependent upon other organisms for food are called heterotrophs. The process by which organisms obtain food from other
organisms is known as heterotrophic nutrition. On the basis of nature of food consumption, they are divided into following types:
i.Parasitic organisms: The organisms that obtain food by living inside or outs the body of other organisms are known as parasitic organisms or parasites. Those organisms whose body is infected by parasites are known as host. Tapeworm mosquito, leeches, etc are a few examples of parasites.
The parasites which are found inside the body of the host are known as endoparasites where the parasites which are found on the outside body of the host are known as ecto parasites.
ii. Saprophytic organisms: The organisms that obtain food from dead and decayed organisms are known as saprophytic organisms or saprophytes. They are also called myco-heterotrophs Bacteria, Fungi, plants without chlorophyll, etc. are the examples of saprophytes.
iii. Holozoic organisms: The organisms that obtain food in the form of solid organic material produced by other organisms are known as holozoic organisms or holozi heterotrophs. The process of consumption food by holozoic organisms is also known as animal method of nutrition. Holozoic organisms are further classified in the following types:
a. Herbivores: The organisms that directly depends upon plants for their food are known a herbivores.
For example: Cow,
Horse, etc.
b.Omnivores: The organism that depends on primary consumer and green plants for their food are known as omnivorous. For example: cats, dogs, foxes, fish, wolves (Buaso), Human,
Bear, crow etc.
c.) carnivores :The organism that depends on secondary consumers and primary consumer for their food are known as tertiary consumers or carnivores or
top level consumers. For example: tiger, lion, eagle, vulture, etc.
Ecosystem: The inter-relationship between abiotic and biotic factors to their environment.
Types of ecosystem:
Mainly ecosystem is classified into two types. They are:,
Ecosystem found on land
is known as terrestrial ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems are of three types. They are
i) Forest Ecosystem
ii) Grassland Ecosystem
iii) Desert Ecosystem
Forest Ecosystem: The ecosystem found in the forest environment is known as forest
ecosystem.
1.Producers: Green plants like grass, trees, etc
2.i) Primary consumer: Deer, Grasshopper, Zebra, etc
ii)Secondary Consumer
Omnivores : Wolf, Jackal, etc.
iii)Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores : Lions, Tigers, etc.
3.) Decomposers or Microorganisms : fungi, bacteria, etc.
The ecosystem which is found in water is known as aquatic ecosystem. Aquatic ecosystem are of two types
i)pond ecosystem
ii)sea and ocean ecosystem.
2.i)Primary Consumers: Zooplanktons, mollusca, Daphnia, etc.
ii) Secondary Consumers: Insects, fishes, crab, etc.
3.Decomposers: Bacteria and fungi, etc.


Food chain can further be
divided into three types.
They are:
1. Grazing food chain: The food chain in which the producers are in the first
trophic level with herbivores in the second and carnivores in the third is known as grazing food chain.
ii. Detritus food chain: The food chain in which the dead and decayed organisms lie in the
first trophic level is also known as detritus
food chain. it is the food chain
that starts with the consumption of dead organism.
Dead leaves → woodlouse → Black bird
Host → Parasites
Animals and Plants → Mosquito or Leech
(First Trophic (Second Trophic)
Food Web: The interconnected network of food chain in an ecosystem which establishes interrelation among various organisms is known as food web. In simple words, it is the network of large number of food chain existing in an ecosystem.
The benefits that we get from the ecosystem are known as ecosystem services. They are classified into the following types:
i. Provisioning services: The benefits that are related with the products of the ecosystem are known as provisioning services.
a. Food and fiber:i.e. crops, spices, sea food, water,etc.
b. Fuel:i.e. biofuel, fossil fuels, timber, wood, etc.
c. Ornamental resources:i.e. Skin and bones of animals, valuable minerals like diamond, etc.
a.Climate regulation: The green plants in our ecosystem minimizes global warming and regulates the weather in a healthy manner.
b. Purification of air and water: The air and water present in the ecosystem purified by various natural processes. Plants maintain moisture in the soil and help natural filtration.
b)primary production. The process of producing organic compounds is known a primary production.This process includes photosynthesis, chemosynthesis etc.
1. 1. Symbiosis/Mutualism
The interactions between organisms of two
different species ,in which each organism benefits from the
interaction in some way. is known as Mutualisms
These types of interaction are common
and unique in ecosystems, Some examples of mutualism:
a) Birds and insects take nectar from flowers and these animals
help in the pollination. In this case, they help
to each other.
b) Human beings have beneficial bacteria in the instestine. These bacteria help human to digest the food and
bacteria get food from the human.
d) Clownfish are found on the
tentacles of sea anemone. Clownfish get food from the sea anemone. Clownfish which is at the tentacles attracts other fishes and that will be the food for sea anemone.
2. Commensalism:
the relation in the
ecosystem where one benefits but the other
organism isn't harmed, but in, parasitism one organism benefits and the other is
harmed is known as Commensalism.
The commensalism can be explained in the following
ways:
a) When the cow is grazing on the field, the insects come out and they become the food
for the birds. In this case, bird does not harm the cow but get benefits.
b) Spider makes web on a
tree but that does not harm the trees.
a)Flea, bed bug and mosquitos suck the blood from the body of human beings. They are called ectoparasites.


are swimming.
when the organisms compete each other for food, shelter etc in the ecosystem is known as Competition ..
a) Sea sponges and coral compete each other to get food in sea.
b) Wolves and fox compete each other for the food.
.

































































































Comments
Post a Comment