Biology Grade - 10 (Science )
15 Human Nervous System &Glandular System
16 Blood Circulation in Human Body
17 Chromosome & Sex Determination
18(A) Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
18(B) Artificial Vegetative propagation in Plants
19 Heredity
Specification Grid -2074
Division of 23 marks in Knowledge(K) ,Understanding(Un), Application(AP), and Higher abilities(HA) types of questions
Areas | S.N. | Units | Total no. of questions & their marks |
Remarks | ||||
K-20% | Un-35% | Ap-24% | HA-21% | Total | ||||
Bio logy | 14
15 16 17 18(A) 18(B)
19 20
| Invertebrates (Ssilk worm ,Honey Bee) Human Nervous System & Glandular System Blooh circulation Human being Asexual & Sexual Reproduction Artificial vegetative propagation in plants. Heredity Environment pollution & Management |
5x1= 5 |
4x2= 8 |
2x3= 6 |
1x4= 4 |
23 marks | Physics-56+ Chemistry-56+ Biolog-56+Geology &Astronomy-12 Periods=180 periods |
7 |
| 5 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 23 marks | ||
Scholastic Areas :-Grading on 9 points Scale
S.N. | Marks range | Grade | Attributes | Grade Points | Remarks |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 90 to 100 80 to below 90 70 to below 80 60 to below 70 50 to below 60 40 to below 50 40 to below 50 30 to below 40 0 to below 20 | A+ A B+ B C+ C D+ D E | Outstanding Excellent Very good Good Satisfactory Acceptable Partially Acceptable Insufficient Very insufficient | 4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 | The minimum qualifying grade in all subjects under scholastic Domain Is C
|
Unit - 14 Invertebrates (Silk worm and honey Bee )
A)Silkworm
Classification
Kingdom –Animalia
Sub-kingdom- Invertebrate
Phylum –Arthropoda
Class –Insecta
Example –Silk worm
1.Introduction
Silk worm is called very useful or beneficial insect because ,it produce silk threads which is used to make different types fashionable clothes .Silk thread is obtained by larva of silk worm ,so it is called silk worm .Silk worm is also called queen of fibre because silk worm gives natural silk ,which is soft ,shiny, strong, durable ,light and longest than that of artificial and natural fibres In Nepal two families of silk worms are cultivated for the production of silk thread.
i)Eri-silk worm (Attacus ricini) :It is reared by feeding castor leaves and produce eri –silk.
ii)Seri-silk worm (Bombyx mori ):It is reared by feeding mulberry leaves and produce seri silk worm .
Seri culture :The rearing of silk worm for commercial purpose is called sericulture .It was started from china .
Vertebrate and invertebrate:The animals which bears vertebral column is called vertebrate and which does not bear vertebral column are called invertebrate .
2.Structure
They are creamy white in colour and just like butterfly but larger than that of butterfly .The body is divided into three parts ie head , thorax and mouth parts ,thorax consist of 3 pairs of legs and 2 pairs of wings and abdomen is hairy and wider .
3.Life cycle : The life cycle of silk worm is completed into 4 stages .it completes its life cycle in about 45 days .The development of egg into adult is known as metamorphosis .
i)Egg (10-12 days)In this stage after fertilization female silk worm lays about 300 eggs in cluster on the mulberry leaves and female silk worm dies within 4-5 days because they do not take food after fertilization. The eggs are white and very in size ie pin shaped .
The eggs of silk worm are stored by keeping in cold place when leave are not available but when leaves are available eggs are kept in18
ii)Larva :(25-32 days)The larva emerge out from egg within 10-12 days is known as caterpillar The larva of silk worm are more active and feeder .They change or shedding their skin 4 times and grow in size ,process is known as moulting .Afer 4rth moulting larva develop a pair of salivary gland on both lateral side which secrete a sticky substance that change into a silk thread in contact of air in which larva wrapped and finally change into a cover is known cocoon.
iii)Pupa :In this stage pupa remains inside a cover is known as cocoon(puparium).Pupa are inactive, does not take food and does not move. The growth of pupa takes place inside cocoon .The process of development of insect inside the puparium is called histogenesis .
In this stage about 1000 feet unbroken silk thread are extracted from a single cocoon by keeping cocoon into hot water or hot air to kill pupa .
iv)Adult :In this stage pupa undergoes active metamorphosis within cocoon and a young silk worm is formed then cut the silk thread into small pieces and comes out a young silk worm ,then life cycle is continued again .
4.)Economic importance of silk worm
i)Silk is used to prepare beautiful and durable clothes ie sari, tie, handkerchief etc.
ii)Silk is to prepare parachute, tyre, cover of telephone wire etc.
iii)Sericulture provides us employments .
B)Honey Bee
Classification
Kingdom - Animalia
Sub- Kingdom - Invertebrate
Phylum - Arthropoda
Class - Insecta
Example - Honey bee
1.)Introduction
Honey bee have developed one of most of the most highly organized societies with division of labour so they are called social insect .They feed on pollen and nectar of flower and manufacture honey and wax .A hive contains about 4000- 8000 bees but male are haploid contains16 chromosomes and female are diploid contains 32 chromosomes .In Nepal only two families are common honey producing bee ie Apis mellifera and Apis cerana.
Apiculture :The rearing of honey bees for commercial propose is known as apiculture .
2.)Structure :
The body of honey is divided into 3 parts ie Head , thorax and abdomen. Head consist of a pair of compound eye ,three small simple on the top of head ,a pair of antennae and mouth parts ,thorax consist of 3pairs of legs and 2 pairs wings and long segmented abdomen .
Types of honey bees : There are 3 types honey bee in a beehive .
i.)Queen bee :-They are larger than that of drone bee and worker bee and small legs .A single hive contains only a single queen bee. Queen bee is the single fertile female in a hive and formed from fertilized egg .They are unable to produce wax and honey or gather pollen or nectar .Queen bee also produce a special smell by which other bee find out their colony .
Functions :-i)Queen bee lays eggs after fertilization.
ii)Queen bee controls and regulate all the bees according to necessary .
ii)Drone bee :-The drone bee is a fertile male which is larger than that worker bee and smaller than that of queen bee .A single hive contains about 100 drone bees and formed from unfertilized egg but they die after mating with the queen. They are more feeder , stingless and do not work .
Functions :- i)The functions of drone bee is to fertilize the new queen bee.
ii)They help to keep the hive warm .
iii)worker bee :-The worker bee are sterile female (reproductive organ inactive) which is smaller than that of queen bee and drone bee . In a hive except queen and drone bee all bee are worker bee .The legs of worker bee are provided with pollen brush and pollen basket to collect pollen .
Functions :-i)Worker bee collect pollen, nectar ,and water for the colony.
ii)They repair the comb and clean the hive .
iii) They use the wings for ventilation and act as the guard at the main entrance hive .
iv)They also guard the stored pollen , honey also feeding developing and fight against enemies .
3.)Life cycle :-The life cycle of honey is completed into 4 stages ie queen in 16 days, drone in 23.5 days, and worker in 21 days .in life cycle when queen become young , she attend a flight where several drone mates with her is also known as mating flight or nuptial flight .
i)Egg:-In this stage after mating queen bee lays about 3000 eggs per day but 2 types of eggs ie fertilized eggs in queen cell and worker to form queen and worker bee and other unfertilized eggs in drone cell to produce drone bee
ii) Larva :- After days eggs change in to larva , the formation of larva of queen and worker depends on the diet received by larva .all larva are fed royal jelly (ie juice collected by worker ie mixture of honey and pollen)but after 3 days worker and drone are fed bee bread and is fed continue royal jelly .They are more active and feeder and moult their skin 4 times .
iii)Pupa:-In this stage worker bee the mouth of cell by wax cap and change into pupa stage and cover is known as puparium . The pupa of honey are inactive, and do not feed so also called rest stage .In this stage development of honey bee takes place inside puparium and process is known as histogenesis .
iv)Adult : The end of pupa stage ,pupa brust the caps and adult bee ie worker , queen, and drone comes out but when new queen comes out ,the old queen leaves out the hive with worker .This is also known as swarming .
4.)Economic importance of honey bee :
i)They supply us honey which is used for food ,medicine and other religious purpose .
ii)The bee hive provides us bee wax which is used for making soap, medicine, polish etc.
iii)They help in agriculture for pollination .
iv)The rearing of honey bee provides us employments.
The End
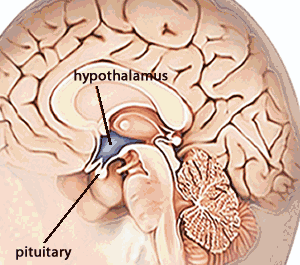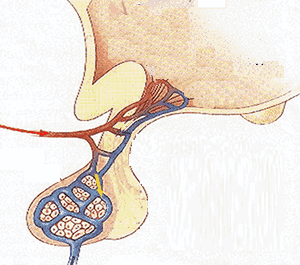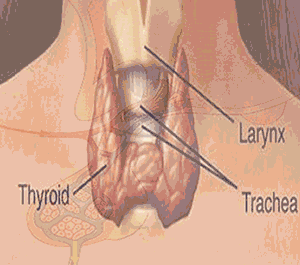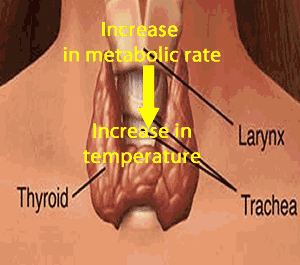
Unit:(15) - Nervous & Glandular system
A)Nervous system:
The group of organs working together to conduction of massage from one part of body to another part and co-ordinates the all activities of body is called the nervous system .
Functions of nervous system : i)It help us to remember ,think and reason .
ii)It controls and regulates all voluntary muscular activities of different parts of body .
iii)It regulate involuntary activities of smooth organ i.e. lungs ,kidney heart ,alimentary canal.
Division of nervous system :-Nervous system is divided into 3 parts :
1.)Central nervous system(CNS) : It consist of mainly two parts :ie A)Brain B) Spinal cord
A)Brain :


The biggest and upper most part of central nervous system is called brain. It is situated in cranial cavity or cranium and surrounded by 3 layers is called meninges ie Duramater ,Piamater and Arachnoidmater .The space between inner two layers is filled with a fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid .It protects brain from injuries and absorb shocks .The brain is also divided into mainly 3 parts :
i)Cerebrum : The largest and upper most parts of brain is called cerebrum .it consist of about 80% parts of brain. It is also divided into right and left hemisphere .
Functions :-i)It stores the past memory .
ii)It controls the sense of movements, hearing ,thinking ,vision, imagination ,feeling of love ,emotion etc
Note :Damage to the cerebrum causes of coma .
ii)Cerebellum : The parts of brain which is situated below the posterior portion of cerebrum and upper portion of medulla oblongata is called cerebellum .It sized and semicircular in structure .
Functions : i)It help to balance our body .
ii)It regulate and co ordinate the movement of voluntary muscles .
iii)It maintenance the muscles tones .
Note : Small injury in cerebellum causes of dizziness that disturb the body balance .
iii)Medulla oblongata : The lower most and small part of brain is called medulla oblongata .The lower portion of it has many nerve tracts that connect with spinal cord .
Functions i)It controls the system ie respiratory ,heart beat ,blood pressure ,breathing etc .
ii)It controls the secretion of enzyme and hormone .
iii)It controls the contractions and expansion of blood vessels .
Note :- injury in medulla oblongata causes of instant death .
B)Spinal cord : A long soft and white rod like structure present inner part of back bone is called spinal cord .It is also surrounded with 3 layers meninges .
Functions : i)It help to connect large parts of nervous system with brain and brain with large parts of nervous system .
ii)It acts as main center of reflex action .
Note : Any injury or shocks to the spinal cord due to disease or accident ,causes of paralysis of the body below the point of injury .
2.)Peripheral nervous system(PNS) :-It consist of mainly following parts i.e.)Cranial nerves or fibers B) Spinal nerves or fibers
A) Cranial nerves :The nerves that directly originate from the brain are called cranial nerves or fibers or tissues .They are 12 pairs in numbers .The cranial nerves help for communication between brain and various organs presents in the head i.e. eyes, ears ,nose tongue etc
B)Spinal nerves :The nerves that originate from spinal cords and form a network of nerves of different parts of body are called spinal nerves or fibers or tissues .They are 31 pairs in numbers .Spinal nerves help for communication between brain and different parts of body or spinal cord .
3.)Autonomic nervous system :(ANS)The nervous system that controls the functions of autonomic activities of smooth organs(internal organs)i.e. respiration , heart beat stomach , intestine ,urinary bladder etc. and certain glands, when we are sleeping or awaking up is known as autonomic nervous system .It is divided into two types and also consist of Ganglion:
i)Sympathetic nervous system :The autonomic nervous system that increase the working rate of smooth organs i.e. respiration , heart beat stomach , intestine ,urinary bladder etc. and decrease the secretion of glands is called sympathetic nervous system.
ii)Para sympathetic nervous system : The autonomic nervous system that restore or balance the working rate of smooth organs i.e. respiration , heart beat stomach , intestine ,urinary bladder etc. and increase the secretion of glands is called parasympathetic nervous system .
Ganglion: The group small nerve tissues made up of grey matter are found near the spinal cord are called ganglion.It help to connect spinal cord with brain .
Neuron or nerve cell :
The structural and functional unit of nervous system is called neuron .It is also called largest cell present in the human body .It consist of following parts :
i)Cell body or cyton : It consist of a nucleus and surrounded by a granular cytoplasm (Nissl’s granules).It produce cytoplasm and controls metabolism in the axon and dendrite .
ii)Dendrite: The branches fibers of neuron is called dendrites .It receives impulses or massage and pass them into the cell body .
iii)Axon: A single long fiber of neuron is called axon .It receives impulses or massage from cell body and send them into the next neuron .Axon is enclosed by a white multilayered sheath is called myelin sheath and between two sheath is called node of Ranvier .myelin help to increase the speeds of impulses conduction .
i)Afferent neuron or sensory nerve :A group of nerve cell that that carries massage or impulses from the different parts of body to the brain is called afferent or sensory nerve .it help to carries massage from different parts of
ii)Efferent neuron or Motor nerve : A group of nerve cell that carries massage or impulses from brain to different parts of body is Efferent neuron or sensory nerve .It help to carries massage from brain to different parts of body .
iii)Connector neurons or mixed neuron(relaying) : A group of nerves which are made up from combination of sensory nerves and motor nerves is called connector nerve .It act as links between sensory nerve and motor nerve for distant transmission of nerve impulses and located in the brain and spinal cord .
Synapse: A small gaps or junction between two neurons where information from one neuron is transmitted to another neuron is called synapse .It help to transmit information from one neuron to another neuron .
Reflex action :An immediate and autonomic response of a body due to external or internal stimulus is called reflex action. It is controlled and conduct by spinal cord. The specific path way taken by nerve impulses in reflex action is called reflex arc .It consist of following 5 parts and shown as following ways :
Glandular system
Gland :A group of cell that help in secretion is called gland .They are two types :
i)Exocrine gland :The gland that have duct are called exocrine gland .They secrete enzyme .The secretion of this gland is carried by the duct to the organs .They lie closely to the target organs. For example :Saliva from salivary gland, tear from tear gland ,sweat from sweat gland etc.
ii)Endocrine gland
The ductless gland are called endocrine gland. They secrete hormone .The secretion of these glands is directly poured into the blood stream. They may lie far from the target organs .For example :Pituitary gland, thyroid gland etc.
Hormone :A special types of chemical which are produced by endocrine gland is called hormone. Hormone carry massage from site of synthesis to the target ,or hormone play an important role to active and stimulate the body cell and functions of other glands so it is called chemical messenger. For example :catalytic hormone ,growth hormone etc.
Enzyme :A special types chemical which are produced by exocrine gland is called enzyme. For example :Pepsin ,rennin etc.
Major endocrine glands in human body :
1.)Gland : Pituitary gland
Location :Below the brain
Hormones : i)Catalytic hormone
Function: i)It control and co ordinate the development and activities of other endocrine gland so it is called master gland .
ii)Growth hormone:
Functions :i)It control physical and mental growth of the body .
Note: Over secretion(hyper secretion) :causes of gigantism and under (hypo secretion)secretion: causes of dwarfism .
Location : In the neck or throat
Hormones : i) Thyroxin hormone
Function : i)It control the rate of metabolism by which body burn calories into energy for mental and physical growth .
ii) it control iodine in blood .
Note : Over secretion(hyper secretion):increase rate of metabolism ,increase pulse rate ,sweating, weight loss, under secretion(hypo section): lack of iodine and causes of enlargement of thyroid gland is known as goiter.
ii)Calcitonin hormone
Functions :i)It regulate the calcium level in blood .
3.)Gland : Para thyroid gland
Location : In backside of thyroid gland in 2 parts 4 in number.
Hormones: i) Parathyroid or parathormone hormone
Function : i)It controls the calcium and phosphate level in the blood .
ii)It controls on exchange of calcium between blood and bone .
iii)It controls the proper development of the bone .
Note : Over secretion (hyper secretion):causes of tumour and stone in kidney and gallbladder , under secretion(hyposecretion): decrease calcium level in blood and twitching of muscles is known as tetany .
4.Adrenal gland : It consist of Two parts:
A)Outer is cortex B)Inner is medulla
Location : In the anterior part of each kidney 2 in number.
A ) Outer Cortex
Hormones : i)Cortisone or corticoids hormone
Function :i)It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates ,fat and protein.
ii) It help to maintain salt and water in the body .
iii)It help to adopt the body in extreme condition i.e. extreme heat ,cold, burn, infection etc-sex
iv)It also produce sex hormone in small amount for later year when sex gland decrease their secretion.
Note :over secretion(hyper secretion) causes of abnormal sexual maturity in early age, under secretion(Hyposecretion) causes of addison’s disease .
B) Inner Medulla
Hormone : i)Adrenalin hormone
Functions: i)It help to prepare the body to face for emergency situation by increasing blood pressure, heart beat and glucose level in blood ,so it is also known as emergency gland.
Note: Over secretion (hyper secretion) cause of high blood pressure ,hyper tension. Under secretion (hyposecretion ) causes of weakness ,low blood pressure, unconsciousness.
5.)Pancrease : It secrete both hormone as well as enzyme ,so it is also called mixed gland.
Location : In the abdominal cavity behind stomach and the top of abdomen.
Hormone : i) Insulin hormone
Functions : i) It help to balance or remove excess sugar from the blood by converting sugar into glycogen and stored in the liver .
Note : Over secretion (Hyper secretion )causes of low blood sugar if sugar level falls drastically causes of come, under secretion (Hyposecretion) causes of diabetes or sugar disease.
ii)Glucagon hormone
Functions :i)It increase sugar level in blood if sugar level become low by converting glycogen into sugar from liver .
6.)Gonads :i.e. Testes and ovary
A)Testes :
Location : In male reproductive organ.
Hormones :Testosteron hormone
Functions : i)It regulate the development of secondary sexual characters i.e.Voice, beard etc.
B)Ovary :
Location: In male reproductive organ.
Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone hormone
Functions: i)It stimulate female sex organs i.e. uterus and ovaries.
ii)it regulate the development of sexual characters i.e. mammary glands, menstrual cycle etc.
The End
Unit - 16 Blood circulation in Human Being
Circulatory system : The group of organs working together to circulate blood from heart to different parts of body and different parts of body to heart is known as circulatory system .
Blood : The red liquid connective tissues which continuously in the human body by carrying O2,CO2, hormone nutrients is called blood .An average human body of male adult consist of about 5/6 litre and female about 4/5 litre blood .It has salty test and PH value of blood is 7.3 to 7.5 .
Structure of blood : It consist of 2 parts :
1)Blood cell : The 45% solid parts of blood is called blood cell . They are 3 types :
i)Red blood cell (RBC) or Erythrocytes
ii)White blood cell (WBC) Leucocytes
iii)Platelets or Thrombocytes
2.)Plasma : The 55% liquid parts of blood is plasma .It consist of about 90% water and remaining 10% consist of hormones ,protein ,glucose ,salt gases ,waste product etc. Plasma without fibrinogen is called serum that used for diagnosis of various kinds diseases
Functions of plasma :
i)It help to transport nutrients absorbed in intestine to the all parts of body .
ii)The blood cell platelets help to prevent the loss of blood from the body by clotting the blood .
ii)It transport waste product from different parts of body to their respective excretory organ ie skin, kidney, liver etc.
iii)It regulate amount of water and minerals in the body.
iv)It transport hormones secreted by endocrine gland to the different parts of body .
v)The albumin protein present in the plasma help tissues repair and growth .
vi)It contains a plasma protein is called fibrinogen that help in clotting of blood by forming insoluble fibrin and globulin that responsible for immunity power of the body .
Functions of blood :-Blood has 3 major functions :
1.)Transportation functions :
i)It transport O2 from lungs to different parts of body and CO2 from different parts of body to lungs .
ii)It transport nutrients absorbed in intestine to the all parts of body .
iii)It transport waste product from different parts of body to their respective excretory organs i.e. skin, lungs, liver , kidney etc.
iv)It transport hormone secreted by endocrine gland to the different of body .
2.)Regulation functions :
i)It maintain body temperature .
ii)It regulate amount of water in the body .
iii)It maintain different chemicals in the body .
iv)It help to regulate PH value by interacting with acid and base .
3.)Protection functions :
i)The blood cell WBC help in the defense system of the body by producing antibody that fight against toxic germs .
ii)The blood cell platelets help to prevent the loss of blood from the body by clotting the blood .
Blood cells :
A)Red blood cell (RBCs) or Erythrocytes
Red coloured non nucleated ,circular blood cell is called red blood cell .One cubic milli meter (mm) blood contains about 45/ 50 lakhs of RBCs .Its life span is about 120 days .They are formed in the bone marrow and destroyed in liver and spleen . They do not contains nucleus but contains protein pigment of iron is called haemoglobin .Haemoglobin help to make blood red in colour and absorb oxygen (i.e.1 molecule of Hb absorb 4 molecules of O2 )from lungs .In a person lack of RBC or haemoglobin causes of Anemia and a person with anemia get tired due to no enough supply of oxygen in the cell.
Functions :
ii)The surface of RBCs absorb the amino acid from the food in alimentary canal and transport into the cells.
B)White blood cell (WBCs) or Erythrocytes :
White coloured ,nucleated ,irregular shaped blood cell is called white blood cell .One cubic milli meter (mm) blood contains about 6000-10000 of WBCs .Its life span is about 12-14 days but the number increase when body is fighting against infection . They are formed in bone marrow and destroyed in the site of infection or in the liver . They contains nucleus but not haemoglobin .
They are 2 two types : i)Granular leucocytes : The leucocytes that have granules in their cytoplasm is called granular leucocytes .It help to engulf bacteria and dust particles present in the blood .They are also 3 types Eosinophils ,Basophils ,and Neutrophils .
ii)Agranular leucocytes : The leucocytes lacking granules in their cytoplasm is called agranular leucocytes .They are also 2 types Lymphocytes and monocytes .Lemphocytes produces antibodies to destroy germs and assist the healing injury and moncytes engulf bacteria .In a person lack of WBCs causes of Leukopenia and excess amount of WBCs in blood causes of blood cancer (Leukamia)
B) Platelets or thrombocytes :
Small ,colourless, and circular blood cell are called platelets .One cubic milli meter (mm) blood contains about 2-4 lakhs platelees.Its life span is about 2-3 days .They are formed in bone marrow and in spleen . They does not contains nucleus and haemoglobin but release thread like fibres is called thromboplastin that help to clot the blood .In person lack of platelets causes of thromobopenis that help in excessive bleeding occurs and excess of platelets causes of thromobocytosis that obstruct blood vessels
Functions i)It help to clot the blood by producing thromboplatin on the skin in the event of an injury and prevent excess flow of blood from the body .
Haemophilia : Haemophilia is a heredity disease in which the blood does not clot .If there is an injury ,more blood may be lost .
1.)Why sodium citrate is treated with donated blood ?
Ans.Some drops of sodium citrate or potassium citrate is put in the blood donation to prevent from clotting of blood ,because it act as anticoagulation .
2.)The blood of a person living in the high mountain contain more red blood cells than that of blood of a person living in the Terai ,why ?
Ans. The amount of oxygen is less in high mountain region and red blood cell is more to take large amount of oxygen for the easy respiration to the body so the blood of a person living in the high mountain region contain more red blood cells.
Blood vessels : The muscular tubular pipe that carry blood through the tissues and organs is called blood vessels .They are 3 types :
1.)Artery :-
The blood vessels which carry the oxygenated blood from the heart to the all parts of body(except pulmonary artery) is called artery .It has thick muscular and more elastic wall because blood remains in high pressure in it. They have no valve. The thinner branch of artery is called arterioles and thicker branch is called aorta.
2.)Vein : The blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from different parts of body to heart (except pulmonary vein) is called vein ).It has thin muscular wall because blood remains in low pressure in it .They have valve that control back flow of blood in it due to low pressure .The thinner branch of vein is called venules and thicker branch is called venacava .
3.)Capillaries :-Very thin and fine network of blood vessels formed by the combination of arterioles and venules is called capillaries. It act act as connection between artery and vein. The exchange of O2 ,CO2 nutrients, and waste product takes place in capillaries .
Heart :
ii)Bicuspid valve or mitral valve or left atrio ventricular valve : The valve which is situated between left auricle and left ventricle is called bicuspid valve .It consist of 2 valve so it is called bicuspid valve .It help to pass and prevent from back flow of blood from left auricle to left ventricle .
iii)Pulmonic valve :The valve which is situated between right ventricle and pulmonary artery is called pulmonic valve .It help to pass and prevent from back flow of impure blood from right ventricle to pulmonary artery .
iv)Aortic valve : The valve which is situated between left ventricle and aorta is called aortic valve .It help to pass and prevent from back flow of pure blood from left ventricle to aorta .
Types of blood circulation _ it is 2 types :
i)Systematic blood circulation : The circulation of blood from the left ventricle to right auricle of heart through the body (except lungs) is called systemic circulation . for example :
ii)Pulmonary blood circulation : The circulation of the blood from fright ventricle of heart to left auricle through the lungs is known as pulmonary blood
1.)Right auricle larger than that of left auricle ,why ?
2.)The walls of ventricle has thicker muscular wall than that auricles ,why?
Ans. The ventricles pumps the blood into artery through aorta and requires more pressure but auricles collect the blood from vena cava through the vein and requires less pressure ,therefore the walls of ventricles has muscular wall than that of auricles .
3.)The wall of right ventricle is thicker than that left ventricle ,why?
Ans. Right ventricle pump only impure blood into the lungs ,and left ventricle pumps the pure blood into all parts of the body, so left ventricle requires more pressure than that of right ventricle .Therefore the wall of left ventricle is thicker than that of right ventricle .
4.)The wall of the vein is thinner than that artery ? or Vein lies just beneath the skin but arteries are deep seated ,why?
Ans. The heart pumps the pure blood into the arteries with in high pressure but blood flow in vein very slowly with less pressure, therefore the wall of vein is thinner than that of artery .
5.)The bleeding from the artery is very dangerous why ?
Heart beat : The periodic contraction and relaxation of heart muscles in order to receive and pump blood is called heart beat .It occurs due to contraction and relaxation of its auricles and ventricles ,in which contraction phase is called systolic phase and relaxation phase is diastolic phase. A normal people have the heart beat rate 72 times per minutes .This rate increase due increase during sickness ,exercise,fear, excitement under stress etc.
Blood pressure : The pressure exerted by the flow of blood on the wall of blood vessels is called blood pressure .It is measured in mili meter of mercury (mm of Hg )by using an instruments is called Syphgmomanometer .
Types of blood pressure : It is 2 types :
i)Systolic blood pressure : The pressure of blood inside blood vessels( i.e. artery)during contraction of heart is called systolic blood pressure .
Normal range : 90 mmHg to 130 mmHg (in medical term normal i.e. 120)
ii)Diastolic blood pressure : The pressure of blood inside the blood vessels (i.e.artery)during relaxation of heart is called diastolic blood pressure .
Normal range : 60 mmHg to 90 mmHg (in medical term normal i.e.80)
High and low blood pressure : When Blood pressure become more than normal range is called high blood pressure (Hypertension) . it can rupture the artery and causes of internal bleeding and death but when blood pressure become less than that of normal range is called low blood pressure (Hypotension) .
Causes of high blood pressure : i)Consumption of more salt and oil in food .
ii)Lack of physical activities and more stress.
iii) over weight .
iv)More use of fatty and fried foods
v)Heredity
vi)Drinking of alcohol and smoking
Symptoms of high blood pressure : i)Causes of headache and faigue.
ii)Causes of blurred vision .
iii)Chest pain and short breath.
iv)irregular heart beat .
v)Blood in urine and internal bleeding .
Control or prevention measure of high blood pressure .
i)By eating healthy foods i.e. low in calories .
ii)Avoiding consumption of more salt ,and oil in food .
iii)Avoid alcohol consumption and smoking .
iv)Maintaining health weight .
v)Avoiding the consumption of soda and cold drink .
vi)Regular exercise and reducing stress.
Diabetes( Blood sugar) : A disease that causes of increase of sugar level in blood due to less production of insulin hormone by pancreas is called diabetes. Insulin convert excess blood sugar into glycogen and store in the liver and glucogon hormone convert glycogen into sugar from liver during lack of sugar level in blood .
Normal range: Fasting sugar level (No food for 8hours ): Between 70 mg/dl to 106 mg/dl
After eating(Post proandial or PP): less than 140 mg/dl or between :80 mg/dl to 140 mg/dl )
Causes of diabetes : i) Lack of physical activities and more stress.
ii) ) over weight .
iii) )More use of fatty and fried foods.
iv) Drinking of alcohol and smoking.
Symptoms of diabetes :
i)Frequent urination .
ii)Excessive thrust .
iii)Excessive hunger and appetite .
iv)Loss of weight .
v)Slow healing and cut of wounds.
Controls or prevention of diabetes :
i)By eating healthy foods i.e. low in calories .
ii) Avoiding consumption of more fat and oil in food .
iii) Avoid alcohol consumption and smoking .
iv) Maintaining health weight .
Uric acid(C5H4N4O3): The acid which is produced as the byproduct of decomposition of purine found in the cell or food is called uric acid .It is formed inside the kidney .It help to provide protein to the body ,protect inner part of blood vessels and help to remove the toxics materials from the body. The concentration of uric acid in blood plasma above the normal range is called hyperuricemia and below the normal range is called hypouricemia .
Normal range : In male -3.4 mg/dl to 7.2 mg/dl
In female -2.6 mg/dl to 6.1 mg/dl
Causes of increasing of uric acid :
i)Over consumption of alcohol and caffeine .
ii)Over weight .
iii)Over consumption of red meat ,pea, and beer and cold drink .
iv)Kidney disorder .
v)Heredity
iv)Consumption of purine rich diet i.e. liver, sea food .
Symptoms of increasing uric acid :
i)Intense joint pain .
ii)Redness , Tenderness, and swelling of joints and skin .
iii)Internal pain in muscles.
Controls or prevention measures of increasing of uric acid : i)Use of lemon juice with hot water .
ii)Eating of straw berry and drinking of black cherry juice .
iii)Less consumption of protein or purine rich foods .
iv)Regular exercise and healthy diet .
v)Drinking of plenty of water .
Chromosome :
The genetic threads like substance present in the nucleus of cell that help in the inheritance of characters from one generation to another generation is called chromosome .They are made up from two components i.e. protein (60%) and DNA (40%).Each chromosome consist two threads like structure are called chromatids .The two chromatids are connected together at point is called centromere .
Gene : A particular segment of DNA molecule which carry heredity characters is called gene. It also called structural and functional unit of heredity located in chromosome .
Functions of chromosome :i)Chromosomes act as heredity vehicles or they transmit characters of parent to their offspring with help of gene .
ii)Chromosome controls the synthesis of protein and help in cell division ,cell growth .
iii)Sex chromosome determine the sex of individual s .
iii)It forms a links between parent and their offspring .
iv)It brings out varriation through crossing over .
Types of cell : on the basis presence of chromosome: they are 2 type:
i)Haploid cell : The cells having x or 2n numbers of chromosome are called haploid cell .This types of cells are formed after meiosis cell division .For example : Gametes
ii)Diploid cell : The cells having 2x or 2n number of chromosome are called diploid cell .This types of cell are formed after mitosis cell division .For example: zygote .
Numbers of chromosomes : There are fixed number of chromosomes in plants and animals cells .Generally in somatic or vegetative cells having diploid (2x or 2n) number of chromosome and in sex or gametes having haploid( x or n) number of chromosome .The number of chromosomes differ from
one species to another species .For example :
Organisms | No. of chromosomes |
1-Human 2-Frog 3-Gorilla 4-Horse 5.Dog 6-House fly 7-Mouse 8-Onion 9-Rice 10-Sugarcane 11-Maize 12.Pea | 46(23 pairs) 26 (13 pairs) 48(24 pairs) 64(32 pairs) 78 (34 pairs) 12 (6 pairs) 40(20 pairs) 16(8 pairs) 24 (12 pairs) 80 (40 pairs) 20 (10 pairs) 14 (7 Pairs) |
Types of chromosome : A)On the basis of position of centromere :They are 3 types :
i)Meta centric chromosome :The chromosome in which the centromere is located in the middle point is called the Meta centric chromosome .In this chromosome two arms are equal in length .
ii)Sub Meta centric :The chromosome in which the centromere is located little away from the middle point is called sub meta centric chromosome .In this chromosome one end of its arm is slightly short and other arm is slightly long .
iii)Acrocentric chromosome : The chromosome in which centromere is located near the end is called acrocentric chromosome . In this chromosome one of its arm is very short and other arm is very long .
iv)Telocentric chromosome : The chromosome in which the centromere is located at one end is called telocentric chromosome .
B)On the basis nature :They are 2 types :
i)Sex chromosome : The pairs of chromosome which determine the sex of individual is called sex chromosome .It single in pair in human being i.e. x and y chromosome in male(44+xy) and xx chromosome in female (44+xx)
ii)Autosome chromosome : The pairs of chromosome which determine the growth and development in the individual are called autosome chromosomes .For example: human being cantains 22 pair or 44 autosome chromosome .
Cell division : The biological process in which a diploid parent cell divides into two or four daughter cells is called cell division .
Types of cell division : There are two types of cell division :
1.)Mitosis or mitotic cell division : The cell division in which a diploid parent cell divides into two diploid daughter cells .They are identical to their parent cell .It occurs only in somatic or vegetative cell ,so it is also called somatic cell division. In this cell division no. of chromosome in daughter cell remains same as in the parent cell so called equational division .
Functions : i)It help for growth and development of plants and animals.
ii)It help in asexual reproduction of plants and animals .
iii)if it become uncontrolled causes of tumour growth .
2.)Meiosis cell division :The cell division in which a parent diploid cell divides into four haploid daughter cells is called meiosis cell division .It occurs in only in reproductive cells at time of gamete formation so it is also called gametic cell division .In this cell division no. of chromosome reduces in the daughter cells so, it also called reductional division .
Functions : It help for producing haploid cells i.e. male gamete(sperm) and female gamete (ovum).
Division of cytokinesis : The process of cytoplasmic division during cell division is called division of cytokinesis .
Division of karyokinesis: The process of nuclear division during cell division is called division of karyokinesis .
Sex determination: The process by which the sex of a person is determined at the time of fertilization is called sex determination .
Mechanism of sex determination in human being: In human being the sex chromosome of male consist of x and y chromosome and sex chromosome of female x and x chromosomes .During gamete formation no. of chromosomes become half i.e. male gamete (22+x or y) and female gamete (22+x), after fertilization fusion of male gamete of x or y chromosome depend on the chances that determine sex of human being .The process of sex determination can be shown as following ways :
Sex linked disease : A disease that occurs only in a particular types sex either male or female is called sex linked disease .These diseases are present in sex chromosome so transfer from one generation to another generation .For example :breast cancer, haemophilia i.e. in female and colour blindness ,baldness i.e. male .etc. Symptoms of haemophilia :i)Excessive internal or external bleeding ,ii)Spontaneous nose bleeding are common.
Chromosomal disorder : The disorder caused by the change in the no. of chromosome or structure of chromosome in human being is called chromosomal disorder .The increase or decrease of no. of chromosomes i.e 45 or 47 due to the failure of completely separation of chromatids during cell division is known as aneuploidy .
Major example of chromosomal disorder :
1.)Down’s Syndrome : The chromosomal disorder which is caused by the presence of an additional chromosome in 21st autosome is called down’s syndrome.It occurs in 21st autosome chromosome so, it is also called trisomy-21 . It was first explained by Johan Longdon Down’s.For example :In case of male will have 45+xy and female will have 45+xx chromosome .The possibility of a baby with down’s syndrome is more the mother of 35 years of age or more.
Symptoms of down’s syndrome:
i)They have flat face i.e. (Mongolian face),a small broad nose ,partially opened mouth ,and short stature .ii)A person will have physically ,mentally and psychologically retarted.
iii)They have undeveloped gonads, respiratory infection, leuakaemia heart
disease etc.
2.)Klinefelter’s syndrome : The chromosomal disorder which is caused by the presence of an additional x chromosome in sex chromosome of an offspring (i.e. male) is called Klinefelter’s syndrome .For example: Male will have 44+xxy chromosomes.
Symptoms of Klinefelter’s syndrome :
i)Male have undeveloped testes and level of testosterone hormone is less .
ii)They are unable to make sperms so they are sterile male.
iii)Breast growth ,less interest in sex ,weaker muscles and less body hair,wider hips .
3.)Turner’s Syndrome: The chromosomal disorder which is caused by the absence of an x chromosome in sex chromosome of an offspring (i.e. emale) is called turner’s chromosome .For example: female will have 44+0x chromosomes .
Symptoms of Turner’s syndrome:
i)Female have undeveloped ovary .
ii)They are unable to make ova or egg so they are sterile female.
iii) Lack of menstrual cycle ,lack of secondary sexual organ, stature etc.
Reproduction : The biological process in which living organism produce new individual their own kinds by sexual and asexual method is called reproduction .It help all the organism for continuity of life .

A)Asexual reproduction: The reproduction which takes place without fusion of male and female gametes is called asexual reproduction .
1.Asexual reproduction in plant : There are 5 types asexual reproduction in plants :
i)Fission: The process of asexual reproduction in which a parent organism divides into two or daughter organism is called fission .It is two types :
a)Binary fission : The in which parent body divides into 2 daughter organism is called binary fission .For example :Bacteria, diatoms etc.
b)Multi fission : The fission in which parent body divides into more than two daughter organism is called multi-fission .For example: Chlamydomonas.
ii)Budding: The process of asexual reproduction which takes place by the formation of the buds is called budding .For example :Yeast
iii)Fragmentation: The process of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into two or more fragments and each fragments develop into new organism is called fragmentation .For example: Spirogyra ,Marchantia etc.
iv)Sporulation: The process of asexual reproduction which takes place by the formation spores is called sporulation .For example:Mushroom, moss Fern,etc.
v)Vegetative propagation : The process of asexual reproduction which takes place by the vegetative parts of plants i.e. root,stem and leaf is called vegetative propagation .They are 2 types :
a)Natural vegetative propagation
b)Artificial vegetative propagation
a)Natural vegetative propagation: The natural process in which the vegetative parts of plants i.e. root ,stem .and leaf takes part in the formation of new plants is called natural vegetative propagation .For example :By roots :sweet potato ,dahlia, etc.

Advantages of vegetative propagation:
i)It is cheaper ,easier ,and faster method of reproduction .
ii)It is used to produce those plants which do not produce good quality of seeds i.e. rose, sugarcane, potato ,banana etc.
iii)The new plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically identical to their parents .
iv)The plants produce by vegetative propagation grow rapidly .
i) i)Fission: The process of asexual reproduction in which a parent organism divides into two or daughter organism is called fission .It is two types :
a)Binary fission : The in which parent body divides into 2 daughter organism is called binary fission .For example :Amoeba, paramecium, euglena etc.
b)Multi fission : The fission in which parent body divides into more than two daughter organism is called multi-fission .For example: Plasmodium..
ii)Budding: The process of asexual reproduction which takes place by the formation of the buds is called budding .For example :Hydra,
1.)What does it mean by the statement that tape worm reproduce by regeneration ?
Ans.It means that when a tape worm is divided into two or more parts each parts of tape worm develop into a new organism.
Advantage or signification of asexual reproduction :
i)It help for continuity of life .
ii)It is cheaper ,easier ,and faster method of reproduction .
iii)It is used to produce those plants which do not produce good quality of seeds i.e. rose, sugarcane, potato ,banana etc.
iv)The new individuals produced by vegetative propagation are genetically identical to their parents .
v)The plants produce by vegetative propagation grow rapidly .
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction:
i)The individual produced by asexual reproduction does no help to bring out varritation in the organism .
2.)Sexual reproduction : The reproduction which takes place by the fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction. The diagram show the process of sexual reproduction in animal.
Gamete: The reproductive cell which are produced by reproductive organ of animal and plants during meiosis cell division is called gamete.It is haploid cell .They are 2 types :
Fig : Ovum
Fig. Sperm
i)Male gamete | ii)Female gamete |
i)The gamete produced by male rep. organ during meiosis cell division is called male gamete . ii)It is smaller in size than that of female gamete . iii)It is active iv)It is motile.(to move) v)For example:Spermi (n animal),Pollen grain(in plant),antherizoid etc | i)The gamete produced by female rep. organ during meiosis cell division is called female gamete . ii)It is larger in size than that of male gamete . iii)It is inactive iv)It is non-motile. v)For example: Ovum(in animal),Ovual(in plant) etc. |
Zygote : The new cell which is formed by the fusion of male and female gamete after fertilization is called zygote .It is diploid cell .
Fertilization: The process of complete fusion of male and female gamete is called fertilization .It is 2 types:
i)External fertilization | ii) Internal fertilization |
i)The fertilization in which fusion of male and female gamete takes place outside of the body of female( i.e. water) is called external fertilization. ii)It takes place in Pisces, amphibian class of animals i.e. fish, frog etc. iii)Copulation does not occurs. iv)There is less chances of fertilization due to absence of copulation . | i)The fertilization in which fusion of male and female gamete takes place inside of the female body is called internal fertilization . ii)It takes place in reptiles ,Aves , and mammalian class of animals i.e. snakes ,pegion, man etc iii)Copulation occurs . iv)There is more chances of fertilization due to copulation . |
i)It help for continuity of life .
ii)The offspring produced by sexual reproduction are genetically different ,so it help to bring out variaition in organism and also lead to evolution .
iii) The offspring produced by sexual rep. have better resistances .
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction :
i) The new individuals produced by vegetative propagation are not genetically identical to their parents .v)The offspring produce by sexual rep. does not grow rapidly .
Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction:
Sexual reproduction | Asexual reproduction |
i)Male and female both involves in reproduction. ii)All division are mitosis . iii)Reproduction units are buds, spore ,fragments etc iv) Fertilization does not takes place. | i)Only single parent involves in reproduction . ii)Meiosis cell division is compulsory for gamete formation. iii)Reproduction units are male and female gametes. iv)Fertilization takes place. |
Sexual reproduction in plants:
Flower :The reproductive organs of plants is known as flower .
i)Calyx(Sepal): The outer most whorls(cover) of flower is calyx .it is small leaf like and green in colour .It help to protect the flower during bud stage .
ii)Corolla(Petal): The 2nd outer most whorls of the flower is called corolla .It is bright ,coloured ,and attractive parts of flower.It help to attract insects towards the flowers for pollination.
Caylax and corolla do not directly involve in the reproduction ,so it also called accessory whorls .
iii)Androcium (stamens): The reproductive parts of plants is called is androcium. It is divided into two parts i.e. filament and anther and anther consist of pollen sac that produce male gamete pollen grains .
iv)Gynocium(pistil or carpel): The female reproductive parts of flower is called gynocium.It is divided into 3 parts i.e. stigma ,style ,and ovary and ovary consist of ovules that contains female gametes eggs .A sac like structure containing 8 cells including eggs cell and present in the ovule is called embryo sac.
Androcium and gynocium directly take parts in reproduction ,so it is called reproductive whorls .
Pollination: The process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of flower is called pollination .It two types :
i)Self pollination | ii)Cross pollination |
i)The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of flower to stigma of same flower or another flower of same plant is called self pollination. ii)Pollination agents are not required for self pollination. iii)It occurs only in bisexual flower. iv)Varriation is not seen. | i)The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther flower of one plant to the stigma of another plant of same species . ii)Pollination agents i.e. wind, air water are required for cross pollination. iii)It occurs in unisexual as well bisexual flower. iv)Varriation occurs. |
Artificial vegetative propagation: The process of preparing large number of plants in short period through vegetative parts by artificial means is called artificial vegetative propagation.It is used to produce large scales of vegetables ,fruits etc.
Types of artificial vegetative propagation : There are mainly 4 types of artificial vegetative propagation:
1.)Layering 2)Cutting
3)Grafting 4)Tissue culture
1.)Layering :The artificial vegetative propagation in which a branch of plant is covered with soil and supplied water to produce roots is known as layering.
Types of layering : There are 5 types of layering :
i)Simple layering: A layering in which low growing branch is buried in the soil and supplied water, after few month roots are developed then ,in rainy season it is separated from parent plant and grow into new plants is known as simple layering .Foe example: Lemon, citrus etc.
ii)Compound layering: A layering in which entire low growing stem is bent down and buried in the soil keeping its tips out of soil and supplied water, after few month each nodes produces roots ,then in rainy season it is separated from parent plant and grow into new plants is known as compound layering .For example: Apple ,pear, nuts etc.
iii)Tip layering: The layering in which the tip of low growing stem of plant is buried in the soil and supplied water ,after few month roots are developed ,then in rainy season it is separated from parent plant and grow into new plant is known as tip layering. For example: Black berry, rasp berry etc.
iv)Mound or stool layering : The layering in which a young plant is cut 5 to 10 cm above from the ground in spring season ,when new buds grow o them the stem are covered with mixture of soil and saw dust ,after few month each buds emerge roots ,then rainy season they are separated from parent plants and grow into new plants is known as mound layering .For example :Mango, guava pear ,plum etc.
v)Air layering : The process of getting new plants through the branch above the ground by suitable process is called air layering .For example:
In this method above 2 years branch of 2-3 cm barks is removed and covered with grafting clay soil and 2 parts and cow dung 1 parts ,then wrapped by water proof plastics ,after 1 to 3 month root will appear ,then branch is cut below bandage and planted in the soil to get new plants .This process of layering is known as air layering .
2.)Cutting :The process of artificial vegetative propagation which takes place by the cutting of vegetative parts of plants i.e. roots ,stem and leaf to produce new plants is called cutting. For example:
By roots i.e. mint
By stem i.e.sugarcane
By leaf i.e. Bryophyllum, Begoniaetc.
3.)Grafting : The process of joining 2 branches of different plants of closely related species is called grafting .For example: Mango, guava, apple, citrus, pear etc.This process consist of 2 parts i.e.During grafting the parts that has strong root system is called stock and other plant whose stem is used is called scion
Types of grafting: It is 3 types :
i.)Whip grafting: The grafting in which scion and stock are cut slanting and join together by tightly bandage ,after 2-3 month scion and stock join together and grafting complete will complete .This process is called whip grafting ..
ii.)Tongue grafting: The grafting in which tongue like deep structure is cut in both scion and stock and both are connected one another, then connected portion is sealed with tightly bandage ,after 2-3 month scion and are connected together and grafting will complete .This process is called tongue grafting .
iii.)Cleft grafting : The grafting in which small hole is made in stock and then pointed end of scion is inserted in the stock and connected portion is sealed with tightly bandage ,after 2-3 month scion and stock join together and grafting will complete. This process is known as cleft grafting .
Unit:19 Heredity
Genetic science: The branch of biology consisting the study of mechanism of heredity and variation is called genetic.Gregor Johan Mendel’s is regarded as the father of genetic science,because he carried out the study in genetic first time .
Heredity: The process of transmission of characters from parents to offspring i.e. from one generation to another generation is called heredity .It is also known as inheritance.
Gene: The structural and functional unit heredity and the particular segment of DNA is called gene .It is located in chromosome and made from DNA .
Heredity characters: The characters which are transfer from parent to their offspring are called heredity characters .They are 2 types :
i)Dominant characters: The characters which appears in F1 generation by covering the other characters are called dominant characters. It is represented by capital letter i.e. T for tall ,R for red colour .
For example: curly hair, isolated ear lobule, Pressure of dimple mark, Straight thumb, Folding or rolling tongue, black skin etc.
ii)Recessive characters: The characters which does not appears in F1 generation but appear in F2 generation are called recessive characters . It is represented by small letter i.e. t for dwarf ,r for white colour . For example: straight hair, joint ear lobule ,absence of dimple mark ,back turned thumb ,Not folding or rolling thumb ,white skin .
Variation: The visible differences between the parent and offspring or between the offspring of the same parent is known as variation.
Causes of variation :
i)Formation of gametes by meiosis cell division.
ii)Environmental influences .
iii)Transfer of character from father and mother both.
iv)Due to structural and functional differences of genes.
Advantages of variation:
i)They form basis of heredity.
ii)They are the source of evolution and development of new organism.
Types of variation : There are main 2 types of variation :
1.)Heredity variation or genetic variation: The variation which transfer from one generation to another generation due to the structural and functional differences of genes is called heredity variation .It also 2 types:
i) Continuous variation: Gradual change in organism due to crossing over between homologous chromosome during gametes formation is called continuous variation. It transfer from one generation to another generation continuously. For example: colour of skin, hair etc.
ii)Discontinuous variation or mutation: Sudden change in nitrogen bases of DNA or genetic materials is called discontinuous variation or mutation. It does not transfer from one generation to another generation and takes place due to various factors i.e. ultra violet rays ,x-rays ,different chemicals. For example :six fingers limbs in human ,cut at lip by birth etc.
Heredity characters: The characters which gets a person through birth due to genes is called heredity characters .For example: five fingers ,two eyes two hands etc.
Acquired characters: The characters which gets a person after birth due to environment and effort is called acquired characters .For example: singing skill, writing skill, drawing skill etc.
Alleles or allelomorphs: A pair of genes controlling contrasting characters is known as alleles. For example: TT (tall), Tt (hybrid tall), tt (Dwarf) etc. They are 2 types :
i)Homozygous alleles: If both alleles of genes are identical are called homozygous alleles .for example:TT (tall),tt (dwarf) etc.
ii)Heterozygous alleles :It both alleles of genes are not identical are called heterozygous alleles .for example.Tt(hybrid tall) .
Phenotype: The physical or external or observable expression of an organism is called phenotype.It may change with time and environment .For example :Tall (TT) and hybrid tall(Tt) are same Phenotypically.
Genotype: The genetic expression of an organism is called genotype .It remains the same through out the life of an individual.For example :Tall (TT) and hybrid tall (Tt) are different genotypically.
Hybrid: The organism which are produced after cross fertilization between two genetically different organism is called hybrid .The process by which hybrid are produced is called hybridization ie monohybrid, dihybrid, polyhybrid etc
F1 generation: The generation obtained by crossing two parent is called F1 generation or first generation.
F2 generation : The generation obtained by crossing F1 generation is called F2 generation or second generation.
Mendel`s select pea plant for his study due to following reasons : i)Pea plants contains large number contrasting characters i.e .tall, dwarf, red flower, white flower, round seeded, wrinkled seeded .
ii)They have short life cycle and can be cultivated easily.
iii)Breeding process can be controlled easily in plant due to the structure of flower .
iv)They produce large n. of offspring .
v)They are easy to handle due size of flower.
vi)The plants are bisexual so can easily be crossed pollinated and self pollinated.
Mendel’s Experiment: The experiments of Mendel’s are divided into two parts :
i.)Monohybrid cross: The cross which involves between only one pair of contrasting characters is called monohybrid cross .For example: The cross between pure tall and pure dwarf pea plants .
1.)When pure Tall and pure dwarf pea plants are cross .What will be that ratio of pure tall and pure dwarf pea plant in F2 generation ?Give its phenotype and genotype ratio with help of the checker board.
Ans. Sign
Pure tall=TT or T
Pure dwarf=tt
Result: i)Phenotype:The phenotypic ratio of pure tall and pure dwarf pea plant is 3:1(75% tall pea plants and 25% dwarf pea plants)
ii)Genotype: The genotypic ratio of pure tall ,hybrid tall and pure dwarf pea plants is 1:2:1(25%pure tall,50%hybrid tall and 25% pure dwarf pea plants)
2.)When Red flower and white flower pea plant are crossed .What will be that the ratio of red flower and white flower pea plant in F2 generation.?Give its phenotype and genotype ratio with help of checker board.
3)When black colour rabit and white colour rabit are crossed .What will be that the ratio black colour and white colour rabit in F2 generation ?Give its phenotype and genotype ratio with help of the checker board.
4.)When round seeded and wrinkle seeded pea plants are crossed ?What will be that the ratio of round seeded and wrinkle seeded pea plants in F2 generation? Give its phenotype and genotype ratio with help of the checker board.
5.)When Pure tall and hybrid tall pea plant are crossed .What will be the that the ratio of pure tall and hybrid tall pea plant in a F1 generation .
6.)When tall and tall pea plant are crossed .What will be that the ratio of pure tall pea plant in F1 generation .
2.Dihybrid cross : The cross which involves between two pair of contrasting characters is called dihybrid cross .For example: The cross involves between Round seeded yellow colour and wrinkle seeded1 green colour pea plant .
1.)When a round seeded yellow colour and wrinkle seeded green colour pea plant are crossed.what will be that the ratio of Round seeded yellow colour ,roud seededgreen clolour ,wrinkle seeded yellow and wrinkle seeded green colour pea plant in F2 generation.Give its phenotype and genotype ratio with help of checker board .
Mendelism or Mendel’s law: On the basis of experiment Mendel’s proposed following 3 laws is known as Mendelism.
1.)Law of dominance: It states that when a pair of pure contrasting character are crossed only one form of the characters appears in F1 generation is called dominance character and other remains unexpressed is called recessive character. For example: in Mendel`s monohybrid cross when pure tall and pure dwarf pea plant are crossed ,in F1 generation only tall plant are plants are seen are called dominance characters but other remain unexpressed are called recessive characters.
2.)Law of purity of gametes or Law of segregation: It states that the dominant factors and the recessive factors in hybrid organism remain together for long time but don’t intermix each other and separate (segerate) at the time of gamete formation and also show that each gamete receive only one factor from a pair of character so law of segregation is also called law of purity .For example :in Mendel’s monohybrid cross when pure tall and dwarf pea plant are crossed in F1 generation dwarf plant are not seen but in F2 generation on basis of segregation dwarf plant are again seen.
3.)Law of independent assortment: It states that when the parents differ from each other in two or more pairs of contrasting characters or factors,and each pair of contrasting characters is independent to other i.e.one character does not effect to other character during inheritance.
Sex link diseases: The diseases which only occurs in a particular sex i.e. Male or Female is called sex linked disease .For example: Haemophilia only occurs in female due to which causes continues bleeding through cut or wound, Baldness only occurs in male.
Differences between DNA and RNA
Deoxy ribonucleic acid(DNA) | Ribo nucleic acid(RNA) |
i)It mainly found in chromosome. ii)It transmit heredity characters from one generation to another generation. iii)It is made up from deoxy ribo sugar. iv)It is double helicle structure consisting of two strands. v)It consist of Nitrogen bases ,Phosphate ,and sugar( N.-P.-S). vi)Its Nitrogen bases consist of Adenine,Guanine,Thymine,Cytocine. | i)It is mainly found in cytoplasm. ii)It is responsible for protein synthesis iii)It is made up from ribose sugar. iv)It is single helicle structure consisting of single strand. v)It consist of Nitrogen base, Ribose, sugar(N.-R.-S). vi)Its nitrogen base consist of Adenine, Guanine ,Uracil, and cytocine. |
The End
Unit:-20 : Environmental Pollution and Management
Pollution: Any undesirable change in the physical ,chemical and biological properties of air, water and land that causes to harm man and other species is called pollution .
Pollutant: The factors that causes of pollution are called pollutant.
Types of pollutants:A)on the basis of degradation: They are 2 types:
1.)Biodegradable pollutants: The pollutants which are degraded by biological action are called biodegradable pollutants. For example: Cow dung ,human stool.
2.)Non-Biodegradable pollutants: The pollutants which are degraded by micro-biological action are called non-biodegradable pollutants. For example :Glasses, plastic, D.T.T.,B.H.C. etc.
B)On the basis of sources of origin: They are 2 types :
1)Primary pollutants : The pollutants which are directly from sources are called primary pollutants. For example :Nitric oxide, Sulphur dioxide, etc.
2.)Secondary pollutants: The pollutants which are formed by the chemical interaction of 2 or more primary pollutants are called secondary pollutants. For example: Nitrogen dioxide.
Environmental pollution : The degradation of one or more components due to natural and artificial causes is called environmental pollution .
Environmental management: The proper management of causative factors of environmental pollution to bring improvement in environmental conservation is called environmental management .
Types of pollution: There are mainly 5 types of pollution:
A.)Air pollution: The condition of degrading of natural quality of air due to mixing of different pollutants in atmosphere is called air pollution.
Sources of air pollution: They are 2 types :
i.)Natural sources : The sources which are originated directly from nature are called natural sources. For example :Volcanic eruption, forest fire, soil erosion, vapoure released by plants .etc.
ii.)Artificial sources : The sources which are not naturally made but caused due to human activities are called artificial sources .For example: carbondioxide(CO2),carbonmonoxide(CO),Nitrogendioxide(NO2),Sulpherdioxide(SO2),wastages from vehicles etc.
Effects of air pollution: Air pollution has short term and long term adverse effects on environment ,climate change, ecosystem, and human health.The majors effects due to air pollution are given below.
i)Reduction in visibility .
ii)Reduction in solar radiation.
iii)Green house effects.
iv)Acid rain.
V)Depletion of ozone layers .
vi)Climate change and destruction of historical monuments.
vii)Inhibition in growth of plants
viii)Bad effect on human health i.e. burning of oesophagus ,nose,heart diseases, cancer etc.
Control measures of air pollution: The air pollution can be controlled by following ways:
i)Filters should be used in industries to remove toxic gases.
ii)Industries should be far from human settlements .
iii)Controlling rapid growth population.
iv)Establishments of atomic power plant should be banned.
v) Afforestation and conservation of them.
vi)Using alternative source of energy to operate industries and vehicles.
vii)Conducting various awareness programs about controlling air pollution.
B)Water pollution: The condition of degrading of natural quality of water due to mixing of different pollutants in water resources is called water pollution .
Sources of water pollution: They are 2 types :
i)Natural sources : The sources which are originated directly from nature are called natural sources. For example : Natural disaster ,Gases, soil, humus, wastages created by living organism present in water and minerals likes sodium, potassium ,calcium lead ,mercury etc.
ii)Artificial sources: The sources which are not naturally made but caused due to human activities are called artificial sources .For example:
i)Agriculture wastages
ii)Household detergents and sewage water(water soil).
iii)Contaminated wastages from industries.
iv)Hot water from industries .
v)Oily water pollution .i.e. leakage of oil from ship.
vi)Bursting of drainage pipe.
Effects of water pollution: The majors effects of water pollution are given below:
i)It causes of different diseases i.e. Diarrhoea, cholera, hepatitis A and B typhoid etc.
ii)Drinking of water excessive level of nitrate causes of lower in blood vessels.
iii)Water lower the oxygen level in water that effects aquatic plants and animals .
iv)Polluted water produced bad smell.
v)Water pollution disrupts food chain and food webs of different ecosystems.
vi)It causes of destruction of useful micro organism ,which are natural cleansing agents of water .
Controls measures of water pollution: Water pollution can be controlled by following ways:
i)By managing waste disposal and sewage treatment.
ii)Reducing excessive use of fertilizer and pesticides.
iii)By treating industrial wastage before discharging into water.
iv)Afforestation and conservation of forest.
v) Stopping movement of domestic animal near water resources.
vi)by maintaining sanitation around water resources.
C.)Soil pollution: The condition of degrading of natural quality of soil due to mixing of different pollutants in the soil is called soil pollution .
Sources of soil pollution:
i)Household wastages.
ii)Excessive uses of chemical fertilizer and pesticides to the soil.
iii)Municipal wastages .
iv)Acid rain that increase the acidic property of soil.
v)Dust particles from mine and industries .
vi)Industrial wastages i.e. lead ,mercury ,copper etc.that degrade the quality of soil.
i)Dust particles from mine and industries causes of lung disorder, and destroy plants life.
ii)Acid rain and chemical fertilizer decreases the crops production.
iii)Polluted land also. pollute water resources
iv)Industrial wastages thrown into soil show toxic effects on the organism.
v)Soil pollution due plastic causes of cancer, skin diseases etc.
Control measures of soil pollution :Soil pollution can be controlled by following ways :
i)The uses of chemical fertilizer must be replaced by compost manure .
ii)The use of chemical pesticides and indectisides must be minimized.
iii)The loss of soil due to soil erosion, land slide ,flood should be replaced by afforestation .
iv)Conducting agriculture activities by agro- forest system.
v)Public awareness should be generated to reduce soil pollution .
vi)Polluted water should not be used for irrigation .
Conservation and management of forest : The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees .It support a myriad of life form, help in maintaining environmental balance of particular place ,provides habitats to various animals ,birds ,and micro- organisms .It also various provides useful materials to human being for various purpose .It also help for rainfall , and provides fresh oxygen by taking carbon dioxide. Following ways can be implemented for the conservation and management of forests .
i)Forest fire should be controlled
ii)Cutting and planting trees by making a advance plan.
iii)Afforestation and conservation of forests.
iv)By implementation of laws for conservation of forest .
v)By plantation in barren ,spare and slope land .
vi)Proper utilization of forest product .
Advantages of forests :
i)Leaves and dead plants increase the fertility of soil.
ii)The level of underground water remain same near the forest .
iii)Forest increase the rate of rainfall .
iv)We can get the medicinal plants from the forest.
v)Forest provides the home for wild animals .
iv)Forest provides woods for furniture.
Water resources is a most important natural resources .It help all form of life on the earth .It provide habitat for all aquatic organisms , help to maintain environmental balance through water cycle. It is used by people for drinking ,cleaning ,washing ,generating hydro-electricity .Following ways
can be implemented for the conservation and management of the water resources :
i)Afforestation to protect land from soil erosion ,flood ,land slide etc.
ii)Banning fishing with the use of poison and electricity .
iii) Generating awareness to control misuse and wastage of water .
iv)By using scientific ways for storing and distributing water.
v)Proper management for controlling water pollution ,storing and transforming surface water in order to conserve water resources .
vi)Re cycling and reusing of polluted water for various purpose .
Advantages of water resources
i)It is used for drinking ,sanitation ,irrigation .
ii) it is used in industries and hydro-electricity .
iii)It is used for fish forming ,alternative transport i.e. boating, rafting ,shipping etc.
iv)It is used in human health.



























































































Comments
Post a Comment