Biology Grade-9/Old Course (Science )
Biology Grade - 9 (Science )
17
Adaptation of Organism
18 Syatem
19 Sense
Organs
20 Evolution
21 Nature and Environment
Specification
Grid
-2074
Division of 23 marks in Knowledge(K) ,Understanding(Un),
Application(AP), and Higher abilities(HA) types of questions
|
Areas |
S.N. |
Units |
Total
no. of questions & their marks |
Remarks |
||||
|
K-20% |
Un-35% |
Ap-24% |
HA-21% |
Total |
||||
|
Bio logy |
16 17 18 19 20 21 |
Classification of Plants and Animals Adaption of organism System Sense Organs Evolution Nature and Environment |
5x1= 5 |
4x2= 8 |
2x3= 6 |
1x4= 4 |
23
marks |
Physics-56+ Chemistry-56+ Biolog-56+Geology &Astronomy-12 Periods=180 periods |
|
6 |
|
5 |
8 |
6 |
4 |
23
marks |
||
Scholastic Areas :-Grading on 9 points Scale
|
S.N. |
Marks range |
Grade |
Attributes |
Grade
Points |
Remarks |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
90 to 100 80 to below 90 70 to below 80 60 to below 70 50 to below 60 40 to below 50 40 to below 50 30 to below 40 0 to below 20 |
A+ A B+ B C+ C D+ D E |
Outstanding Excellent Very good Good Satisfactory Acceptable Partially Acceptable Insufficient Very insufficient |
4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 |
The minimum qualifying grade in all subjects under scholastic Domain Is C |
Unit – 16 Classification of Plants and Animals
Classification :The process of grouping of the living being into various groups and sub groups on the basis of similar and dissimilar characteristics is called classification .
Importance of classification :
i)It makes the study of plants and animals easier ,scientific and systematic .
ii)It help the understand the relation between various group of plants and animals .
iv)It gives the ideas about the evolution of plants and animals .
v)It help to brings uniformity in the study of living organism all over the world .
Nomenclature :The system of providing scientific name to all the living organism is called nomenclature .
Binomial system of nomenclature :The naming of each organism by two words a generic name and specific name is known as binomial system of nomenclature .For example :scientific name of human being is Homo sapiens ,where Home is the name of the genus and sapiens is the name of species .
Genus :A genus is the closely related species .For example :All true cats like lion ,tiger,and domestic cats are kept in the genus Panthera or Felis .
Species : The closely related organisms having almost similar characteristics ,and can interbreed freely and produce healthy offspring is called species. For example : All types of human being through out the world are kept in
same species i.e. sapiens
Scientific name of some common organism
Common name Scientific name
1.Pea plant Pisum satvum
2.Onion Alium cepia
3.Mango Mangifera indica
4.Wheat Triticum astivum
5.Soya bean Glylcine max
6.Sun flower Helianthus annus
7.Rice Oryza sativa
8.Orange Citrus sinensis
9.Papaya Carica lupus
10. Tiger Panthera Tigris
11. Fox Vulpes vulpes
12Horse Equus caballus
13. Buffalow Babalus bubalis
14. Cat Felis domesticus
15. Cobra Naja naja
16. Lion Panthera leo
17. Tiger Panthera Tigris
18. Horse Equus caballus
Two system of classification of organism :Carolous Linnaeus divided living organism into two kingdom i.e. 1)Plant kingdom 2.)Animal kingdom .This is known as two system of classification of organism .It is also called oldest system of classification .
Drawbacks of two system of classification of organism :
i)Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are put together .
ii)Green and non green plant are put together .
iii) Bacteria could not be classified as plants or animals in two system of classification .
Five system of classification of organisms : American scientist Robert H. Whitaker divided living organism into five into five kingdom .This is known as five system of classification .It is also regarded as best and widely accepted classification of system .
Advantages of five system of classification of organisms :
i)Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are kept separately .
ii)The unicellular and multi cellular are kept separately .
iii) The green and non green plants are kept separately .
A.1) Kingdom Monera
B.2) Kingdom Protista
C.3) Kingdom Fungi
D.4) Kingdom animalia
E.5) Kingdom plantae
A.)Kingdom Monera :
Characteristics :
i)They are simple and primitive .
ii)They are prokaryotes because they do not have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
iii)They are unicellular and microscopic.
iv) They have naked D.N.A.
v)They are autotrophic or heterotrophic .
For example : Bacteria ,green algae ,azobactor et

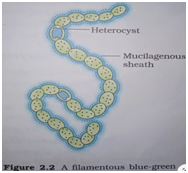
Fig. Bacteria Fig. Green algae
B.)Kingdom protista
Characteristics
i) They are eukaryotes because they have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
ii)They are unicellular and microscopic.
iii)They are autotrophic or heterotrophic .
For example :Amoeba, paramecium, euglena ,plasmodium etc.
Fig. Euglena
C.) kingdom Fungi
Characteristics
i.)They are eukaryotes because they have nucleus or cell organelles i.e. mitochondria, golgi bodies, chloroplast.
ii.)They are non green unicellular or multi cellular.
iii)They are heterotrophic .
For example :Yeast, mushroom ,mucor etc
D.) Kingdom plantae
Characteristics :
i)They are green autotrophic due to presence of chlorophyll .
ii)They are mostly aquatic .
iii)They store food in the form starch .
iv)They are unicellular or multi-cellular.
v)They have cell wall made of from cellulose .
For example :Spirogyra, volvox, chalmydomonas ,ulothrix, etc .


Fig. Spyrogyra
2.)Division :Bryophyta
Characteristics :
i)They are multi cellular plants .
ii)They mostly grow in moist and shady places .
iii)They are green autotrophic due to presence of chlorophyll.
iv)They requires water for fertilization so also called amphibian plants .
v)They show alternation of generation in their life cycle i.e. saprophyte and gametophyte .
vi)They are green autotrophic due to presence of chlorophyll .
For example :Moss , liver worts , marchantia ,riccia, etc.
Division :Trachaeophyta
Characteristics :
i) They are green autotrophic due to presence of
chlorophyll .
ii)They have vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem.
iii)The plant body is well develop.i.e. differentiae into root stem and leaf .
iv)They are mostly terrestrial .
v)The division trachaeophyta is divided into three sub-division :i)Pteridophyta ii)Gymnosperm iii)Angiosperm
1.)Sub-division :Pteridophyta
Characteristics :
i) They are green autotrophic due to presence of
chlorophyll .
ii)They have vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem.
iii)The plant body is well develop.i.e. differentiae into root stem and leaf .
iv)They mostly grow in moist ,shady, and cool places .
For example :Fern ,Lycopodium ,horsetail, selaginella etc.
2.)Sub –division :Gymnosperm
Characteristics :
i)Plants are commonly trees or shrubs .
ii)They are cone bearing plants .
iii)They have naked seeds, which are not enclosed in fruits .
iv)Leaves are long or needle shaped .
v)They have unisexual flower .
vi) They have vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem.
For example :Cycas ,pinus etc.
3.)Sub division –Angiosperm
Characteristics :
i)They are found in water and land.
ii) They have vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem.
iii)They have well develop flower and fruit .
iv)The seeds are enclosed inside fruits .
v)They have unisexual bisexual flower .
vi)The sub division angiosperm on basis of present of cotyledon on their seeds is also divided into two classes :a)Monocotyledon b)Di cotyledon
a)Class -Mono cotyledon: The plants which contains only one cotyledon in their seeds are called monocotyledon plants .
Characteristics :
i)They have only one cotyledon in their seeds .
ii)They have adventitious or fibrous root system.
iii)They have parallel venation in their leaves .
iv)Vascular bundles re scattered in the stem .
v) They are usually non-woody plants.
For example :wheat ,barley, bamboo, sugarcane ,onion, garlic etc.

Fig . Showing monocotyledon roots and seed
b) Class –Di cotyledon: The plants which contains two cotyledon in their seeds are called Di cotyledon plants .
Characteristics :
i)They have two cotyledon in their seeds .
ii)They have tap root system .
iii)They have reticulate venation in their seeds .
iv)Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring structure around the stem .
v) They are usually woody plants
For examples :Pea, gram, bean, orange, mustard etc.




Fig. Showing dicotyledon root, seed, and leaf
5.)Kingdom-Animalia
B.)Sub Kingdom-Vertebrate
A.)Sub kingdom-Invertebrate:The animal which does not contains vertebral column is called invertebrate .Invertebrates are divided into 8 phylum :
1.)Porifera :
Characteristics :
i)They are aquatic ,mostly marine.
ii)They do not move from one place to another place ,so they are called sessile.
iii)They bears numerous pores to their body i.e. small pores are called ostia, and large pores are called osculum. Water enters to their body through ostia and leaves through osculum.
iv)They are simplest, multicellular, diploblastic i.e. body consist of 2 layers i)ectoderm ii)endoderm.
v)They are hermaphrodite i.e body bears both male and female sex.
For example : Sycon, spongilla, sponge .
2.)Coelenterata :
Characteristics :
i)They are aquatic ,mostly marine.
ii)They have hollow internal cavity is called coelenterons.
iii)They are multi cellular and diploblastic .
iv)Tentacles are present in the mouth that help to capture the prey.
v)They are unisexual or bisexual .
For example :Hydra, Jelly fish, sea anemone, corals .
3.)Phylum-Platyhelminthes :
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly parasite .
ii)They are dorso-ventrally flattened like leaf, so also called flat worm
iii)They are triploblastic i.e. body contains three layers i)ectoderm ii)mesoderm iii)endoderm
iv)The body is bilaterally symmetrical
v)The mouth is surrounded by hooks that help to attachment with host and consist of sucker to absorb blood from host.
vi)They are hermaphrodite .
For example :Tape worm ,Planeria, Liver fluke etc.


Fig. Liver fluke Fig. Tape worm
Fig . Planaria
4.)Nemathelminthes :
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly parasite .
ii)The body is cylindrical ,elongated ,and unsegmented .
iii)The body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic .
iv)They are unisexual .
For example :Round worm, Hookworm etc.


Fig. Hook worm Fig .Round worm
5.)Phylum –Annelida
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly aquatic and moist place.
ii)They are cylindrical ,elongated and segmented .
iii)They are hermaphrodite .
iv)The body is triploblastic and bialaterally symmetrical .
For example :Leech, Earthworm, Nereis etc.
6.)Phylum-Arthopoda
Characteristics:
i)They are found in air water and land everywhere .It is also called largest phylum of invertebrate .
ii)The body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen but in some head and thorax are fused to form cephalothorax .
iii) The body is triploblastic and bialaterally symmetrical .
iv)The body consist of joint legs .
v)They are unisexual .
vi) The phylum arthropoda is also divided into 4 classes :
For example :Butterfly, Mosquito,Crab, Scorpion etc.
a)Class-Crustacea
Characteristics :
i)They have 5 pairs of legs .
ii)The body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen .
iii)The head bears two pairs of antennae .
iv)Respiration takes place by gills .
For example :Crab, Prawn etc.
Fig. Prawn
b)Class –Insecta
Characteristics :
i)They have 3 pairs of legs .
ii)Body is divided into head ,thorax and abdomen .
iii)The head bears one pairs of antennae .
iv)Respiration takes place by trachea .
For example .;Mosquito, House fly, Cockroach etc.
Fig .House fly
c)Class –Arachnida
Characteristics :
i)They have 4 pairs of legs .
ii)The body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen .
iii)The bears one pairs of legs .
iv)Respiration takes place by trachea .
For example :Spider, Scorpion ,Mite etc.
Fig. Spider
d)Class -Myriapoda
Characteristics :
i)They have many pairs of legs.
ii)The body divided into head and trunks .
iii)The bears one pairs of antennae .
iv)Respiration takes place by trachea .
For example :Centipede ,Millipede etc.
7.)Phylum-Mollusca
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly found in aquatic and damp place. It is also called second largest phylum of invertebrate .
ii)The body is soft ,unsegmented ,and covered with hard shell called calcareous shell .
iii)The body is triploblastic ,and bialaterally symmetrical .
iv)Respiration takes place by gills or lungs .
For example :Pila ,Slug, Octopus ,Snail etc.
8.)Phylum –Echinodermata
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly found in marine .
ii)The body are provided with numerous spines.
iii) The locomotion takes place by tube feet .
iv)They are unisexual .
v)Respiration takes place by gills ,respiratory trees .
For example : Starfish ,Sea urchin, Sea cucumber, sea lily etc.
B)Sub kingdom :-Vertebrate :It consist of phylum chordate
Phylum : Chordata
Characteristics :i)They possess an unsegmented elastic rod like structure called notochord in the dorsal axis of the body .
ii)They have red blood due presence of hemoglobin in RBCs.
iii)Reproduction takes place only by sexual method .
iv) It is also further classified into four sub phylum :
1)Hemichordata ii)Urochordata
iii)Cephalochordata iv) Vertebrata
Sub Phylum :Vertebrata
Characteristics :
i)They vertebral column in their body .
ii)The brain lodged into a box i.e. cranium.
iii)The endoskeleton is made up from bone or cartilage .
iv)All vertebrate have a heart and a closed circulatory system .
v)They may be cold blooded or worm blooded .
vi) They are oviparous or viviparous .
vii) it is also further divided into 5 classes :
1)Pisces 2) Amphibia
3)Reptilia 4) Aves
5)Mammals
1)Class : Pisces
Characteristics :
i)They have streamline bodies adopted for aquatic life.
ii)Endoskeleton is made up from bone .
iii)Body is covered with scales and respire with gills .
iv)They have fins for locomotion .
v)They have 2 chambered heart .
vi)They are cold blooded ,oviparous ,and fertilization is external .
For example :All types of fishes i.e. rohu, Sea horse, Flying 

Fig. Fish Fig. Sea Horse
2)Class : Amphibia
Characteristics
i)They live in both land and water ,so also called amphibian.
ii)They have thin moist and smooth skin .
iii)Body is divided into head and trunk .
iv)They have 2 chambered heart .
v)They are cold blooded ,oviparous ,and fertilization is external .
v)They respires through skin and lungs .
For example : Toad ,Hyla( tree frog) ,Frog , salamander etc.

Fig. Frog Fig. Hyla
3)Class : Reptilia
Characteristics
i)They are mostly terrestrial and some are aquatics .
ii)body is dry and covered with scales .
iii)They are creeping animal .
iv)They have 3 chambered heart .
v)They are cold blooded ,oviparous and fertilization is internal .
vi)The body is divided into head ,neck trunk and tail .
For example :Wall lizard , garden lizard , turtle , snake ,squirrel crocodiles etc.

Fig . Wall lizard Fig King Cobra
4)Class :Aves
Characteristics
i)The body is covered with feathers .
ii)The body is divided into head ,neck trunk and tail .
iii)They are worm blooded ,oviparous and fertilization is internal .
iv)They have 4 chambered heart .
v)They have 2 pairs of limbs .The fore limbs are modified into wing and hind limb into wings .
For example :All birds i.e. Parrot ,Pigion, danphe etc.
5.) Class :Mammalia
Characteristics
i)They are adopted in all habitat .i.e. land, water and air .
ii)The body is divided into head ,neck ,trunk and tail .
iii)The body is covered with hair .
iv)They have mammary glands .
v)They have 4 chambered heart .
vi)They are worm blooded ,viviparous and fertilization is internal .
For example : Man , Whale , bat ,Rabbit, cow etc.
1.)Classify the following animals with a suitable characteristics :
1)Chlamydomonas
Classification
Kindom :Plantae
Division :Algae
Example: Chlamydomonas
Characteristics :
i)They are mostly aquatic .
2.)Marchantia
Classification
Kingdom:Plantae
Division: Bryophyta
Example :Marchantia
Characteristics
i)They are green autotrophic due to presence of chlorophyll.
3.)Fern
Classification
Kingdom:Plantae
Division : Trachaephyta
Sub-division :Pteridophyta
Example: Fern
Characteristics
i)They have vascular tissues i.e. Xylem and Phloem
4) Pinus
Classification
Kingdom: Plantae
Division : Trachaephyta
Sub-division: Gymnosperm
Example: Pinus
Characteristics
i)They have naked seed ,which are not enclosed in fruit .
5)Mango
Classification
Kingdom :Plantae
Division: Trachaephyta
Sub- division :Gymnosperm
Class : Di cotyledon
Example :Mango
Characteristics
i)They have only two cotyledon in seed .
6.)Rice
Classification
Kingdom :Plantae
Division: Trachaephyta
Sub-division : Gymnosperm
Class :Monocotyledon
Example: Rice
Characters
i)They have fibrous root .
2.)Classify the following animal with one suitable characteristics .
i)Sponge
Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum :Porifera
Example: Sponge
Characteristics
i)They are mostly marine .
2.)Hydra
Classification
Kingdom :plantae
Phylum : Coelenterata
Example : Hydra
Characteristics
i)Tentacles are present in the mouth .
3.)Earthworm
Classification
Kingdom :Animalia
Phylum :Annelida
Example :Eartworm
Characteristics
i)They are hermaphrodite .
4.)Starfish
Classification
Kingdom:Animalia
Phylum: Echinodermata
Example :Starfish
Characteristics
i)They are mostly marine .
5.)Sea horse
Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub- phylum :Vertebrata
Class : Pisces
Characteristics :They respire with gills .
6.)Frog
Classification
Kingdom :Animalia
Phylum :Chordata
Sub-phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Amphibia
Example :Frog
Characteristics:
i)They live in both land and water .
7)Man
Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub-Phylum: Vertebrata
Class :Mammalia
Example :Man
Characteristics
i)They respire with lungs .
Mosquito
Mosquito
Classification
Kingdom:Animalia
Phylum:Arthopoda
Class :Insecta
Example :Mosquito
1.)Introduction
Mosquitoes are harmful insect because they are causes of several diseases i.e. malaria, filarial, encephalitis etc .The division of mosquito is arthropoda,and class insecta.They are generally found in tropical and sub-tropical region (Terai and mountain)of different places i.e.houses, garden ,grasses ponds ,fields in monsoon and spring season .
2.)Structure :
The body is divided into three parts ie head , thorax and abdomen,head consist of mouth parts i.e.a pair of compound eyes,antennae,and proboscis but the proboscis of female is larger well developed than that of male so male mosquito generally feed juice of flower fruits but female feed both plant juice as well as blood of man and animal ,thorax consist of 3 pairs of legs and 2 pairs of wings and abdomen is wider . There are mainly two types of species of mosquito in nepal i.e. Anopheles mosquito ,culex mosquito .
3.)Life cycle of mosquito :The life cycle of mosquito is completed into 4 stages :
Fig. Life cycle of mosquito
1.)Egg :In this stages after fertilization female mosquito lays eggs in the night in the stagnant water i.e. pond, field etc. Female anopheles mosquito lays about 40 to 100 eggs in clean water. They are separate and boat or spindle shaped but Culex mosquito lays about 300 eggs in dirty water .They are attached together and cigar shaped .The eggs float on the surface of water .
2.)Larva: After 2 to 3 days egss change into larva .Larva are elongated ,hairy ,segmented more active and feeder are also called wrigglers .They eats bacteria and decaying organic matter on the surface of water .The larva of anopheles floats horizontally on the surface water but larva of culex floats hanging downward from the surface of water. The 8th segments of abdomen consist of respiratory tube or siphon ,the respiratory tube of anopheles is short and wide and culex is large and conical in size .
3.)Pupa :In this stage pupa enclosed in a cover is called puparium. The growth of pupa takes place inside the puparium. .The process of development of insect inside the puparium is called histogenesis .There is no movement ,no feeding except for occasional tumbling so pupa of mosquito is also called tumbler .The pupa of anopheles are green and have a short respiratory trumpets but culex are colourless and have a long respiratory trumpets .
4.)Adults :At end of pupal life the skin of pupa splits and a young mosquito comes out are called imago It is unable to fly immediately but after some time flies away on air . The body of adult is divided into three parts ie head , thorax and abdomen,head consist of mouth parts i.e. a pair of compound eyes, antennae, and proboscis but the proboscis of female is larger well developed than that of male, thorax consist of 3 pairs of legs and 2 pairs of wings and abdomen is wider .
Differences between egg, larva , pupa and adult stage of anopheles and culex mosquito :
Anopheles | Culex |
A)Egg stage 1.)Eggs are bat shaped having lateral air floats. 2.)They are laid singly . 3.)Anopheles lays about 40 to 100 eggs at a time . 4.)They are found in clean water . B) Larva stage 1)While resting larva remains parallel to the surface of water . 2.)The respiratory tube or siphon is shorter and wider .
C.)Pupa stage 1.)It is green in colour . 2.)Respiratory trumpets are shorter . D)Adult stage 1.)Dark spot are found on wings and can not fly for long time . 2.)Maxilary palp are equal in length with proboscis in male and female . 3.)While resting the body makes an angle with the surface of earth .
| 1.)Eggs are cigar shaped without lateral air float . 2.)They are laid in groups. 3.)Culex lays about 300 eggs at a time. 4.)They are found in dirty water . 1.)While resting larva makes an angle with the surface of water by hanging its head downward. 2.)The respiratory tube is longer and conical 1.)It is colourless . 2)Respiratory trumpets are larger .
1.)Wings are transparent and can fly for long time . 2.)Maxilary palp are shorter in female and larger in male with proboscis . 3.)While resting the body remains parallel with surface of water .
|
Methods of control measures of mosquitoes
i)Thy can be controlled by spraying insecticides in open drains and ditches ,because it destroys eggs ,larva ,and pupa and adult .
ii)They can be controlled by spraying kerosene and petrol ,because larva and pupa die due to blockage of respiratory opening .
iii)They can be controlled by draining the stagnant water .
iv)By poultry of fishes around the houses .
Methods of controls measures mosquito bites
i)By using mosquito net ,mosquito cream .
ii)By burning mosquito mat .
iii)By using mosquito insecticides around the house .
iv) By removing the stagnant water around the house .
Methods of transmission of malaria by mosquitoes
Malaria is caused due to the infection of plasmodium in our blood .When female anopheles mosquito bites an infected person ,1000 of malarial parasites in the form of sporozoites are sucked up along with blood meal. Then malarial parasite complete a part of its life cycle in the body of mosquito .When such infected female anopheles mosquito bites a healthy person ,1000 of sporozoites along with saliva enter into the blood stream ,where they grow, develop and reproduces .In this way female anopheles mosquitoes spread malaria .
Unit
:-17 Adaptation of Organism
Adaptation :-The adjustment of the organism to their particular environment modifying
their body structure for existence is
called adaptation .It help to know about habitat and
food behavior of an organism .
Effects of environmental
adaptation on organism :
i)Living organism change their colour ,physical
structure, shape, and food etc, according to their environmental condition. For example :stripes on the skin of tiger .
ii)They become extinct when the environment is not
suitable for them .For example :Animal like dinosaur
are not found today .
Adaptational features :The characteristics which help an organism for adjustment to their
particular environment are called adaptational features .
A.)Hydrophytes (Aquatic plant ):The plants which lives in water are known as hydrophytes :There are
mainly 3 types hydrophytes :
1.)Free floating plant : The plant which remains floating on the surface of water are called free
floating plant .For example :Pistia ,Lemna, wolffia
,Hyacinth etc.
2.)Submerged plant :The plant which
are fully present inside water are called submerged plant .For example :Hydrilla ,vallisneria etc.
3.)Amphibian plant :-The plant whose lower part of the body remains under water and upper
parts remains above water are called amphibian plant .For
example :Lotus ,water lily etc.
Aquatic adaptation : The adjustment of the organism to water modifying their body structure
for existence is called aquatic adaptation.
Adaptational features of aquatic
plants :
i)Some aquatic plants have air
storage tissues or air sac which help them float in water .For example :Hydrila ,water hyacinth .
iii)Some aquatic plants have thin and flat leaves which help them to float on water surface .
Adaptational features of aquatic
animals :
i)They have streamlined body
,flat short head, long tail smooth outer
surface which help for locomotion in water . For example : Fish
ii)Body is provided with air
sac which help for floating on the surface of water .
iii)The body is provided with fins which help for swimming ,balancing and changing
the direction of body .
v)The body temperature changes according to
environment which help to adapt in both cold and worm climate .
B)Terrestrial Plants :The plants which lives on land are known as terrestrial plants .The terrestrial plants divided into mesophytes and xerophytes according their geographical
structure and climate condition :
1.)Mesophytes :The plants which grow on average moisture and temperature are called mesophytes plants.For example :Mango , Banyan etc.
2.)Xerophytes :The plants which can grow dry and hot climate (i.e.desert) are called xerophytes plants .For example :Cactus, Calotropis, Acacia etc.
C)Terrestrial animals :The animals which lives on land
are called terrestrial animals .The terrestrial animals are divided into 5 types on the basis of their habitat :
1)Cursorial animals :The animal which lives on open place and adopt them for running on land
are called cursorial animals .For example: Tiger ,
lion, elephant, deer, dog ,horse etc.
2.)Fossorial animals :The animals which live on burrow or holes are called fossorial animals .For example :Rabbits ,rats ,moles etc.
3.)Arboreal :The animals which dwelling on trees are called arboreal animals .For example :Monkey, squirrel ,chameleon etc.
4.)Aerial animals :The animals which are able to fly in the air or most of time they lives
in the air are called aerial animals .For example :Pigeon,
sparrow etc.
5.)Desert animals :The which lives in desert adapt
themselves against heat ,food, and water are called desert animals .For example :Camel, lizard, Rodent etc.
Terrestrial adaptation :The process of adjustment of living
being organism on land is called terrestrial
adaptation .
Adaptational features of terrestrial plants :
i)Root and shoot
system are well developed .
ii)The conducting tissues
i.e. xylem and phloem are well developed for conduction food and water .
iii)They large ,broad and
thin leaves and have numerous stomata.
iv)Climber plants have hooks
,and tendrils for support .For example :Mango, Cucumber etc.
2.)Adaptational characters of
xerophytes plants :
i)The roots deeply seated in
the soil and numerous root hair for search of water .
iii)The stem of plants are flattened
and fleshy for storage the water .
iv)The surface of stem and
leaves are covered with thick cuticle to prevent from loss of water .
v)The stomata are deep
seated to prevent the loss of water.
vi)In most of plant stomata open at night time to prevent from loss of water .For example :Cactus .opunita etc.
Adaptational features of terrestrial animals
1.)Adaptational features of
cursorial animals :
i)They have streamlined body
that help to adapt fast movement.
ii)They have long and strong
limbs with short digits for adapt to fast movement .For example :Tiger Deer etc.
2.)Adaptational features of fossorial animals
i)The head is small ,snout
is strong that help to adapt to digging holes in the soil.
ii)They have strong and
short forelimb and small eyes that help to adapt lives in holes .For example :Rabbit ,rat etc.
3.)Adaptational features of arboreal animals
i)They have sharp claws
that help to adapt climb up and down on branches.
ii)They have strong and
muscular limbs and tail for holding the branches .For example :Squirrel,
monkey etc.
i) They have hollow bone that make body light and help to fly .
ii)They have one pair of
limbs modified as wings help for fly
For example :Pigeon, squirrel etc.
5.)Adaptational features of
desert animals
i)They have water pouches
to preserve water .
ii)They have thick skin
to prevent from loss of water .
iii)They have humps on its
back to store foods .
iv)The hooves are covered
with a large sole that to move fast on hot and sandy place .For example :Camel .
Micro-Organism :The organism that
are seen only through a microscope are called micro-organisms or microbes .The micro –organisms that
are harmful and causes of diseases are called Pathogens
(Patho=diseases ,gnes =causing)
Microbiology :The branch of biology
consisting the study of micro-organism is called microbiology
.
Classification of micro-organism :Micro- organism
are divides into 5 majors groups :
1)Virus 2)Bacteria 3)Protozoa
4)Fungi 5)Algae
1.)Bacteria :Bacteria are the most primitive ,simplest ,and smallest unicellular microscope organisms .It was discovered by
Antony van Leeuwenhoek in 1676 A.D. They are
found everywhere i.e. in water, in soil, in animals
,in plants etc. The branch of biology consisting
the study of
bacteria is called bacteriology .Bacteria
show characteristics of both animals as well as plants therefore, they are also called
boarder of line between plants and animals
. Bacteria are found in different shape
.
On basis of shape they are
classified into four types :
1) Coccus: They are oval in shape .
2)Bacillus:They are rod shaped .
3.)Spirillum :They are spiral in shaped .
4)Filament or mycelia :They are thread like or filamentous in shape .
Characteristics of bacteria :
i)They are unicellular
and microscopic organism .
ii)The
Bacterial cell are prokaryotic cell .i.e. It does not contains nucleus .
iii)They
have cell wall .
iv)They
contains chlorophyll but some contains bacterial chlorophyll .
v)They may be heterotrophic,
or autotrophic, or
saprophytic
.
vi)Large
number of bacteria are the parasite and causes of
different diseases .
Advantages of bacteria :
i)Bacteria
i.e. Lactobacillus and acidophilus help in
making curd from milk .
ii)They
decompose waste matter into harmless substances
.i.e. compost manure .
iii)They
help to produce vinegar .
iv)They
help to produces some alcohol .
v)Some
bacteria present in soil help to convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and
increase the fertility of soil .
v)Some
bacteria produce vitamins B complex groups .
vi)Some
bacteria are used to make antibiotics .
Disadvantages
i)A
large number of bacteria are the causes of diseases
in human beings i.e. cholera, typhoid .
ii)Some
bacteria are causes of plants diseases I.e. leaf spot .
iii)Some
bacteria are the causes of the food poisonous .
iv)Some
bacteria destroys cooked foods ,fruits, vegetables during summer month .
v)Some
bacteria reduces the fertility
of soils .
Controls measures of bacterial
diseases :
i)By burning the diseases plants .
ii)by
using diseases free seed .
iii)By
spraying antibacterial drugs .
iv)By
using antibiotics .
v)By vaccination against diseases .
2.)Fungi :Fungi are a group of non green plants i.e. yeast ,mushroom etc. They do not contains chlorophyll so they can not form their own foods ,Therefore some fungi are saprophytic are found on decaying organic materials of dead organism and some are parasite are found on tissues of living organism .The branch of biology consisting the study of fungi is called mycology
Characteristics of fungi .
i)The
plant body of fungi is not divided into root ,stem and leaf .
ii)They
do not bear
chlorophyll .
iii)They
are unicellular or multi cellular .
iv)They
are parasite or saprophyte .
v)They
reproduces both asexually and sexually .
Advantages of fungi :
i)Edible
mushroom are rich in proteins vitamins and minerals.
ii)
Large number of antibiotics are made from
species of fungi .
iii)Large
numbers of vitamins i.e. Vitamins-B complex, vitamins
–E are obtained from yeast .
iv) Large numbers of enzyme
are made from yeast .
v)Saprophytic
yeast help to decompose dead plants animals that increase the fertility
of soil .
Disadvantages of fungi :
i)A
number of diseases are caused by the species of
fungi .
ii)High
fever and allergies are the causes of fungi .
iii)They
are also causes of large number of plants diseases
.
iv)Some
species of fungi also destroys the articles of
i.e. leather ,clothes ,electric appliances in
monsoon season
Controls measures of fungi :
i)It
can be controlled by keeping the milk, foods ,meats, and vegetables in cold places .
ii)It
can be controlled by using salt .
iii)It
can be controlled by adding sugar .
iv)Fungal
growth in human skin can be controlled by personal
cleanliness.
3)Virus :A microscopic
obligatory parasite that causes of various disease in plants and animals is
called virus. The branch of biology consisting
the study of viruses is called virology .Viruses can exist outside of the living cell
for long period of time but they can reproduces only
inside the specific cell of living host so viruses are called obligatory parasite .Virus show the
properties of both living being and non living being
,so virus are called borderline of living being
and non living being .
Types of virus :On the basis of nucleic acid :-They are 2 types :
i)D.N.A. virus :e.g. Bacteriophase ,small
pox virus .
ii)R.N.A. virus :e.g. Polio virus ,Paramyxo virus .
On the basis of host :They are 3 types :
i)Animal virus :Rhino virus ,HIV virus .
ii)Plant virus :Tobacco mosaic virus .
iii)Bacteriophase virus .The virus that
attack the bacteria is called bacteriophase
virus .
Living characteristics of viruses
:
i)They
reproduce in large number .
ii)They
contains genetic materials i.e. D.N.A. and R.N.A.
iii)They transmit heredity
characteristics from one generation to another generation .
iv)They
infects other organism and causes of various diseases .
Non living characteristics of
viruses :
i)Viruses
do not have a cellular structure .
ii)They
do not perform metabolic activities .
iii)They
do not respiration .
Mode of transmission :The particular virus attack on particular
organism and particular organs and they
transmit by means of air, water, food ,blood etc
.
Controls measures of viral
diseases:
I)By
burning the viral diseased plants.
ii)By
destroying the insects like aphids .
iii)Human
beings can protected from viral diseases by the use of
vaccines .
Unit :-18 Tissue and System
Cell :-The structural
and functional unit of life is called cell. Or
Basic unit of living being is called cell
.
Tissues :-A group of
cell which is similar in structure and function is called tissue .for example :Bone ,blood , muscle, etc are the animal tissues ,and xylem and phloem etc. are the example
of plant tissues .They are two types :
A)Animal tissues
B) Plant tissues
On the basis of division the plants tissue are classified into two types :
1.)Meristematic
tissue
2.)Permanent tissue
A)Meristematic
tissue :The tissue which is
made up of from meristematic cells is called meristematic tissue :
Characteristics of meristematic tissue :
i)It has capacity of
cell division .
ii)It has thin wall .
iii)Cytoplasm is dense
.
iv)Intercellular space
is absent .
Types of meristematic tissue :On the basis of occurrence and position in the plant ,meristematic tissues are divided into 3 types :
1)Apical meristem: The meristematic tissues which are at the tip of stem ,root and their branch is called apical meristem .It help to increase the length root and stem .
2.)Lateral meristem :The meristematic tissue which occurs on the
side of root and shoot is called lateral
meristem .It help to increase the thickness
of root and shoot .
3.)Intercalary meristem :The meristematic tissue which are present at
he base of leaf ,base of inner node, or at the base of leaf is called
intercalary meristem .It help for elongation of organs .
B.)Permanent of tissue :A group of cell that do not have power of cell division but have
permanent shape for special function is called permanent tissue .The major function
of permanent tissue are to conduct food, and water
to different parts of plants ,to provide mechanical support and secrete
substance i.e. oil, resin, latex etc.
1)Simple Permanent Tissues
:
The permanent tissue that consist of only one type of cell and are similar in
origin ,structure and function is called simple permanent . These are of three types –
i)Parenchyma
ii)Collenchyma
iii)Sclerenchyma
i)Parenchyma tissue :The simple permanent tissue in all the soft parts of the plant body is called parenchyma tissue .They are found in soft parts of the plant body i.e. cortex (Outer region ) and pith (central region )of root and stem .
Features :
I)They have inter cellular spaces
between them.
ii)The cells of this tissue are thin
walled and polyhedral in shape
Functions :
They act as
storage for food and water.
They provides
temporary support to the plants .
Types of Parenchyma :They
are also 2 types :
a)Aerenchyma :When parenchymatous tissue having large air spaces is called Aerenchyma.These help in gaseous exchange and provide buoyancy to plant. Or to
float the plants .
b)Chlorenchyma :When the parenchyma cell contains chlorophyll is called chlorenchyma.They are found in leaf , sepals, etc. It help in photosynthesis .
ii).Collenchyma :The simple parenchyma tissue in which cells are living thick walled and have no inter cellular is
called collenchymas tissue .They are found in the leaf,
stalk etc.
Features :
i)They cell of this tissue are thick
walled and longer than that of parenchyma.
ii)They have no inter cellular space between them.
iii)The cells may be oval
,spherical, or polygonal in shape and chloroplast .
Functions :
i)They provide mechanical support to
the growing plants i.e. youn stem, petiole of leaf .
iii). Sclerenchyma :The simple permanent tissue in which cells are thick walled and dead is called sclerenchyma tissue .They are found in stem ,root, veins of leaves and hard covering of seed
.
Features .
i)The cells of this tissue are dead
and thick walled .
ii)They have no inter cellular
spaces .
Functions :
i)They provides mechanical support
to the plants organs .
2)Complex permanent
tissues :The Permanent tissue which are made from xylem and phloem tissue i.e.living and dead cells
is called complex permanent tissue .
Complex tissues are of following two types.:
1.)Xylem tissue:The
complex permanent tissue in which cells are thick,
tubular, and often dead and
responsible for conduction of water from root to leaves is called xylem.
The xylem elements are of 4 types : xylem tracheids, vessels, fibers and parenchyma.
i.)Xylem Tracheids :
They help in conduction of water in pteridophytes and gymnosperms and provide
mechanical support plants.
ii)Xylem Vessels :
The cross wall (end wall) at both
the ends dissolves and form a pipe like channel.
They help in ascent of sap in
angiosperms.
iii)Xylem Fibers :
It provides tensile
strength and mechanical strength.
iv)Xylem Parenchyma :
They store food materials.
2.)Phloem tissue: The complex permanent tissue in which cells are tubular and living and responsible for conduction
of food from leaves to different parts of the plants body is called Phloem
tissue .
The phloem elements are of
four type : Sieve tubes, Companion cells, phloem
Fibres and phloem paranchyma.
i)Sieve Tubes :
They help in conduction of food
material.
ii)Companion Cells :
They support the sieve tube in transport of
food.
They are absent all monocots and
some dicots.
iii)Phloem Fibers (bast
fibers) :
They provide mechanical support to
the plant.
iv)Phloem Parenchyma
The chief function of parenchyma is
to store food material and other substances like mucilage, tanins and resins.
3.)Special Tissue :The special plant tissue which is formed by glandular and lactiferous tissues to perform a
particular function is called special
tissue .Glandular tissue produce resin ,oil gum
etc. and lactiferous tissue produce milky or yellow
watery juice called latex .
Skeleton :The group of different types of bone and
cartilage which provides the supporting framework for muscles and delicates
organs is known as skeleton .There are two types of skeleton in human
being .The skeleton present on the outer surface of is called Exoskeleton The hard part present beneath the skin consist bone ,cartilage
,and ligament is called endoskeleton
Bone :The hard connective tissues which contains Ca,
and Mg salt and also contains bone
marrow i.e. red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow are called bone .Bones are
connected with another bones by help of ligaments and with muscles by
help of tendons.
Cartilage bone :The hard connective tissues which are tough
,elastic and flexible normally found between two bones are known as cartilage .
Functions of bones :
i)It give definite shape and height to the body .
ii)it help to protect delicate organs i.e. heart ,lungs etc.
iii)It help to
the moving body parts
.
iv)It also help to form blood cells in bone marrow.
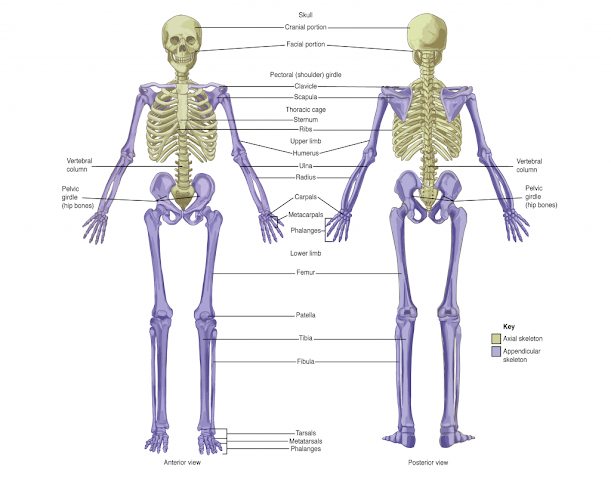
Skeleton system :The system formed by the combination of axial
and appendicular skeleton is called skeleton system .In human being
endoskeleton system consist of 206
bones in adult and 213 bones infant . Out of theses 7 bones i.e. 1 supporting tongue bone and 6 bones of ears or ossicele i.e.2x3 ,the remaining 199 bones are divided into 2 groups .
B)Appendicualr skeleton
Functions of skeleton system :
i)It provides rigid
framework for the body .
ii)It protect the
delicate internal organs i.e. lungs, heart etc.
iii)It help to
maintain the shape of the body .
iv)It help for the
movement of the body .
A)Axial skeleton :The skeleton formed by the bones of skull,
vertebral column ,ribs, and sternum is
called axial skeleton .It forms the axis or the central bony core of human body
.it consist of 80 bones .
1.Skull :The bony framework of the head is called skull .It is divided
into cranial bones i.e. 8 and
facial bones 14 .There are total 29 bones in skull .
Cranial bones (8)
-Parietal bones (2)
-Temporal
bones (2)
-Sphenoid
bone .(sometimes counted
as facial)
-Ethmoid
bone (sometimes counted
as facial)
Facial bones (14)
-Nasal
bones (2)
-Maxillae (upper jaw) (2)
-Lacrimal
bone (2)
-Zygomatic
bone (cheek bones) (2)
-Palatine
bone (2)
-Vomer (1)
-Mandible (1)
2.)Ear ossiceles(6): The 3 bones that present in the middle ear
are called ear ossiceles .There are 3 bones i.e. Malleus, incus, and Stapes in each ear.
3.)Hyoid(1) :A U shaped bone located in neck region below
the mandible that support the tongue is called Hyoid.
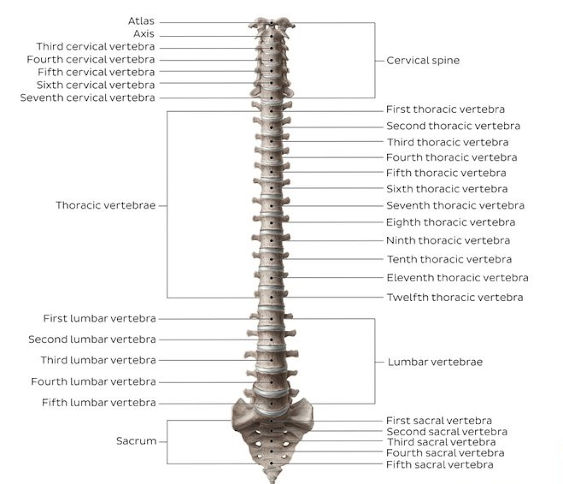
4.)Vertebral column :Each bones of vertebral column is called vertebra .They are drum shaped and consist of circular cartilage bones ,which absorb shock and provides flexibility to the back bone ,each vertebra has big hole in middle and spinal cord lying centrally passes through it .The bones of vertebral column are divided in to 5 region and naming according to location .They are 36 in infant and 26 in adult in number
i.)Cervical vertebra :They are 7 in number and are located at neck region .The first piece is called atlas. It hold the head and second piece is called axis .It help to move the head .
ii)Thoracic vertebra :They are 12 in number and are
located at thoracic region .The bones of each pair of rib are attached at the back to these vertebra .
iii)Lumber vertebra :they are 5 in number and larger
,heavier than other .They help to support for heavy load .
iv)Sacral or sacrum vertebra (I=5,A=1):They are 5 in number in infant
but in adult ,they fused together to form single bone and is called sacrum .It
is located in the hip region .
v)Coccyx or Coccygeal
vertebra (I=4,A=1):There are 4 vertebra in infant but in adult ,they are
fused together to form single bone is called coccyx .In animal they form tail so it is also called tail bone .
5.)Thoracic cage or Ribs
cage or thorax :It consist of sternum
and 12 pairs of ribs or 25
pieces of bones .The 12 pairs ribs
act as cage by connecting each piece at front to the sternum .This cage help to
protect vital organs i.e. lung ,heart etc. The thorax is divided
in to two parts :
a)Sternum :It is flat, narrow, dagger shaped bones
located in the middle of the chest .The 12 pairs of ribs are directly or
indirectly attached to it .
b)Ribs :Ribs are long ,flat, semi circular bones that
emerge from vertebral column and may or may not attached with sternum .On the basis of their sterna parts they are
divided into 3 parts :
i)True ribs :The first 7 pairs of ribs that directly
attached to the sternum are called true ribs .
ii)False ribs :The 3 pairs of ribs i.e. 8th,9th,10th,
that are attached to seventh pairs of ribs are called false ribs .
iii)Floating ribs :The last 2 pairs of ribs i.e. 11th ,and 12th, that emerge from the thoracic vertebra and are not attached to the sternum are called floating ribs.
B)Appendicular skeleton :The skeleton formed by the bones shoulder girdle with bones of upper limb and pelvic girdle with the bones of lower limbs is called appendicualr skeleton .
1.)Pectoral or
shoulder girdle (4):
it consist of 4 bones two on each sides of the limbs i.e.
i)Clavicle :S –shaped bone -2 in number
ii)Scapula :2 in number
2.)Fore limb(60) :It consist of 60 bones .They are
i)Upper arm bones :2
-Humerus (2)
ii)Lower arm bones (4 bones
in total, 2 on each side) left bone
-Ulna (2)
-Radius (2)
iii)Hand (54 bones in total; 27 in each hand)
-Carpals-16
-Metacarpals (10 bones in total; 5 on each side)
-Proximal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 on each side)
-Intermediate phalanges (8 bones in total; 4 on each side)
-Distal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 on each side)
3.)Pelvic girdles (2): The girdle that connect the bones of the hind
limb to the posterior end of vertebral column is called pelvic girdle .It is 2 in number .Each pelvic girdle made up from 3 fused bones i.e. Ilium, ischium, and pubis . The
pelvic girdle is wider female than that of
male ,which help in growth
and development of fetus or baby in uterus for child birth.
4.)Hind limb :It consist of 60 bones .There are a total of 60 bones:
bones in the legs.
-Femur (2 bones)
-Patella or kneecap (2 bones)
-Tibia (2 bones)
-Fibula (2 bones)
-Foot (52 bones in total, 26 per foot)
-Tarsals -14
-Metatarsals (10 bones)
-Proximal phalanges (10 bones)
-Intermediate phalanges ( 8 bones)
-Distal phalanges ( 10 bones)
Digestive System in Human Being
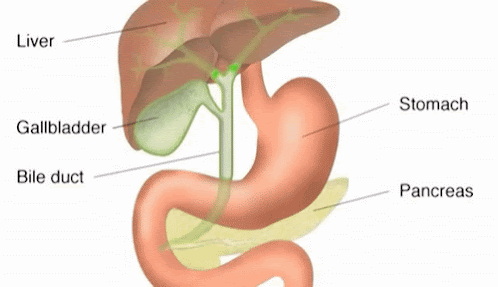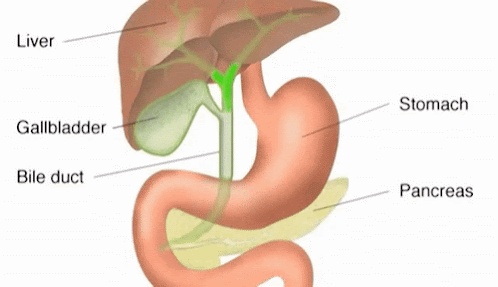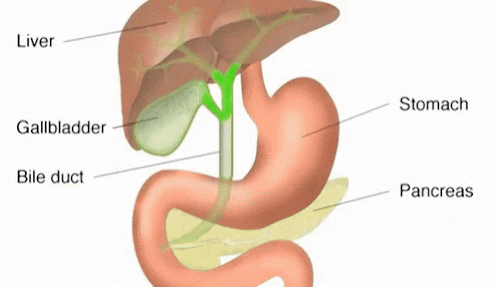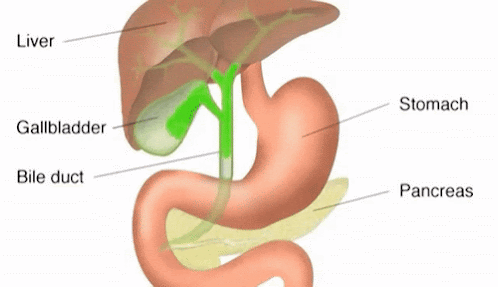
Digestive System :The group of organs working together to break down complex foods into simple water soluble molecules for convert food into energy is known as digestive system .The digestive system consist of mainly two parts i.e. alimentary canal and digestive gland .
A)Alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract :It is long tube which extends from the mouth
to anus .It is divided into following parts :
i)Teeth :It help for grinding ,chewing and crushing the
food particles into small pieces
ii)Salivary gland :it produced the saliva that help to make
the moister the food before the tongue pushes the food
into the pharynx.
iii)Tongue : During chewing, the tongue moves food about and manipulates it
into a mass called a bolus. The
bolus is pushed back into the pharynx (throat) and is forced through the
opening to the esophagus.
2.)Pharynx :The digestive tube that connect the mouth
with esophagus is called pharynx .It help to pass food from mouth to esophagus .
3)Oesophagus or esophagus :The digestive tube that
connect the pharynx with the stomach is called esophagus .It pass
the food to the stomach through the food pipe . The esophagus separate food
into small units known as a bolus.
3.) Stomach
Stomach is a muscular large bag like organs which is situated towards the
left side of the abdominal cavity. This vital organ acts as a storage for the
food and provides enough time to digest meals. There the food is partially digested and has the consistency of liquid is called chime .The digestive glands present on the wall of stomach produces
the following digestive juice :
-Mucous: It is an aqueous
secretion produced by the mucous membranes. It functions by protecting the
stomach lining and gastric pits from the acid.
-Digestive enzymes: They are the group of enzymes i.e. pepsin, Renin etc. which
functions to break down the foods into
their smaller and simpler substances.
-Hydrochloric acid: It is the digestive fluid formed by the
stomach during the process of digestion. It functions by destroying harmful
microorganisms present in the food particles.
4.)Small intestine :It is longest coiled parts of alimentary
canal .It is the center of digestion of
carbohydrates ,fat, and protein
for this purpose small intestine produces intestinal juices and receive the
juice secreted by pancreas and liver . In small intestine 90% of the digestion and absorption of food occurs, the other 10% taking place in the stomach
and large intestine.The inner layer of
intestine consist of numerous finger like
projection is called villi
that increase surface area of intestine for effective digestive .Small
intestine is divided into 3
parts :
i)Duodenum :It receives chyme from stomach
with the bile produced by liver and pancreatic juice produced by pancreas. It
further breakdown the chyme .
ii)Jejunum :It is the mid part of small intestine that
connect the duodenum with ilium .It help to absorb the amino acid and fatty
acid .
iii)Ilium :It is final section of small intestine which
join to large intestine .it absorb vitamin B12 and excessive bile .
5.)Large intestine :It is also known as colon. It absorb the
remaining nutrients and water from
undigested food and remaining waste material is changed into feces( stool) .The rectum store the feces .The faces is removed from the body
through the anus .This process is called egestion .
B)Digestive gland :The glands which produce different digestive
juice and are found inside or outside the alimentary canal are called digestive
glands For example :Salivary
gland , Gastric gland, Pancreas, liver etc.
|
Organ
|
Gland |
Digestive Juice |
Enzyme |
Functions |
|
Mouth |
Salivary gland |
Saliva
|
Amylase |
Softening Food by converting starch into
maltose |
|
Stomach |
Gastric gland |
HCl |
|
Kill harmful germs |
|
Gastric juice |
Pepsin Renin Lipase
|
Protein
into peptose Milk protein into Casein Fat into fatty acid
|
||
|
Duodenum |
Liver |
Bile juice |
|
Neutralize acid |
|
Pancreas |
Pancreatic juice |
Trypsin Lipase Amylase
|
Peptone into peptide Fat into fatty acid Starch into maltose |
|
|
Small intestine |
Intestinal glands |
Intestinal juice |
Erepsin Sucrase Lactose Maltose |
Peptide into amino acid Sucrose into Glucose Lactose into Glucose Maltose into Glucose |
|
Large intestine |
|
|
|
Absorb the excessive water , minerals ,
nutrients , Stores remaining waste materials for egestion |
Respiratory System in Human Being
Types of respiration :There are two types of respiration :
1)External Respiration :The process of exchange of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide between the
environment and organisms is known as External respiration .
2) Internal Respiration :The metabolic process in which the digested food is oxidized in
order to release energy is called internal Respiration .
The
group of organs working together for respiration is known as respiratory System
.The respiratory system consist of following organs :
i)Nose :It is a external
organs that help to transmit air in and out of the lungs ,sensation of
smell.Its nasal cavity consist of tiny hairs are called cilia that help to trap dust particles .Nasal cavity made up rich blood vessels that help to maintain suitable temperature for air passing to
the lungs .
ii)Pharynx :It
is a muscular funnel that connect the mouth and nasal cavities to the larynx and oesophagus .It is place where wind place and food pipe
are connected each other is called epiglottis .It open and divert
air towards the wind pipe during
the respiration but while drinking or eating it close the wind pipe and divert the food
towards the food pipe .
iii) Trachea
:It is also called wind pipe that connect the pharynx and larynx to the bronchi .It is a clear passage for air to enter and exit .It also
produce a mucus that traps dust and other particles from entering the lungs .
iv)Bronchi and Bronchioles :The two branches of trachea that act as airway into each lungs
are called bronchi and each bronchi further divided into numerous smaller branches inside the lungs are
called bronchioles .The bronchioles ends
into tiny air sac are called alveoli .The alveoli are tiny air sacs made of rich
blood capillaries where the exchange of gases
takes place between O2 and CO2 .
vi)Diaphragm :Diaphragm is the sheet of skeletal muscles
present at the bottom of the lungs that help in the inhalation and exhalation
of air from the lungs because when
muscles contract the size of chest increases which force the expansion of lungs causing inhalation but when muscles relax the size chest decreases which force the contraction of lungs causing
exhalation .
Excretory System in Human Being
Excretory System :The group of organs working together to remove
the excess and unnecessary materials from the body is known as excretory system
.It consist of following organs :
1.) Skin:The
skin is the largest organ in the body. It help to excretes sweat that
contains NaCl, urea etc.
2.)Lungs :It
helpto excrete carbon dioxide during respiration and some amount of
water in the form of vapour.
3)Liver :It
help to excret amino acid, excess fats and cholesterol. From
the blood.
Kidneys are
the main organ of the human excretory system. It is 2 in numbers .They are located one on each side of the spine at the
level of the liver. Kidneys are divided into three regions. i.e.i)the renal cortex which is the
outer layer. Ii)the renal medulla which is the
inner layer. Iii)the renal pelvis which carries
the urine from the kidney to the ureter.The
structural and functional unit of kidney is called
Nephron
The nephron is the functional unit of a kidney.
Each kidney consists of millions of nephrons. They all function together to
filter blood and expel waste products. It consists
of the following parts:
i-Bowman’s
capsule– It is
the first part of the nephron. It is a cup-shaped structure and receives the
blood vessels. Glomerular filtration occurs here. The blood cells and proteins remain in the
blood.
-Proximal
Convoluted Tubule– The Bowman’s capsule extends downwards to form the
proximal tubule. Water and reusable materials from the blood
are now reabsorbed back into it.
-The loop
of Henle– The
proximal tubule leads to the formation of a u-shaped loop called the Loop of
Henle. It has three parts:
i.e.the descending limb, the u-shaped bend, and
the ascending limb. It is in this area in which urine becomes concentrated as water is reabsorbed. The
descending limb is permeable to water whereas the ascending limb is impermeable
to it.
-Distal
Convoluted Tubule– The Loop of Henle leads into the distal convoluted tubule.
It is where the kidney hormones cause their
effect.
-Collecting
Duct– The
Distal Convoluted Tubule of each nephron leads to the collecting ducts. The collecting ducts together form the renal pelvis. Through renal pelvis, the urine passes into the ureter
and then into the bladder.
Ureters
There is one ureter that comes out of each. It is a thin muscular tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Urinary Bladder
The bladder
is a sac-like structure. It stores the urine
until micturition. Micturition is the act of expelling urine from the
body.
Urethra
The urethra
is a tube that arises from the urinary
bladder. Its function is to expel the urine outside by
micturition. In addition, it is shorter in females and longer in males. in
males, it functions as a common path for sperms and urine.






























































































Comments
Post a Comment