Physics Grade -9(New Course )
Unit -7
Force and Motion
Force :- A physical quantity which change the state of an object is called force. Its S.I. unit (N) and measured by spring balance . It is a vector quantity. Eg. Pulling force, Gravitational force etc.
Force(F)=Mass(m)×acceleration(a) or mass(m)×acceleration due to gravity (g)
1N force :-The force which when acting on a body of mass 1kg to produces 1m/s2 acceleration is called 1 N force .
1 N =105 dynes
1 dyne force :- The force which when acting on a body of mass 1gm to produce 1m/2 acceleration is called 1dyne force .
Dyne =gcm/s2
We know that
Force (F) =mass (m) x acceleration (a)
S.I. unit of force = kg m/s²
i.e. N = kg m/s2 一 (1)
Let us use C.G.S. unit of kg and m in equation 一 (1)
1 newton = 10 dynes [ dynes = gcm/s²] which is the required relationship between S.I. and CGS unit of force.
Balanced force :-When numbers force acting simultaneously on a body do not bring about any change in the state of rest or motion in a straight line then the force acting on the body is called balanced force .In balanced force the magnitude of resultant is always zero. For example :In a rope pulling by two teams the rope does not move in any direction .
Unbalanced force :-When a number of forces acting simultaneously on a body bring about a change in its state of rest or motion in a straight line ,then the force acting on the body is called unbalanced force In unbalanced force the magnitude of resultant force is always more than zero.For example :Kicking the football on the ground ,pushing the small box on the table ,pushing a piece of stone forward etc.
i)It can change the position of the body .
ii)It can change the speed of the body .
iii)It can change the direction or motion of the body .
iv)It can change the shape of body .
Motion:-If a body change its position with respect to its surrounding as the passage of time is called motion .For example :A man walking on the road ,vehicles, bus ,etc.
Differences between uniform motion and non uniform motion
Uniform motion | Non –uniform motion |
i)The motion in which a body covers equal distance in equal interval time is known as uniform motion. ii)For example :The motion of planet ,satellite, watch etc. | i)The motion in which a body covers unequal distance in equal interval time is called non – uniform motion . ii)For example :The motion of vehicles ,flying birds, etc. |
Reference point :-The place from which a location is observed and measured is called reference point or the origin point .
Distance :The length of actual path travelled by the moving body in any direction depend upon the length of path is known as distance .It is scalar quantity .
Displacement: The distance covered by a body in a particular direction in a certain interval time is called displacement . It is a vector quantity .
Vector quantity :-The quantities which have both magnitude as
well as direction is known as vector quantities .For examples : displacement, velocity,
acceleration, force, momentum etc.
Scalar quantity :The quantities which does not have direction but only magnitude is known as scalar quantity .For example: mass, volume ,speed , work ,energy, temperature,time,distance,power, etc .
Speed:The distance covered by a body per unit time is called speed .It S.I. unit is m/s .It is scalar quantity because it have only magnitude but not direction
Speed or average velocity =Distance covered (m)/Time taken(t)
Velocity :-The distance covered by a in a particular direction per unit time is called velocity .or
Displacement per unit time is called velocity .Its S.I. unit is m/s .It is a vector quantity because it have both magnitude as well as direction .
Non-uniform velocity :-if a body does not covers equal distance in equal interval time is known as non- uniform velocity .
1.)A student runs 5m/s .What does this mean ?
Ans. It means that he covers a distance of 5 meters in a per second .
Acceleration:-The rate of change of velocity per unit time is called acceleration .orVelocity change in per unit time is acceleration .It S.I. unit is m/s2.It is vector quantity.
a =v-u /t Where, a = acceleration , V= final velocity , u =Initial velocity , t= time taken
Equation of motion:-The mathematical equation that show the relation between initial velocity (u),final velocity (v),acceleration (a),time taken(t), and distance covered by the object(s) is known as equation of motion .The equation of motion are
V=u+at 一 i
S=u+v/2×t 一 ii
S=ut +1/2 at2 一 iii
V2 =u2+2as 一 iv
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
Now,
According to definition of acceleration
a= v-u /t
or v-u =at
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance travelled =s
Now, average velocity = =u+v/2 (i)
Again ,distance covered =average velocity× time taken(t)
Suppose here ,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =S
Now average velocity ==u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average velocity ×time(t)
Or S = u+v/2×t (i)
Putting the value of v at equation (i)
Or S=(u+v+at/2) ×t ( we know that v=u +at )
Or S =(2u+at/2) ×t
Or S = (2u/2+at/2)×t
Or S =ut + at2/2
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =s
Now average velocity = u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average velocity ×time taken(t)
Or S = u+v/2×t (i)
Putting the value of t at equation (i)
Or S = u+v/2 × v-u/a ( we know that t = v-u/a)
Or S = v2-u2/2a
Or v2 –u2 =2as
Representation of motion of particle can be graphically illustrated in three different ways
They are (i) Time-displacement graph,
(iii) Time-acceleration graph.
i)Time-displacement (s-t) graph: The graph obtained
by plotting displacement of particle along y-axis against time along x- axis is called time displacement (s-t) graph.

ii)Time-velocity (v-t) graph: The graph obtained by plotting velocity of a moving partide along y-axis
against time along x-axis is called time velocity
graph.
Positive velocity Zero
acceleration
Positive velocity Positive acceleration
Inertia :-The property or tendency of a body or mass to resist any change in its state of rest or uniform motion in straight line is called inertia . or
The inability of a body to change its state by itself from rest to motion or motion to rest is known as inertia .
The relation between mass and inertia :The inertia of a body depend upon its mass For example : The a body having greater mass the inertia will be high and for a body having smaller mass the inertia will be less , therefore the inertia of body is directly proportional to the mass of the body .
Inertia∝
Types of inertia :They are 2 types :
:i)A passenger sitting in a bus falls backward when the bus moves suddenly
ii)The dust particles fall downward when a blanket is given a sudden jerk.
ii)A person jumping from the a moving bus gets injured .
1.)The fruits fall down when the branches of a fruit tree are shaken .Explain why ?
Ans. In the beginning both the branches as well as the fruit remains in the state of rest , when branches of tree is shaken the branches comes in the state of motion but due to inertia of rest fruit remains in state of rest .As result the fruits are separated from the branches and fall down .
2.)A coin placed on a card is placed over a glass .when the card is flipped quickly ,the coin drops into the cup ,why ?
Ans. Initially both the card as well coin remains in the state of rest , when the card is flipped quickly the card comes in the state of motion but due to inertia of rest card remains in the state of rest .As result the coin is separated from the card and drops in to the cups .

3.)A carpet is beaten with a sticks to remove the dust particles .why ?
4.)When a car suddenly starts moving ,the passenger sitting in it falls backward .why ?
Ans. Initially both the passenger and bus remains in the state of rest ,when the car suddenly start moving both car as well as lower parts of passenger comes in the state of motion but due to inertia of rest upper part of passenger remains in the state of rest ,as result when a car start suddenly moves the passenger sitting in it falls backward .
5.)When a moving bus suddenly stops ,the passenger sitting in it fall forward .why?
6.)The blades of a fan continue to rotate when the current is switched off. why?
The product of mass and velocity of moving body is known as momentum of moving body or linear momentum .Its S.I. unit is kgm/s.
Momentum =mass ×velocity
Or
=mv where
Newton’s law of motion :Newton’s used three laws to describe the effect of force on an object are known as Newton’s law of motion .They are as following :
1.)Newton’s first law of motion :If a body is at rest ,it will continue to remain at rest and if it is in motion it will continue to move in a straight line with uniform velocity ,unless it is acted upon by an external force .This is known as Newton’ s first law of motion .
i)The fruits fall down when the branches of a fruit tree are shaken .
ii) When a car suddenly starts moving ,the passenger sitting in it falls backward .
iii) When a moving bus suddenly stops ,the passenger sitting in it fall forward.
2.)Newton’s second law of motion :Acceleration produced in a body is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass . This is known as Newton’s second law of motion .
a ∝
a
or
The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force in the direction of force .This is known as Newton’s second law of motion .
Force (F) = change in momentum/time taken
For example :i)A cricket player lowers his hand while catching a cricket ball .
Prove that F =ma
Suppose ,the mass of a body =m
Applied force =F
and produced acceleration =a
According to Newton’s second law of motion
a∝ F ( i)
a
combining eqn(i) and eqn(ii)
a ∝ F/m
F∝
Or F = k ma (where k is a constant )
Or F =k ma ( iii)
If a force required to produce an acceleration of 1m/s2,on 1kg mass is called 1N force
Now ,1 =k 1.1
Or K = 1
Putting the value of k in eqn (iii)
F = 1 ma
F = ma proved
3.)Newton’s third law of motion : For every action ,there is an equal and opposite reaction .This is known as Newton’s third law of motion .
For example: i) A gun recoils on firing .
Reasons
i)Explain ,why a gun recoils when a bullet is fired from it ?
Ans. When bullet is fired the bullet comes out from the gun is action and gun recoils is backward is reaction so gun recoils when bullet is fired because we know that according to third law of motion for every action there is equal and opposite reaction .
ii)If a man jumps out from a boat ,the boat moves backward .why ?
Ans. A man jumps out from the boat is action and the boat moves backward is reaction ,so if a man jumps out from a boat ,the boat moves backward because we know that according to Newton’s law of motion for every action there is equal and opposite reaction .
iii)When a balloon filled with air and its mouth downward is released ,the balloon moves upward .why ? (Air release downward from balloon is action and balloon moves upward is reaction )
iv)While rowing ,a boatman pushes the water in he pond backward , why ?
( Boatman push the water backward is action and boat move forward is reaction )
Elasticity :The ability of a body to regain its original configuration due to the removal of deformed force is
called elasticity.
Or
A body having higher elasticity can resist more deforming force and sets fast to its original form. Steel has more elasticity. So, it is used to construct strong house, bridge etc. When applying a force greater than the elastic limit of the material it loses its elasticity and gets permanently deformed or bend permanently or crack the body. The elastic limit represents the maximum force that can be applied per unit area before complete deformation.

If the force is continuously applied on permanently-deformed body, it may break or fracture. Materials that show plasticity are plastics. Deformation of plastic materials irreversible.

Differences between elasticity
and plasticity
|
Elasticity |
Plasticity |
|
1.Elasticity is the ability of an object or material to
resume its normal shape after being stretched or
compressed. |
1.Plasticity is the quality of being easily shaped or
moulded. |
i)a =v-u/t
ii)v=u+at
iii)s = u+v/2×t
iv)s =ut +1/2 at2 or s=ut+i/2gt2 (When object throwing upward g=-9.8m/m2 or downward g=9.8 m/s2)
v)v2 = u2+2as or v2 =u2 +2gs
Note : i)When starting from rest u= 0m/s2
ii)When stopped or break applied u=0m/s2
iii)In retardation a = –m/s2
1.)A bus starts from rest .if the acceleration of the is 0.5m/s2,what will be its velocity at the end of 2 minutes and what distance will it cover during that time ?
Ans.soiution ,here
Initial velocity (u)= 0m/s
Acceleration(a)=0.5m/s2
Time taken (t)=2 min =2×60 =120 sec
Final velocity (v) =?
Distance covered (s)=?
We have
V=u+at
Or v = 0 +0.5 ×120
Again ,We know
S = u+v/2× t
Or S = 0+60/2×120
Or s =60×60
Distance covered (S) =3600 m/s
2.) A car starts to move from rest .If the car assumes an acceleration of 3m/s2 in 15 second , calculate the final velocity of the car .Also calculate the distance covered by the car .(Ans. v= 45 m/s S= 337.5 m)
3.)A motor bike starting from rest on Fewa lake accelerate n a straight line at rate of 5 m/s2 for 10 seconds .How long distance does the boat travel during this time .(Ans. S =250 m)
4.)A truck is moving with velocity of 72km/hr ,when the driver applies brakes the truck is stopped in 2 second .calculate the distance covered and retardation of the truck .if the mass of the truck is 5000kg ,calculate the force applied by the brakes to stop the truck .
Ans.Solution here, Initial velocity (u) = 72km/hr
= 72x1000/60x60=20 m/s
Final velocity (v)= 0m/s
Time taken (t) =2 Sec
Mass of truck (m) = 5000 kg
Distance covered (s) =?
Retardation (a) = ?
Force applied by brakes (F) =?
We know that
Or a =v-u/t
Or a =0-20/2
Or a =-10 m/s2
Therefore retardation (a)= -10m/s2
Again ,we know that
S = u+v/2× t
Or S = 20+0/2 × 2
Or s = 20 m
Therefore distance covered (s) = 20m
Again, we know that
F = ma
Or F = 5000 × - 10
F= - 50000 N
Therefore force applied by break (F) = - 50000N
5.)A bus is moving with velocity of 90 km/hr .If the bus covers the distance of 625 m before coming to rest ,calculate the retardation of the bus .(Ans. -0.5 m/s2 )
6.) How much retardation should be produced to stop a truck moving with the velocity of 72 km /hr in 5 second ? Calculate the distance covered by the truck within that time .(Ans. a = -4m/s2 ,S = 50 m )
7.)To estimate the height of a bridge over karnali river ,a stone is dropped freely in the river from the bridge .The stone taken 2 seconds to touch the surface water .Estimate the height of the bridge from the water level .
Ans.Solution ,Here
Initial velocity (u) = 0m/s
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8m/s2
Time taken (t) = 2 sec
Height of the bridge (h) =?
We know that
h = ut + ½ gt 2
or h = 0 . 2 + ½ . 9.8 ×2.2
or h = 0 + 9.8 ×2
h = 19.6 m
Therefore height of the bridge (h) =19.6 m
8.)A body falling from the top of a building reaches the ground 2.5 s later . How height is the building .(Ans. h = 30.62 m)
9.)If a stone takes 5 seconds to reaches the maximum height with what velocity is it thrown up ?
Ans.Solution here ,
Final velocity (V) = 0m/s
Acceleration due to gravity ( a) =-9.8m/s2
Time taken (t ) = 5 Sec
Initial velocity (u) =?
We know that ,
V = u+ gt
Or 0 = u + (-9.8) ×5
Or 0 = u – 49
u = 49 m/s
Therefore initial velocity (u) = 49 m/s
10.) A ball is thrown vertically upward at the velocity of 30m/s .Calculate the height covered by the ball in 5 second .(Ans. S = 27m )
Unit: = Force
Group 'A' (1 Mark Each)
1. What is force? Write down its SI unit.
2.Define rest and motion.
3.Define IN force.
4.Define speed and velocity.
5.What is inertia?
6.On which factor does the inertia of a body depend? Write.
7.What is inertia of motion?
8.What is the relation between the mass and inertia of a body?
9.What is displacement?
10.What is acceleration' Write down its unit in SI
11."Every action has equal but opposite reaction." Which law of Newton is stated by this statement?
12.State Newton's second law of motion.
13.What is momentum? On which factors does it depend? Write.
14.What is unbalanced force ? Write with one example.
15.State Newton's first law of motion.
Group 'B' (2 Marks Each)
16.Write any wo differences between speed and velocity.
17.A coin, kept on a postcard on the glass, drops in the glass when the postcard is flipped suddenly. Why ? Give reason.
18.Write any wo differences between velocity and acceleration.
19.Why do passengers tall forward when a moving bus is stopped suddenly? Give reason.
20. Athletes run a long distance belore taking a long jump. Give reason.
Group 'C' (3 Marks Each)
21. What is the relationship among initial velocity, distance covered, acceleration produced and final velocity of a moving body? Give an example that describes Newton's first law of motion.
22.Prove that: F=ma
23.Write any three practical applications of Newton's third law of motion.
24.Explain Newton's third law of motion with an example.
Group 'D' (4 Marks Each)
25.A truck is moving with the velocity of 72 km/h. When the driver applies brakes, the truck is stopped in 2 seconds. Calculate the distance covered and retardation of the truck. If the mass of the truck is 5000 kg, calculate the force applied by the brakes to stop the truck.
26.Write one difference between action and reaction. A bus is moving with the velocity of 60 km/h. By seeing a baby 11m ahead the driver applied the brakes and the retardation produced is 13.88m/se. Calculate the distance covered by the bus and time taken to stop the bus.
27.Prove that
(i)v2 = u2 + 2as
s=ut+1/2at2
Unit - Test
Unit 2: (Force)
Time: 40 min. F.M.: 22
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the questions.)
समूह 'क'
(Group 'A') 1x6=6
1.Define IN force
2.On which factor does the inertia of a body depend? Write.
3. What is velocity? Write down its sl unit.
4.What is acceleration? Write down its unit in SI system.
5 State Newton's first law of motion.
6.What is balanced force ? Write with one example
समूह 'ख' (Group 'B') 3 x2 =6
7.Write any two differences between speed and acceleration
8.A soldier is running very fast. Can he stop immediately when he gets command to stop? Why?
9. Why do fruits fall down when the branch is shaken?
समूह 'ग' (Group 'C') 2x3=6
10.A vehicle is moving with the velocity of 25m/s. If the vehicle is stopped within 5 seconds by applying brakes, calculate the retardation. If the mass of the vehicle is 1000kg, how much force is to be applied to stop it?
11. Mention any three points that should be remembered while solving numerical problen is related to motion.
समूह 'घ' (Group 'D') 1x4
27.Prove that
(i)v2 = u2 + 2as
ii)s=ut+1/2at2
The End
Lesson : 3
(Machine )
Machine : The instruments that make our work easier ,faster and
more convenient are known as machine . They are 2 types :
1.)Complex machine :The instruments whose structure are very complex and make our work easier ,faster, and more convenient are known as complex machine .For example : Fan, bicycle, bus ,truck etc.
2.)simple machine : The instruments which is very simple in structure and make our work easier ,faster and more convenient are known as simple machine .For example : scissor ,beam balance, bottle opener etc.
i)It increase the rate of doing work .
ii)It multiplies the applied force .
iii)It help to change the direction of force .i.e Pulley
iv)It helps to do our work safe .
v)It help to transfer force from one point to another point.
Some terminology related to simple machine :
Load:-The force exerted by machine on the resistance after application of effort is called load .It is denoted by L and S.I. unit is Newton(N).
Fulcrum :The fixed point or axis of simple machine that help to move or rotates freely the machine is called fulcrum .
Load distance and effort distance : The distance covered by load is called load distance .It is denoted by L.d. and S.I. unit is metre (m)
Input work =Effort ×Effort distance
Out put work =The work done by machine on the load is called out put work (useful work).It S.I. unit is Joule (J). It is always less than that of input work ,because it is affected by friction .
Out put work =Load ×Load distance
Mechanical advantage (MA) =Load/Effort
1.)The mechanical advantage of simple machine is 5 .What does it mean ?
Ans. It means that work become 5 times easier if machine is
used .
or simple machine can overcome 6 times heavier load than that of applied force
.
Note or special case :
i)M.A.
< 1 or L<E
It means that Load is smaller than that of effort and more effort is
required to lift smaller load so in this case Effort is not multiplied when
simple machine is used .
It means that Load is greater than
that of effort and less effort is required to lift heavier load so in this case
load is multiplied when simple machine is used .
It means that Load and effort are equal and
equal amount of effort is required to lift equal amount of load so in this case load is not magnified when
simple machine is used .
1.)The velocity ratio of simple machine is 5 .what does it mean ?
Ans. It means that the distance covered by effort is 5 times more than that of distance covered by load .
i)applying grease or oil between the movable part of a machine ,
ii)by making smooth surface ,
iv)By rolling instead of sliding.
Factors affecting efficiency :
i)Frictional force
ii)Gravitational force
iii)Weight of machine
Out put work = in put work
Real machine or practical machine :-The machine in which efficiency is always less than that of 100% or out put work is always less than that of input work is called real or practical machine .
Principle of simple machine :-It states that if there is no friction in simple machine output work is always equal to input work in the simple machine .
L×L d = E × E d
1.)A machine has 70% efficiency .what does this means ?
Ans. It means that 70% input work is converted into out put work and remaining 30% of input work is wasted due to friction in the machine .
1)Lever 2)pulley 3) Wheel and axle 4) Inclined plane 5)Screw 6) Wedge
i)L.d> E.d or E>L
It means that Load distance is greater than that of effort distance and more effort is required to lift smaller load so in this case Effort is not magnified when simple machine is used.
It means that Effort distance is greater than that of Load distance and Less effort is required to lift heavier load
so in this case Effort is magnified when simple machine is used.
iii) E.d = L.d or L = E
It means that Effort distance is greater than that of Load distance and Less effort is required to lift heavier load
so in this case Effort is magnified when simple machine is used.
In third class of lever effort distance is always less than that of effort distance ,so effort cannot be magnified.
Load ×load arm =Effort ×Effort arm
The velocity ratio of combined pulley = N. of pulley used in system .(Except single movable pulley )
Or
Velocity ratio of pulley (V.R.) =No .of rope of segments that support the load
V.R. =2π R/2π r
V.R. =R/r
Ans. In wheel and axle just like lever force is applied in wheel and load is lifted in axle and rotates continuously until the load reaches the required height , therefore wheel and axle is called continuous lever .
Velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)= Length of inclined plane (l) or distance covered by effort/Height of inclined plane (h) or distance covered by effort
1.)6 km long road in the western slope and 4 km long road in eastern slope of a mountain are constructed to reach the peak .Which one of them is easier to climb the mountain with a bicycle and why ?
Ans. Through 6 km long road in the western slope is easier to climb the mountain with a bicycle ,because according to principle of inclined plane if the length of inclined increases the mechanical advantage also increase i.e. less effort is required to climb the mountain .
ii)Pitch :The distance between two successive threads is called pitch .For example : Jack screw , Nail driller etc.
V.R. =2rp Where r = radius of circular part of screw , P = pitch of the screw .
Anticlockwise moment :-If a body rotates anticlockwise under the application of force ,the moment is called anticlockwise moment .
Mathematically
Total clockwise moment = Total anticlockwise moment
1.)Why is a longer a spanner (wrench) is used to open a rusted knot or big knot ,?
Ans. A longer spanner has greater moment arm as result it multiplies the force and produce greater moment ,whereas big not or rusted knot requires more moment to be opened .Therefore ,a long spanner is used to open a rusted or big nut .
2.)The probability of breaking a branch of tree is more when a person moves a long it towards its end .why?
Ans. When a person moves towards end of branch the moment arm is increased as result larger moment is produced by the person on the branch .Therefore the probability of breaking a branch of tree is more when a person moves along it toward its end .
3.)The probability of breaking a taller tree is greater than shorter tree at the time of storm ,why ?
Ans. The taller tree has greater moment arm as result it multiplies the force applied by storm and produce greater moment than that of shorter tree .Therefore the probability of breaking a branch of tree is more than shorter tree at time of storm .
Mechanical advantage (M.A,)= Load /Effort
Velocity ratio (V.R.) =Load distance /Effort distance
Velocity ratio of pulley (V.R.)=N. of pulley used in system (Except single movable pulley ) or
N. of rope segments that support load
Velocity ratio of wheel and axle (V.R.)= Radius of wheel(R)/Radius of axle(r)
Moment =Force ×Perpendicular distance from the force to the fulcrum .
Law of moment =Total clockwise moment=Total anticlockwise moment
1.In uplifting 450N load with the help of 1m long lever takes 150 N effort. What will be the efficiency of a machine if the fulcrum is kept 25 cm far from the load .
Load (L) =450N
Effort (E)=150N
Load distance(Ld)=25cm
Effort distance (Ed)=75 cm
Efficiency (ጎ ) =?
According to the formula
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)= Load /Effort
=450/150=3
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= Effort distance /Load distance
= 75/25
We know that
Efficiency (ጎ ) =M.A./V.R.×100 %
=3/3× 100 %
Efficiency (ጎ) = 100%
3.) What is the efficiency ,if an effort of 150N is applied to raise a load of 200N using two pulley system ?
Ans. Here, Given
Load(L)= 200N
Effort(E)=150N
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= 2 (Since the number of pulley =2)
Efficiency (ጎ )=?
Now, according to formula
Mechanical advantage(M.A.)= Load/Effort
=200/150=1.33
Again ,Efficiency (ጎ )= M.A./V.R.×100% = 1.33/2×100% = 66.5%
؞The efficiency of given pulley system is 66.5%
Ans. Given,
Efficiency (ጎ )= 75%
Load(L)=500N
Velocity ratio (V.R.)=2 (Since V.R. of movable is 2)
Effort (E)=?
Now, according to formula
Efficiency ( )M.A./V.R.×100%
75% = ×M.A./2100%
Or 100 M.A. =75 ×2
Or M.A. = 75x2/100=1.5
Again, M.A.= Load /Effort
Or 1.5 =
Or Effort =500/1.5
؞Effort =333.33N
5.)If a pulley system with efficiency 80% has mechanical advantage 4 .how many pulleys are there in the system ?What is the effort necessary to lift the load 1000N ?
Ans. Given,
Efficiency( ጎ)=80%
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)=4
Load(L)=1000N
Number of pulley (V.R)=?
Effort (E) =?
Now, according to formula
Efficiency (ጎ ) =M.A./V.R.×100%
80% =4/V.R.×100%
Or 80 V.R. =4×100
Or V.R. =4x100/80=5
؞Number pulley (V.R.) =5
Again ,M.A. =Load /Effort
Or M.A. =1000/Effort
Effort =1000/4=250
؞Effort =250 N
6.)What effort is needed to balance a load of 800N in a wheel and axle with efficiency 80% .If radius of the wheel is 8cm and that of axle is 2 cm ?
Ans. given
Load(L)=800N
Efficiency (ጎ ) =80%
Radius of wheel (R) =8cm
Radius of axle (r) =2 cm
Velocity ratio (V.R.) =?
Effort (E) =?
Now, according to formula
Velocity ratio (V.R.) = R/r
=8/2 =4
Again ,Efficiency (ጎ )= M.A./V.R.×100%
Or 80% =M.A./4×100%
Or 100 M.A. =80×4
Or M.A. =80x4/100 =3.2
؞M.A. =3.2
Again, M.A.= Load/Effort
Or 3.2 =800/Effort
Or Effort =800/3.2=250
؞Effort =250N
7.)In a wheel and axle ,the radius of wheel is 70 cm and that of axle is 5cm .If an effort of 50N is needed to lift a load of 500N what is the efficiency of machine ?(V.R. =14, M.A. =10, Efficiency =71.43%)
8.)Study the given diagram and calculate M.A. ,V.R, and efficiency of the inclined plane .
Effort (E)=250N
Effort distance or length (l)=15m
Load distance or height (h)= 5m
M.A.=?
V.R.=?
Efficiency( )=?
Now,According to formula
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)= Load /Effort
= 500/250=2
؞ mechanical advantage (M.A.)=2
Again, Velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)= l/h
Or =15/5 =3
؞ velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)=3
Again, Efficiency (ጎ )= M.A./V.R.×100%
Or = 2/3×100% =66.6%
؞Efficiency (ጎ )= 66.66%
8.) An effort of 20N is required to unscrew a joined nut by using a 20cm long spanner .Calculate the moment produced .
Ans.given,
Effort (E)= 20N
Length of spanner =20cm =20/100 = 0.2m
Moment(M)=?
Now,we know that
Moment(M)= Effort ×Effort arm
Or = 20 ×0.2 =4
؞ Moment produced (M)= 4Nm
Group 'A' (1mark Each)
1.Define simple machine.
2.What is mechanical advantage?
3.How is the mechanical advantage of a machine calculated? Write.
4.What is velocity ratio? Write down is formula.
5.What is efficiency?
6.Write down the formula to calculate the efficiency formula.
7.Define input work and output work.
8.What is a pulley? Why is it used?
9.What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a simple machine?
10.What is an inclined plane? Why is It used ?
11.What is velocity ratio of an inclined plane? Write.
12.What is a wheel and axle? Why is it used?
13.Write down the formula to calculate the velocity ratio of wheel and axle..
14.What is moment?
15.State the law of moment.
Group 'B' (2 Marks Each)
1.What is meant by mechanical advantage of a machine is 3? Velocity ratio has no unit. Why?
2.What is meant by the velocity ratio of a machine is 2? The efficiency of a machine is always less than 100%, why?
3.The efficiency of a machine can be increased by applying oil or grease. Why?
4.The probability of breaking a tree branch increases while moving towards the tip of the branch. Give reason.
5.Small spanner is made to open a small nut and long spanner is made to open a big nut. Why?
Group 'C' (3 Marks Each)
1.Write down two advantages of using simple machines. What is a perfect machine? Why is it impossible to get a perfect machine in practice?
2.How can we increase the efficiency of a simple machine? Give any two methods. Write any two applications of simple machine.
3.What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a simple machine? How can the efficiency of a simple machine be increased? Write.
4.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever. Justify this statement.
5.What is moment? Write down its formula and Sl unit.
6.What are two factors that affect the turning effect of force (moment)? No one machine has 100% efficiency. Justify this statement.
Group 'D' (4 Marks Each)
1.A simple machine of velocity ratio 20 is used to lift a load of 600N by applying an effort of 40N. Calculate the mechanical advantage and efficiency of the machine.
2. Draw a neat and labeled diagram of each of the given simple machines.
1)Lever ii) Pulley iii)Wedge iv) wheel and axle
3.A 20cm long spanner is used to open a rusted nut of a bicycle. If the effort is 60N, calculate the moment produced. Write any two differences between ideal machine and practical machine.
Unit - Test
Unit 2: (Force)
Time: 40 min. F.M.: 22
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the questions.)
समूह 'क' (Group 'A') 1x6=6
1.Define simple machine.
2.What is mechanical advantage?
3.How is the mechanical advantage of a machine calculated? Write.
4.What is velocity ratio? Write down is formula.
5.What is efficiency?
6.Write down the formula to calculate the efficiency formula.
समूह 'ख' (Group 'B') 2x3 =6
7.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever? Justify this statement.
8.Probability of breaking a tree branch increases on moving towards the tip of the branch. Explain it on the basis of law of moment.
9.What is meant by the velocity ratio of a machine is 2? The efficiency of a machine is always less than 100%, why?
समूह 'ग' (Group 'C') 2x3=6
10.Write any three utilities of simple machines.
11.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever. Justify this statement.
समूह 'घ' (Group 'D') 1x4
12.A simple machine of velocity ratio 20 is used to lift a load of 600N by applying an effort of 40N. Calculate the mechanical advantage and efficiency of the machine.

Unit -9
Energy:- The
capacity of doing work is called energy .Its S.I.unit is joule
(J) and C.G.S. unit is Calorie (cal). According to the principle of
conservation of energy, The energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it
can only be converted into one form to another form".
2.) Secondary source of energy :- The source of energy which arederived from primary source of energy are called secondary source of energy . For example :bio gas ,hydro electricity ,petrol, diesel, kerosene.etc.
1.)Renewable source of energy:- The source of energy which are produced continuously in nature and can be used again and again are called renewable source of energy .Such types of source energy are never depleted .For example : solar energy ,hydro electricity, wind energy ,bio mass energy, gobar gas or biogas ,wind energy, tidal energy, geothermal energy etc.
Some renewable source of energy :-
1.)Solar energy:- The energy produced by the is called solar energy .The sun is also considered as ultimate or major source of energy ,because all source of energy present on the surface of earth directly or indirectly depend on the energy released by the sun .For example :Hydro electricity is called outcome of solar energy ,because for hydroelectricity stock of water is required ,for water stock water cycle is required and for water cycle sun energy is required .
Process of formation of solar energy:-In sun 27×1023kw energy
released per second by
thermo nuclear fusion reaction. In which 1.4kw solar energy is received by the surface of earth per square meter . During thermo nuclear fusion reaction in
the sun .
Sign
1 H1 = Free
proton or protium ,
4 1H1 → 2He4 +2 1e0+2 0v0+20ɤ0
1)Very high temperature is required in the for formation of free proton or protium.
2)Very high pressure is required in the sun for fusion of free proton.
3.)The sufficient amount of hydrogen atom is required in the sun for formation of free proton .
4)The sufficient amount of helium formation is required to produce large amount energy .
1)It is renewable source of energy and can be used again and again .
2)It can be used as alternative source of energy .
3)It help to us protect from energy crisis in future .
4)It is a pollution free source of energy .
Solar Energy Technology
Solar Taki is a portable(To carry easy)solar lamp unit with white LED bulbs designed to provide rural Nepal an alternative traditional kerosenetuki (lamp). It is composed of three main components:
ii)Storage battery(Li-ion)
iii)Two 0.4watt white
A single charge can operate the lamp for about 4-5 hours and it is used for power a radio and charge a mobile phone The charging time of the lamps depends upon its exposure to the
Solar street lights are used as light sources which are powered by solar panels. The solar panels charge rechargeable battery, which powers fluorescent or LED lamp during the night. It is composed of following main components:
i)74 watt solar PV module
ii)12V,75Ah tubular battery with battery box
iii)Charge controller cum inverter (20-35KHz)
iv)11 watt CFL Lamp with fixtures
v)4 meter steel lamp post above the ground level with weather proof paint and mounting hardware.
Solar dryers are used to eliminate the moisture content from crops, vegetables, and fruits.
The solar dryer consists of a box made up of easily available and cheap material like cement, iron, brick, and plywood. The top surface of the dryer is covered by transparent single and double-layered glass sheets. The inside surface is colored black to absorb the incoming solar radiation., and the inside temperature of the box is raised. The air is ventilated through the small holes at the top and the bottom of the box.
Working:
The inside air gets warm, it rises by the natural circulation
Solar water heater is a device that helps in heating water by using the energy from the SUN. Solar energy (sun rays) is used for heating water. Water is easily heated to a temperature of 60-80 0 C.
i)Solar Collector( to collect solar energy)
ii)Insulated tank (to store hot water)
iii)Supporting stand.
iv)Connecting pipes and instrumentation etc.
Working
The Sun's rays fall on the collector panel (a component of solar water heating system). A black absorbing surface (absorber) inside the collectors absorbs solar radiation and transfers the heat energy to water flowing through it. Heated water is collected in a tank which is insulated to prevent heat loss.
A device which uses the energy of direct sunlight to heat, cook and other food materials by means of reflective panels that concentrate the light on to a dark-coloured pot in an insulated box is called solar cooker. It is also called a type of solar thermal collector. Because it “gathers” and traps the Sun's thermal (heat) energy. Heat is produced when high frequency light (visible and ultraviolet) is converted into low frequency infrared radiation.
Main Components Of Solar cooker:
i)A black box,
ii)glass cover,
iii)plane mirror reflector
iv) cooking containers are the main components of a box-type solar cooker
Working:
The solar cooker works on the principle that the sun warms the pot where the food is prepared. By converting light energy into heat energy, the pot is warmed. The sun's rays are focused onto a receiver by means of reflective panels. For example a cooking pan, by the


2.) Hydro electricity:-The
electricity generated by rotating turbine with help of water is called hydro
electricity .The estimated capacity of our country is about
83000 mega watt ,but present production capacity of our country is about
1000 mega watt . It is second water richest country and most area of this
country provided with mountains or inclined surface .
2)Most of area of this country provided with mountains or inclined surface .
Causes of difficulties to produce hydro electricity in Nepal:-
Advantages of hydro electricity :-
1) 1)It is renewable source of energy and can be used again and again .2)It can be used as alternative source of energy .
3)It help to us protect from energy crisis in future .
4)It is a pollution free source of energy .
5)It is easy to transmit and use .
6)In long term basis ,it is cheaper than that of other source of energy .
7)It is used to run T.V. ,Radio, computer ,industries, etc
3.)Bio-mass
energy:-The energy obtained by burning bio-mass is bio-mass energy .
Briquettes:
There are two main types of briquettes:
Carbonized briquettes are compressed blocks of charcoal. To make briquettes, charcoal is prepared by burning wood, weeds, carbon materials in low oxygen. This is called the charring method. After grinding the charcoal it is mixed with the binder and placed in a moulder and pressure is applied to produce briquettes of a certain size. When making briquettes, clay, crushed corn flour, vegetable starch, wood powder etc. are used as binders.

2.Non-carbonized Briquettes
Non
Carbonized briquettes are pressed blocks cow dung chaff
wood dust, leaves, paper
etc .Non-carbonized briquettes are made by applying high pressure to biomass like wood dust, leaves, paper cow dung
,chaff etc. A high pressure blowing machine is used to make non-carbonized
briquettes i.e. Piston press, skew press and
roller press techniques are used to make
non-carbonized briquettes.
1) 1)It is renewable source of energy and can be used again and again .
2)It can be used as alternative source of energy .
3)It help to us protect from energy crisis in future .
4)It is used for cooking food and other human activities.
5)It help to minimize air pollution.
4.)Bio-gas or Gobar gas :- Mixture
of methane ie 60%,carbondioxide ie.40% hydrogen sulphide is
called bio-gas .
It is produced by decomposition of animal wastes ie.dung in
presence of water due to anaerobic bacteria in the bio- gas plant.
1) 1)It is renewable source of energy and can be used again and again .2)It can be used as alternative source of energy .
4)It produce more heat while burning easily.
5)Due to agriculture country ,waste materials for this gas easily available in our country.
6)It is used for cooking food ,burning light etc.
Unit : 10
Wave
Wave:-A periodic disturbance that carries
energy away from an object through a medium during motion
is called wave.
Mechanical wave : A waves which require a medium in order to transport their energy from one location
to another. Through medium is called
Mechanical wave.. A
sound wave is an example of a mechanical wave.
Types of mechanical wave :They are two types:
1.Transverse wave :-A wave in which the particles of the
medium vibrate
up and down perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave is
called transverse
wave. For
example: All electromagnetic waves are transverse wave i.e. :Infra red
,Gamma ray, Ultra violet ray, light wave, wave on the surface of water.
Crest:-In transverse
wave the
maximum displacement of particle in the upward is crest.
Trough:-In transverse wave
the maximum
displacement of
particle is called trough.
Wave length:-The distance
between two
trough or two crest is called wave length. Its S.I. unit is meter & denoted
Lymda (ƛ).
2.Longitudinal wave:-A wave in which the particles of the
medium vibrate
along the direction of propagation of the wave is called longitudinal wave
.These waves are also called mechanical wave because they requires materials medium
i.e.: solid,
liquid, or gas for its propagation. For example: Sound wave, wave on
stretched spring.
Compression:-In longitudinal wave
the region in the space where the density of particles is high are
called are called compression.
Rarefaction:-in longitudinal wave the region in the space
where the density
of particles is low are called rarefaction.
Wave length:-The distance between two successive
compression or rarefaction is called wave length. Its S.I. unit is meter(m) &denoted
by lymda(ƛ).
Frequency:-The number of complete wave produced in per
second is called frequency. Its S.I. unit hertz(Hz) & denoted by f.
Wave velocity or sound
velocity :The distance travelled
by the sound wave in per second is sound velocity. Its S.I. unit is m/s.
Sound velocity (v)=wave length
(ƛ)×frequency(f)
V=ƛ×f
Amplitude:-The maximum
displacement of particles of the medium from its mean position is called
amplitude. The wave of more amplitude has more energy and the wave of less
amplitude has less energy.
Amplitude ∞ wave length.
Relation between velocity ,wave length ,and
frequency
We know that
wave length ‘ ƛ’ is the distance travelled by a wave when a particles of the
medium complete
one vibration
The particle takes time T equal to time period to complete one vibration .
Let V be the velocity
of wave
V = Distance
travelled by the wave(ƛ ) /time taken(T)
Therefore , V=ƛ/T
( i)
Or T = ƛ/V
Or T = ƛ/ ƛ ×f
Or T=1/ f(frequency)
Putting the value of T in equation (i)
Or V= ƛ/1/ f ( because T =1/ f )
Now , V = ƛ ×f
Or velocity sound
= wave length × frequency
Electromagnetic wave :-The wave which are not
affected by electric and magnetic field and do not need material medium for propagation
are called electromagnetic wave .
For example :i)Gamma ray ii)X ray iii)Ultra violet radiation iv)
Visible light v)Infra red radiation vii)Micro wave viii)Radio
wave .
1.Electromagnetic waves are non-mechanical waves. They do not require any material medium for propagation.
Electromagnetic
spectrum :A continuous
series of all the electromagnetic waves are arranged according to
their frequency and wave length is known
as electromagnetic
spectrum. They are divided into
two sections on the basis of wave length .The shortest waves Gamma rays and longest waves are radio
wave .
Types
of electromagnetic spectrum :On the basis of visibility :They are two types :
1.Visible
spectrum of electromagnetic wave :The spectrum of electromagnetic wave
which strikes
on the retina of our eyes and produce sensation of vision is called visible spectrum of electromagnetic
wave.For example :Visible
light i.e. seven different colour of
light .
2. Invisible spectrum of electromagnetic wave :The spectrum of
electromagnetic wave which strikes on the retina of our eyes but don not exite
our retina to produce sensation of vision
but damage
the retina is known as electromagnetic wave.
Application of electromagnetic
waves
1.Radio Waves (AM Radio ,TV, FM Radio)
The electromagnetic
radio which have longest wave length and shortest frequency is called Radio wave. Radio waves are
the type of electromagnetic wave used for communication such as broadcasting television and radio,
communications and satellite transmissions.It is harmless in nature .
Working
Radio waves are transmitted easily through air and they can be reflected to change their direction These properties make them ideal for communications. Radio waves can be produce by oscillations in electrical circuits. When radio waves are absorbed by a conductor they create an alternating current. This electrical current has the same frequency as the radio waves. Information is coded into the wave before transmission, which can the be decoded when the wave is received. Television and radio systems make use of this principle to broadcast information.
Uses of radio waves
i. Various
frequencies of radio waves are used for television and FM and AM radio broadcasts, military
communications, mobile phones, wireless computer networks .
ii. Radio signals sent from global positioning
satellites are used by
receivers for a precise indication of position.
iii The application of radio range, radio
compass (or direction finder), and radio time signals are widely used,For navigation of ships and aircraft .
The electromagnetic wave which have more wave length and less frequency than infrared wave but less wave length more frequency than that of radio wave is called micro wave. It is harmless in nature.

Uses of micro wave:
i. Micro waves can penetrate clouds of smoke but are
scattered by water droplets,
so they are used for mapping meteorologic
disturbances and in weather forecasting,
ii. Microwave radar is widely used for guiding airplanes and vessels and for
detecting speeding motorists.
3.Infrared wave
i..Infrared waves are used in remote controls for sending signals to electronic devices.
ii.It is used for making night-vision cameras, security cameras, or in war.
The electromagnetic wave which have more wave length and less frequency than ultra violet wave but less wave length more frequency than that of infrared wave is called visible wave. It is harmless in nature. The visible light waves is the segment of the electromagnetic wave that the human eye can view.

i:Plants use light waves for the process of photosynthesis.
ii. Light waves are used in photography and illumination.
5.Ultra violet waves
The electromagnetic wave which have more wave length and less frequency than x-ray wave but less wave length more frequency than that of visible wave is called ultra violet wave. It is harmful in nature. Ultraviolet rays when fall for longer time on human body can cause cancer and eyes defects.
i. Ultraviolet rays are used to produce vitamin-D in animals and plants.
iii. Ultraviolet rays are used in sterilisation of medical equipments.
6.X-Ray wave:
The electromagnetic wave which have more wave length and less frequency than Gamma ray wave but less wave length more frequency than that of ultra violet wave is called X-ray wave. It is harmful in nature. X-rays can penetrate through human body but they are stopped by bones.
Uses of X-rays
i. X-rays are used in
i. X-rays are used in
i. X-rays are used in detection of fractures in bones, teeth, etc.
iv. X-rays are used in airports to check security cases.
i.Gamma rays are used for sterilizing of medical equipment.
iii.In industry, gamma rays are used
iii.In industry, gamma rays are used
iii.In industry, gamma rays are used to check the oil pipeline and detect its weak points.
from a source propagate through a medium and strike to
surface i.e. wall ,rocks. hill.etc then return and go back to the same medium
surface i.e. wall ,rocks. hill.etc then return and go back to the same medium
surface i.e. wall ,rocks. hill.etc then return and go back to the same medium is called reflection of sound. The application of reflection of sound is Eco, reverberation.
i.Reflection of sound is used to find depth of oceans, lakes and rivers.
ii. Reflection of sound is used to locate the brain tumor, stone in kidney in human body.
iii. Reflection of sound is used to study the development of zygote in female's uterus
iv. Reflection of sound is used to find the condition of enemie's gun.
v. Reflection of sound is used to predict the presence of minerals and ores in earth crust.
Eco:-The repetition of sound due to reflection of sound

1.The source of sound and surface of reflection should be required.
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be more than 17 m.
Reverberation:-The prolongation of sound due to mixing of several reflected sound and original sound is called reverberation. For example: The sound produced by hall, cinema hall, musical studio etc.
1.The source of sound and surface of reflection should be required.
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be
2.The distance between source of sound and surface of reflection must be less than 17 m.
Applications
1. for determination of depth of a sea.
ii. to detect submarines
il to locate the prey of bat and dolphin or the obstacles in the path.
iv. for medical diagnosis by ultra sonography.
Acoustic protection
The process of application of soft and porous material to absorb unwanted sounds and noises is known as Acoustic protection . This is done to control the reflection in the room, auditorium, sound recording studio (sound recording studio) etc.
Some of the ways of acoustics protection are a follows:
i)Unwanted sound and noises can be absorbed by using panels on the walls ,ceiling of the big halls and auditorium.
ii) Unwanted sound and noises can be absorbed by using Thick carpets for acoustic protection .
1.Astronauts use electrical devices to talk in the space. Why?
Ans.Sound wave is mechanical wave. So, it needs material medium for propagation. As there is no medium in space, sound waves cannot propagate. Electric device can produce electromagnetic waves which can even propagate in absence of medium. S astronauts use electrical devices to talk in the space.
Ans.Sound absorbing materials reduce echo and reverberation. Due to this process the dialogues can be heard clearly in cinema halls. So, the walls and the ceiling of cinema halls are covered with sound absorbing materials.
3.The ceiling of concert halls, cinema halls and auditorium are curved, why?
Ans.The ceiling of concert halls, cinema halls and auditorium are curved so that the sound after reflection reaches all the corners of the hall.
Ans.Big cinema halls are carpeted and made of rough materials to absorb the sound and prevent the formation of echo and reverberation. So, the dialogues can be heard clearly.
1.Ultrasonography
The technique of using ultrasound to produce pictures of structures of the internal body organ is called Ultrasonography,it is also known as video x-ray, For example to check the facial features of the child inside the uterus. The picture which are produced during ultrasonography by help of computer receiving data is known as sonogram.
Working
It consist of a transducer during ultrasonography it produce high frequency of ultra sound.when high frequency of ultra sound reflect from our body and again is received by transducer and transducer provide data to computer and computer produce sonogram by help of these data.This technique is known as ultrasonography.
The technique of using ultrasound to check, the heart rate, the state of the valves and its functions is called
A photographic technique in which X-rays are used to produce pictures of internal organs of the body is called x-ray photography.
It is used for checking fractures (broken bones), chest x-rays can spot pneumonia,Mammograms x-rays to look breast cancer.
In traditional X-ray picture is produced in photographic film but. In modern technology picture can be observed on the computer screen.
An X-ray image made using a form of tomography in which a computer controls the motion of the X-ray source and detectors, processes the data, to produces the image is called CT Scan.
Tomography scan (Computerized Tomography scan CT scan) is a technology developed from X-ray photo. A computerized tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body.
A CT scan produces a three-dimensional image that help to provide a doctor with a clearer view of a patient's inner organs, blood vessels and soft tissues than a traditional x-ray.It is used to check internal wounds, blood clots, tumours, brain condition, sexual condition, etc.

Numerical problems
Velocity or speed of sound (v)=wave length (ƛ)×frequency (f)
Frequency (f)= 1/T
1.)If a radio station transmit at 219 m wave length and 1370 KHz,
calculate the velocity of waves .
Given ,
Wave length (ƛ) = 219 m
Frequency (f) =1370 KHz = 1370 ×1000 = 1370000 Hz
Wave velocity (v)=?
We
know that
Velocity of sound (V)= ƛ× f
Or v = 219×1370000
Or = 300030000 m/S
؞ velocity of wave (V) =3.00 ×10 8 m/s
2. What are the shortest and the longest wave length of the sound that
the human ears can hear ? Speed of sound in air is 330 m/s and the audible
range of frequency is 20 Hz to 20 KHz .
Given ,
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
We
know that
Velocity of sound (v) = ƛ × f
Or ƛL = v/fS
Or ƛL =330/
20 =16.5 m
Therefore the longest wave length of audible
sound (ƛL) =16.5 m
Again
,
We known that ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs)
=V/fL
Or
ƛS
= V /fL
Or ƛS =
330 /20000
Or ƛs =0.0165
m
Therefore ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =0.0165 m
3.The frequency of sound wave is 200 Hz .What is its time period ?
Given ,
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
We
know that
Time period (T) = 1/f
Or T = 1/ 200 = 0.005
Therefore , time period (T) = 0.005 sec
4.A boy hears an echo of his own voice from a distant hill after 1 s
.The speed of sound is 340 m/s .What is the distance of hill from the boy
?
Given ,
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
We
know that
V= d /t
Or distance (d) = v × t
Or d = 340 ×0.5 = 170
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
The distance of boy from the hill (d) = 170 m
Numerical problems
Velocity or speed of sound (v)=wave length (ƛ)×frequency (f)
Frequency (f)= 1/T
1.)If a radio station transmit at 219 m wave length and 1370 KHz,
calculate the velocity of waves .
Given ,
Wave length (ƛ) = 219 m
Frequency (f) =1370 KHz = 1370 ×1000 = 1370000 Hz
Wave velocity (v)=?
We
know that
Velocity of sound (V)= ƛ× f
Or v = 219×1370000
Or = 300030000 m/S
؞ velocity of wave (V) =3.00 ×10 8 m/s
2. What are the shortest and the longest wave length of the sound that
the human ears can hear ? Speed of sound in air is 330 m/s and the audible
range of frequency is 20 Hz to 20 KHz .
Given ,
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
We
know that
Velocity of sound (v) = ƛ × f
Or ƛL = v/fS
Or ƛL =330/
20 =16.5 m
Therefore the longest wave length of audible
sound (ƛL) =16.5 m
Again
,
We known that ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs)
=V/fL
Or
ƛS
= V /fL
Or ƛS =
330 /20000
Or ƛs =0.0165
m
Therefore ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =0.0165 m
3.The frequency of sound wave is 200 Hz .What is its time period ?
Given ,
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
We
know that
Time period (T) = 1/f
Or T = 1/ 200 = 0.005
Therefore , time period (T) = 0.005 sec
4.A boy hears an echo of his own voice from a distant hill after 1 s
.The speed of sound is 340 m/s .What is the distance of hill from the boy
?
Given ,
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
We
know that
V= d /t
Or distance (d) = v × t
Or d = 340 ×0.5 = 170
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
The distance of boy from the hill (d) = 170 m
Numerical problems
Velocity or speed of sound (v)=wave length (ƛ)×frequency (f)
Frequency (f)= 1/T
1.)If a radio station transmit at 219 m wave length and 1370 KHz,
calculate the velocity of waves .
Given ,
Wave length (ƛ) = 219 m
Frequency (f) =1370 KHz = 1370 ×1000 = 1370000 Hz
Wave velocity (v)=?
We
know that
Velocity of sound (V)= ƛ× f
Or v = 219×1370000
Or = 300030000 m/S
؞ velocity of wave (V) =3.00 ×10 8 m/s
2. What are the shortest and the longest wave length of the sound that
the human ears can hear ? Speed of sound in air is 330 m/s and the audible
range of frequency is 20 Hz to 20 KHz .
Given ,
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000
=20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
We
know that
Velocity of sound (v) = ƛ × f
Or ƛL = v/fS
Or ƛL =330/
20 =16.5 m
Therefore the longest wave length of audible
sound (ƛL) =16.5 m
Again
,
We known that ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs)
=V/fL
Or
ƛS
= V /fL
Or ƛS =
330 /20000
Or ƛs =0.0165
m
Therefore ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =0.0165 m
3.The frequency of sound wave is 200 Hz .What is its time period ?
Given ,
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?Velocity or speed of sound (v)=wave length (ƛ)×frequency (f)
Frequency (f)= 1/T
1.)If a radio station transmit at 219 m wave length and 1370 KHz, calculate the velocity of waves .
Given ,
Wave length (ƛ) = 219 m
Frequency (f) =1370 KHz = 1370 ×1000 = 1370000 Hz
Wave velocity (v)=?
We know that
Velocity of sound (V)= ƛ× f
Or v = 219×1370000
Or = 300030000 m/S
؞ velocity of wave (V) =3.00 ×10 8 m/s
2. What are the shortest and the longest wave length of the sound that the human ears can hear ? Speed of sound in air is 330 m/s and the audible range of frequency is 20 Hz to 20 KHz .
Given ,
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20 KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
We know that
Velocity of sound (v) = ƛ × f
Or ƛL = v/fS
Or ƛL =330/ 20 =16.5 m
Therefore the longest wave length of audible sound (ƛL) =16.5 m
Again ,
We known that ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =V/fL
Or ƛS = V /fL
Or ƛS = 330 /20000
Or ƛs =0.0165 m
Therefore ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =0.0165 m
3.The frequency of sound wave is 200 Hz .What is its time period ?
Given ,
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
We know that
Time period (T) = 1/f
Or T = 1/ 200 = 0.005
Therefore , time period (T) = 0.005 sec
4.A boy hears an echo of his own voice from a distant hill after 1 s
.The speed of sound is 340 m/s .What is the distance of hill from the boy
?
Given ,
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
We
know that
V= d /t
Or distance (d) = v × t
Or d = 340 ×0.5 = 170
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
The distance of boy from the hill (d) = 170 m
Given ,
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2 =0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
We know that
V= d /t
Or distance (d) = v × t
Given ,
We know that
A complete wave consist of a crest and a trough
؞ 20 crest and 20 trough = 20 waves
Now, 20 completes wave produces in = 0.2ses
Now, 20 completes wave produces in = 0.2ses
؞ 1 complete wave produces = 0.2/20 = 0.01 sec
Now Time period (T) = 0.01 sec
Now Time period (T) = 0.01 sec
Again, we know that
Frequency (f) =1/T
Or f = 1 /0.01 = 100 Hz
Therefore frequency of wave (f) = 100 Hz
Unit :- 11 (Eleven )
Current electricity :The rate of charge through conductor is called electricity .
Or The flow of electrons through a conductor per unit time is called
current electricity .Its S.I. unit is Ampere and measured by AmmeterElectric
current (I)=Amount of charge (Q)/Time(t)
1 coulomb = 6 x 1018 electrons
1 ampere = 1000 milli ampere (mA)
1 Ampere =1000000 micro ampere (
1mega Ampere = 1000000 A
One ampere current :When one coulomb charge( 6x1018 electrons) flow through a conductor in one second then current flow the conductor is called one ampere current .
i.)Closed circuit :The
circuit in which the loads are functioning due to continuous
flow of current through the circuit is called closed circuit .
ii.)Open circuit :The circuit in which
the loads
are not functioning due to switch off ,broken of wire or the fuse is gone off
is known as open circuit
Conductor :The substance through
which electricity can flow easily are called conductor. For example :Aluminum,
Copper , Iron, etc.
Types of conductor: On the basis of nature of conductor they
are 3 types .
Direction of real current :The actual flow of
electrons from negative terminal to positive terminal of cell or circuit
is called real direction of current ,but conventional current direction is
still used in circuit diagram .
Potential difference (p.d.)=Work done (w)/Quantity of charge(Q)
Resistance :The property of
conductor i.e. wire by which the conductor oppose the flow of current through
it is called resistance .Its Symbol is R and its S. I. unit is oham (Ω
Resistor :The substance that
oppose the flow of current through it is known as resistor .For example
:Nichrome, Tungesten , manganin etc.
Factors affecting the resistance
of conductors :
i)Nature of
conductors :Different substance have different concentration of free electrons, so
resistance of conductors depends on the nature of conductor .For example:
a)Good conductor have very less resistance i.e . Copper ,Aluminum ,
b)Semi
conductors have more resistance i.e. Nichrome, tungsten
c) Insulators have very high resistance i .e. Rubber ,Plastics
ii) Length of conductors :Resistance of conductors is
directly proportional to the length of conductors . R∝ l
ii)Thick of conductor :Resistance of conductors is inversely proportional
to the thickness of the conductors . R∝ 1/A
iv)Temperature of conductors :Resistance of conductors is directly proportional
the temperature of the conductors . i.e R∝ Temperature
v)The
resistance of conductors also depend upon the shape and size of conductor .For example In straight wire and coil
wire coil wire have more resistance.
V∝ I
Or V =R I (Where R is resistance )
Or V =R I (Where R is resistance )
؞ V = R I proved
The resistance of conductor is numerically equal to the potential difference across its ends when unit of current flows through it .
Or It I = 1 then V = R
Where V= potential difference ,R= Resistance , I = Electric current .One Oham’s resistance : When a potential difference of 1 volt is applied across the ends of the conductor due flow of one 1 ampere current ,then resistance is called one Oham’s
1oham =1volt/1ampere.
N. of cell | Reading of voltmeter (p.d) | Reading of Ammeter | R=V/I |
1 2 3 4 | 1.5 3.00 4.5 6.00 | 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 | 5 5 5 5 |
Resistor :The substance which oppose the flow of current through it
is called resistor .for example :Nichrome ,Tungsten
Combination or connection of
resistor :They
are connected by two ways:
I.)Series combination of
resistor or load :The combination of
resistor in which resistors are joined end to end in such way that same current
passes through each of them is called series connection of resistor .
Total resistance (T)= R1+R2+R3+…………Rn
Total resistance (1/R) =1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3 ………1/Rn
Electric power : The rate of doing work of electrical device at
which it convert electrical energy into other form of energy is called
electrical power .Its S.I. unit is watt .
Electric power (P)=
Current (I) x Voltage (V)
Or P
= Ix V
Prove
that P = I×V
We know that,
Power (P) =work done (w) /time taken
 P = W / t
(i)
P = W / t
(i)
Again,
Potential difference (V.) = Work done (W) / Charge (Q)
 Or w = V×Q (
ii)
Or w = V×Q (
ii)
From eqn (i) and (ii)
P
= V x Q / t
Or
P = V×Q /t (because I =Q /t )
؞ P = I× V Proved
iii)Magnetic effect of electricity iv)Chemical effect of electricity.
1)Heating effect of electricity :-The conversion of electrical energy into heat energy by passing electricity through a wire of high resistance is called heating effect of electricity .For example: Electric heater , electric kettles etc. change electrical energy into heat energy.
Nichrome wire :-It is an alloy Nickel and chromium. It is used as heating element due to following reason or features:.
ii)It does not react with oxygen ,even at very high temperature .
i)It has high resistivity and high melting point so It can convert electrical energy into light energy because it becomes white hot and emits light energy .
ii)It react with oxygen with air at very high temperature so it is always kept inside glass .
Electrical power consumption :- The energy power conversion by different electric load into other forms of energy in domestic circuit are called electrical power consumption .Its S.I. unit is kilo watt hour(kwh) or unit .
Or E = P(inkw) × N × t(inhr)
Cost of electricity(C) =Total consumed unit × price of one unit
One unit :-Power consumed by electric load of power 1kw in one hour is called one unit power consumption.
1unit = 1kwh
Rating of electrical device :- The maximum value of current (I),potential difference (v) and power (P) that can be supplied to a particular electrical device for its operation is called rating of electrical device .
i)Tube light = 40 watt
ii)Fan = 60watt
iii)Refrigerator = 100 watt
iv)Television = 100 watt
v)Electric kettle= 750 watt
vi)Electric iron = 1000 watt
vii)Air conditioner = 2000 watt- 3000 watt
ix)Immersion rod = 1000 watt
1.)What is meant by the rating of an electric bulb is 60 watt(j/s)?
Ans. It means that electrical bulb convert 60 j of electrical energy into heat energy and light energy per second .
Formula :
i)P = I×V
ii) V =R×I
Given,
Voltage(v)=220 v
Current (I) =10 A
Time consumption per day (t)= hours
Rate of electricity(R) =Rs 9 per unit
By formula
Electrical power(P)=I×V
Or P =10 ×220
Or p = 2200watt
Now, Per day electrical power consumption(E)=P(kw) × N × t(hr)
Or E= 2200×1×5
Or E =11000whr =11000 /1000 =11kwhr or unit
؞One month electrical power consumption (E)=11×30
Or E =330 kwhr or unit
Again, by formula
One month cost of electricity(C) = Total consumed unit × price of one unit
=330×9
Total cost of 30 days(C) =Rs2970.
2.)A circuit with 220 v is supplied with fuse of 5A. How many bulbs of 100 watt can be safely used in the circuit .
Given,
Voltage(v)=220 v
By formula
Total power (P) =I×V
Or P =5×220
Total power (P)1100 watt
Power of bulb (P’) =100watt
For the safety of the circuit
P =P’×n
؞Number of bulb safely used (n) = P /P’
Or n =1100 /100 = 1
Given,
By formula
Per day electrical consumption
i)for 12 tube ligt(E1) =P(kw) × N × t(hr)
E1 = 40×12×4
E1= 1920 whr. =1920 /1000 =19.2kwhr or unit.
ii)For television(E2)=p(kw) ×N×t(hr)
E2 =40×3×4
E2=480 whr =480 /1000 = 0.48 kwhr or unit
iii)For electrical immersion rod(E3) =P(whr) × N × t(hr)
E3 =750×2×2
E3 =3000 whr =3000 /1000 =3kwhr or unit
iv)For electric bulb(E4) =P(kw) ×N× t (hr)
E4 = 100 ×2×2
E4 = 400 whr =400 /1000 =0.4 kwhr or unit
Total electrical consumption of on day (E)=E1+E2+E3+E4
=19.2+0.48+3+0.4
=5.08 kwhr or unit
Total electrical power consumption of 30 days (E)=5.08 ×30
By formula
Cost of one month ( C) =Total consumed unit× Cost of 1 unit
=174 ×7 =Rs 1218.
.

























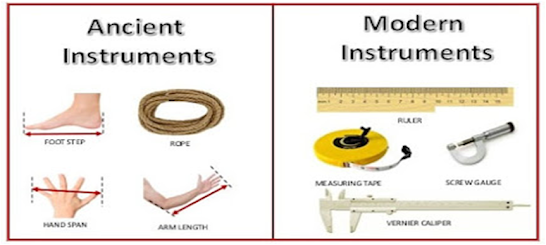








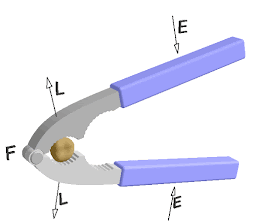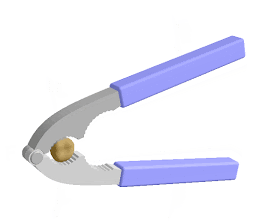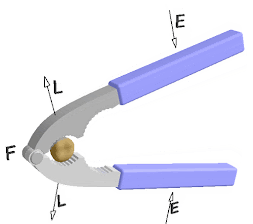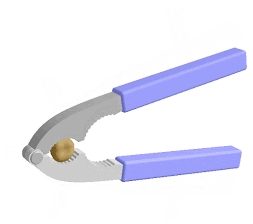
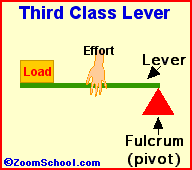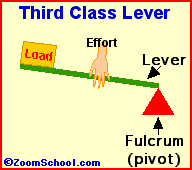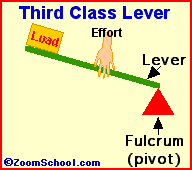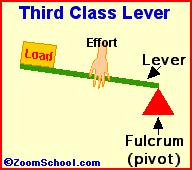


















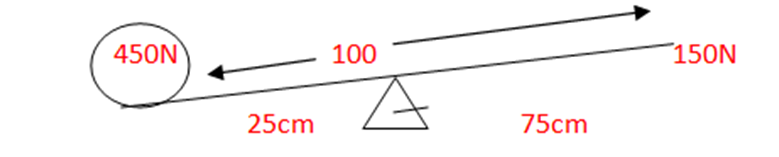
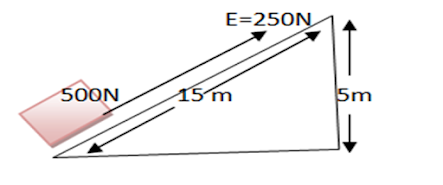



































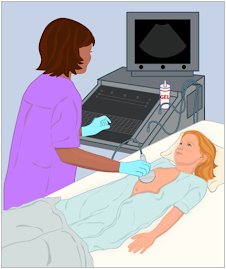


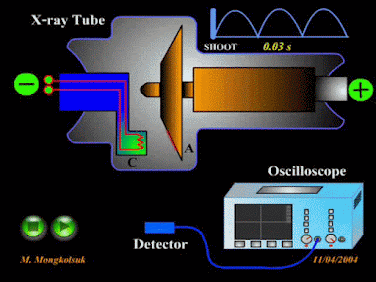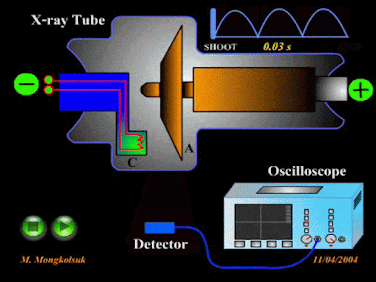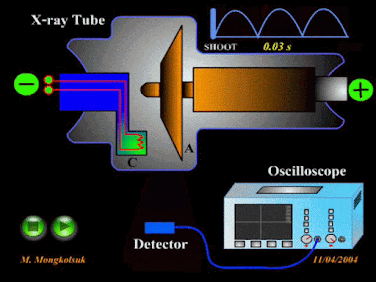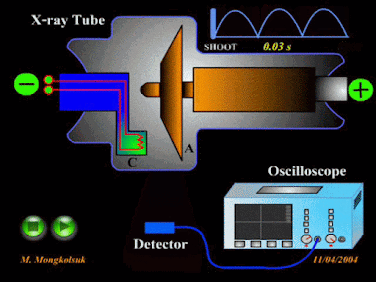





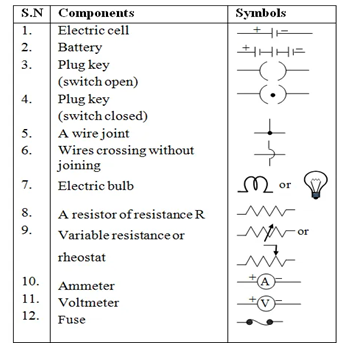

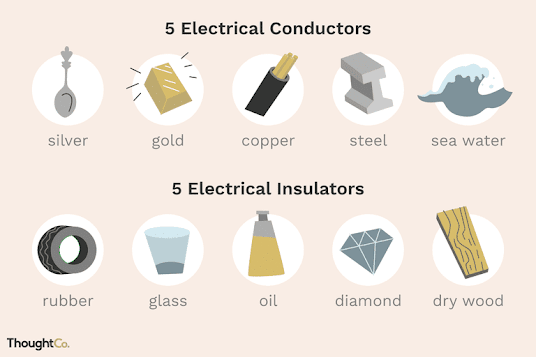









Comments
Post a Comment