Physics Grade --9 /Old Course (Science )
Physics Grade - 9 (Science )
Unit Topics
2 Force
3 Machine
4 Work, Energy
and Power
5 Light
6 Sound
7 Current Electricity and Magnetism
Specification Grid
-2074
|
Areas |
S.N. |
Units |
Total
no. of questions & their marks |
Remarks |
||||
|
K-20% |
Un-35% |
Ap-24% |
HA-21% |
Total |
||||
|
Physics |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Measurement Force Machine Work, Energy and Power Light Sound Current Electricity & Magnetism |
5x1= 5 |
4x2= 8 |
2x3= 6 |
1x4= 4 |
23
marks |
Physics-56+ Chemistry-56+ Biolog-56+ Geology &Astronomy-12 Periods=180 periods |
|
6 |
|
5 |
8 |
6 |
4 |
23
marks |
||
Scholastic Areas :-Grading on 9 points Scale
|
S.N. |
Marks range |
Grade |
Attributes |
Grade
Points |
Remarks |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
90 to 100 80 to below 90 70 to below 80 60 to below 70 50 to below 60 40 to below 50 40 to below 50 30 to below 40 0 to below 20 |
A+ A B+ B C+ C D+ D E |
Outstanding Excellent Very good Good Satisfactory Acceptable Partially Acceptable Insufficient Very insufficient |
4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 |
The minimum qualifying grade in all subjects under scholastic Domain Is C |
Force :- A physical quantity which change the state of an object is called force. Its S.I. unit (N) and measured by spring balance . It is a vector quantity. Eg. Pulling force, Gravitational force etc.
Force(F)=Mass(m)×acceleration(a) or mass(m)×acceleration due to gravity (g)1N force :-The force which when acting
on a body of mass 1kg to produces 1m/s2 acceleration is called 1 N force .
1 N =105 dynes
1 dyne force :- The force
which when acting on a body of mass 1gm to
produce 1m/2 acceleration is called
1dyne force .
Dyne =gcm/s2
Balanced force :-When numbers force acting simultaneously
on a body do not bring about any change in the
state of rest or motion in a straight line then the force acting on the body is
called balanced force .In balanced force the magnitude
of resultant is always zero. For example :In a rope pulling by two teams the rope does not move in any
direction .
Unbalanced force :-When a number of forces acting
simultaneously on a body bring about a change
in its state of rest or motion in a straight line ,then the force acting on the
body is called unbalanced force In unbalanced force the magnitude of resultant force is always more than zero.For example :Kicking the football on the ground ,pushing the small box on
the table ,pushing a piece of stone forward etc.
Effects or properties of force :
i)It can
change the position of the body .
ii)It can change the speed
of the body .
iii)It can change the
direction or motion of the body .
iv)It can change the shape
of body .
Rest: If a body does not change its position with respect to its surrounding as the passage of time is called rest .For example : A book lying on the table ,electric poles , houses ,trees ,etc.
Motion:-If a body change
its position with respect to its surrounding as the passage of time is
called motion .For example :A man walking on the road
,vehicles, bus ,etc.
Differences between uniform motion and non uniform motion
|
Uniform motion |
Non –uniform motion |
|
i)The motion in which a body covers equal distance in equal interval time is
known as uniform motion. ii)For example :The
motion of planet ,satellite, watch etc. |
i)The motion in which a body covers unequal distance in equal interval time is
called non – uniform motion . ii)For example :The motion of vehicles ,flying birds, etc. |
Reference point :-The place from which a location is
observed and measured is called
reference point or the origin point .
Distance :The length
of actual path travelled by the moving body in
any direction depend upon the length of path is known as distance .It is scalar quantity .
Displacement: The
distance covered by a body in a particular direction
in a certain interval time is called displacement . It is a vector quantity .
Vector quantity :-The quantities which have both magnitude
as well as direction is known as vector quantities .For examples : displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, momentum etc.
Speed:The
distance covered by a body per unit time is
called speed .It S.I. unit is m/s .It is scalar
quantity because it have only magnitude but not
direction
Speed or average velocity =Distance covered (m)/Time taken(t)
Velocity :-The distance covered by a in a particular
direction per unit time is called velocity .or
Displacement per unit time is called velocity .Its S.I. unit is m/s .It is a vector quantity
because it have both magnitude as well as direction
.
Non-uniform velocity :-if a body does not covers equal distance in equal interval time is known as non-
uniform velocity .
1.)A
student runs 5m/s .What does this mean ?
Ans. It means that he covers a distance of 5
meters in a per second .
Acceleration:-The rate
of change of velocity per unit time is called acceleration .or
Velocity change in per unit time is acceleration .It S.I. unit is m/s2.It is vector quantity.
a =v-u /t Where, a = acceleration , V= final velocity , u =Initial velocity , t= time taken
Equation of motion:-The mathematical equation
that show the relation between initial velocity (u),final
velocity (v),acceleration (a),time taken(t), and
distance covered by the object(s) is known as
equation of motion .The equation of motion are
V=u+at 一 i
S=u+v/2×t 一 ii
S=ut +1/2 at2 一 iii
V2
=u2+2as 一 iv
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
Now,
According to definition of acceleration
a= v-u /t
or v-u =at
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance travelled =s
Now, average velocity = =u+v/2 (i)
Again ,distance covered =average velocity×
time taken(t)
Suppose here ,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =S
Now average velocity ==u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average
velocity ×time(t)
Or S =
u+v/2×t
(i)
Putting the value of v at equation (i)
Or S=(u+v+at/2) ×t ( we know that v=u +at )
Or S =(2u+at/2) ×t
Or S = (2u/2+at/2)×t
Or S =ut + at2/2
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =s
Now average velocity = u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average
velocity ×time taken(t)
Or S = u+v/2×t (i)
Putting the value of t at equation (i)
Or S = u+v/2 × v-u/a
( we know that t = v-u/a)
Or S = v2-u2/2a
Or v2 –u2 =2as
Inertia :-The property or
tendency of a body or mass to resist any change in its state of rest or uniform
motion in straight line is called inertia . or
The inability of a body to change its state by itself from rest to motion or motion to rest is known as inertia .
The relation between
mass and inertia :The inertia of a
body depend upon its mass For example : The a body having greater mass the
inertia will be high and for a body having smaller mass the inertia will be
less , therefore the inertia of body is directly
proportional to the mass of the body .
Inertia∝
Types of inertia :They are 2 types :
i)inertia of rest :The inability of a body at change its position from rest to motion by itself without the help of an external force is called inertia of rest .For example
:i)A
passenger sitting in a bus falls backward when the bus moves suddenly
ii)The dust particles fall downward when a blanket is
given a sudden jerk.
i) A
passenger sitting in a bus falls forward when the bus stop suddenly.
ii)A person jumping from the a moving bus gets injured .
Reasons
1.)The
fruits fall down when the branches of a fruit tree are shaken .Explain why ?
Ans. In the beginning both the branches as well as the fruit remains in the state of rest ,
when branches of tree is shaken the branches comes in the state of motion but due to inertia of
rest fruit remains in state of rest .As result the fruits are
separated from the branches and fall down .
2.)A
coin placed on a card is placed over a
glass .when the card is flipped quickly ,the coin drops into the cup ,why ?
Ans. Initially both the card as well coin
remains in the state of rest , when the card is flipped quickly the card comes in the state of motion but due to inertia of rest card
remains in the state of rest .As result the coin is separated from the card and drops in to the
cups .
3.)A
carpet is beaten with a sticks to remove the dust particles .why ?
4.)When
a car suddenly starts moving ,the passenger sitting in it falls backward .why ?
Ans. Initially both the passenger and bus remains in the state of
rest ,when the car suddenly start moving both
car as well as lower parts of passenger comes in the state of motion but
due to inertia of rest upper part of passenger remains
in the state of rest ,as result when a car start suddenly moves the
passenger sitting in it falls backward .
5.)When
a moving bus suddenly stops ,the passenger sitting in it fall forward .why?
6.)The
blades of a fan continue to rotate when the current is switched off. why?
Momentum: The physical
quantity that describe the quantity of motion of
a body is called momentum .
The product of mass and velocity of moving
body is known as momentum of
moving body or linear momentum .Its S.I. unit
is kgm/s.
Momentum =mass ×velocity
Or
=mv where
= linear
momentum , m = mass of the body , v =
velocity of the body .
Newton’s law of motion :Newton’s used
three laws to describe the effect of force on an object
are known as Newton’s law of motion .They are as following :
1.)Newton’s first law of motion :If a body is at
rest ,it will continue to remain at rest and if it is in motion it will
continue to move in a straight line with uniform velocity ,unless it is acted upon by an external force .This is
known as Newton’ s first law of motion .
i)The fruits fall down when the branches of a fruit tree
are shaken .
ii)
When a car suddenly starts moving ,the passenger sitting in it falls backward .
iii)
When a moving bus suddenly stops ,the passenger sitting in it fall forward.
2.)Newton’s second law of motion :Acceleration produced in a body is directly proportional to the
force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass . This is known as
Newton’s second law of motion .
a ∝
a
or
The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional
to the applied force in the direction of force .This is known as
Newton’s second law of motion .
Force
(F)
For example :i)A cricket player lowers his hand while catching a cricket ball .
Prove that F =ma
Suppose ,the mass
of a
body =m
Applied force =F
and produced
acceleration =a
According to Newton’s second law of motion
a∝ F ( i)
a
combining eqn(i) and eqn(ii)
a ∝ F/m
F∝
Or F = k ma (where k is a constant )
Or F =k ma ( iii)
If a
force required to produce an acceleration of 1m/s2,on 1kg mass is
called 1N force
Now ,1 =k 1.1
Or K = 1
Putting the value of k in eqn (iii)
F = 1 ma
F = ma proved
3.)Newton’s third law of motion : For every action ,there is an equal and opposite reaction .This
is known as Newton’s third law of motion .
For example: i) A gun recoils on firing .
Reasons
i)Explain ,why a gun recoils when a bullet is fired from
it ?
Ans. When bullet is
fired the bullet comes out from the gun is action and
gun recoils is backward is reaction so gun recoils when bullet is fired
because we know that according to third law of motion for every action there is
equal and opposite reaction .
ii)If a man jumps out from a boat ,the boat moves
backward .why ?
Ans. A man jumps
out from the boat is action and the boat moves backward
is reaction ,so if a man jumps out from a boat ,the boat moves
backward because we know that according
to Newton’s law of motion for every action there is equal and opposite reaction
.
iii)When a
balloon filled with air and its mouth downward is released ,the balloon moves
upward .why ? (Air release downward from
balloon is action and balloon moves upward is reaction )
iv)While rowing ,a boatman pushes the water in he pond
backward , why ?
( Boatman push
the water backward is action and boat
move forward is reaction )
Numerical problem
i)a =v-u/t
ii)v=u+at
iii)s
= u+v/2×t
iv)s
=ut +1/2 at2 or
s=ut+i/2gt2 (When object throwing upward
g=-9.8m/m2 or downward g=9.8 m/s2)
v)v2
= u2+2as or v2 =u2 +2gs
Note : i)When starting from rest
u= 0m/s2
ii)When stopped or break applied u=0m/s2
iii)In retardation a = –m/s2
1.)A bus starts from rest .if the acceleration of the is
0.5m/s2,what will be its velocity at the end of 2 minutes and what
distance will it cover during that time ?
Ans.soiution ,here
Initial velocity
(u)= 0m/s
Acceleration(a)=0.5m/s2
Time taken (t)=2
min =2×60 =120 sec
Final velocity
(v) =?
Distance covered
(s)=?
We have
V=u+at
Or v = 0 +0.5
×120
Again ,We know
S
= u+v/2× t
Or S = 0+60/2×120
Or s =60×60
Distance covered (S) =3600 m/s
2.)
A car starts to move from rest .If the
car assumes an acceleration of 3m/s2 in 15 second , calculate the
final velocity of the car .Also calculate the distance covered by the car
.(Ans. v= 45 m/s S= 337.5 m)
3.)A
motor bike starting from rest on Fewa lake accelerate n a straight line at rate
of 5 m/s2 for 10 seconds .How
long distance does the boat travel during this time .(Ans. S =250 m)
4.)A
truck is moving with velocity
of 72km/hr ,when the driver applies brakes the truck is stopped in 2
second .calculate the distance covered and retardation of the truck .if the
mass of the truck is 5000kg ,calculate the force applied by the brakes to stop
the truck .
Ans.Solution here, Initial velocity (u) = 72km/hr
= 72x1000/60x60=20 m/s
Final velocity
(v)= 0m/s
Time taken (t) =2
Sec
Mass of truck (m)
= 5000 kg
Distance covered
(s) =?
Retardation (a) =
?
Force applied by
brakes (F) =?
We know that
Or a =v-u/t
Or a =0-20/2
Or a =-10 m/s2
Therefore
retardation (a)= -10m/s2
Again ,we know
that
S
= u+v/2× t
Or S = 20+0/2 × 2
Or s = 20 m
Therefore
distance covered (s) = 20m
Again, we know
that
F = ma
Or F = 5000 × -
10
F= - 50000 N
Therefore
force applied by break (F) = - 50000N
5.)A
bus is moving with velocity of 90 km/hr .If the bus covers the distance of 625
m before coming to rest ,calculate the retardation of the bus .(Ans. -0.5 m/s2 )
6.) How much retardation should be produced to stop a
truck moving with the velocity of 72 km
/hr in 5 second ? Calculate the distance covered by the truck within that time
.(Ans. a = -4m/s2 ,S = 50 m
)
7.)To estimate the height of a bridge over karnali river
,a stone is dropped freely in the river from the bridge .The stone taken 2
seconds to touch the surface water .Estimate the height of the bridge from the
water level .
Ans.Solution ,Here
Initial velocity
(u) = 0m/s
Acceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8m/s2
Time taken (t) =
2 sec
Height of the
bridge (h) =?
We know that
h = ut
+ ½ gt 2
or h = 0 . 2 + ½ . 9.8 ×2.2
or h = 0 + 9.8 ×2
h = 19.6 m
Therefore
height of the bridge (h) =19.6 m
8.)A body falling from the top of a building reaches the
ground 2.5 s later . How height is the building .(Ans. h = 30.62 m)
9.)If a stone takes
5 seconds to reaches the maximum height with what velocity is it thrown
up ?
Ans.Solution here ,
Final velocity
(V) = 0m/s
Acceleration due
to gravity ( a) =-9.8m/s2
Time taken (t ) =
5 Sec
Initial velocity
(u) =?
We know that ,
V = u+ gt
Or 0 = u + (-9.8)
×5
Or 0 = u – 49
u = 49 m/s
Therefore
initial velocity (u) = 49 m/s
10.) A
ball is thrown vertically upward at the velocity of 30m/s .Calculate the height
covered by the ball in 5 second
.(Ans. S = 27m )
Unit: = Force
Group 'A' (1 Mark
Each)
1. What is
force? Write down its SI unit.
2.Define rest and motion.
3.Define IN force.
4.Define speed and velocity.
5.What is inertia?
6.On which factor does the inertia of a body depend? Write.
7.What is inertia of motion?
8.What is the relation between the mass and inertia of a body?
9.What is displacement?
10.What is acceleration' Write down its unit in SI
11."Every action has equal but opposite reaction." Which
law of Newton is stated by this statement?
12.State Newton's second law of motion.
13.What is momentum? On which factors does it depend? Write.
14.What is unbalanced force ? Write with one example.
15.State Newton's first law of motion.
Group 'B' (2 Marks
Each)
16.Write any wo differences between speed and velocity.
17.A coin, kept on a postcard on the glass, drops in the glass
when the postcard is flipped suddenly. Why ? Give reason.
18.Write any wo differences between velocity and acceleration.
19.Why do passengers tall forward when a moving bus is stopped
suddenly? Give reason.
20. Athletes run a long
distance belore taking a long jump. Give reason.
Group 'C' (3 Marks Each)
21. What is
the relationship among initial velocity, distance covered, acceleration
produced and final velocity of a moving body? Give an example that describes
Newton's first law of motion.
22.Prove that: F=ma
23.Write any three practical applications of Newton's third law
of motion.
24.Explain Newton's third law of motion with an example.
Group
'D' (4 Marks Each)
25.A truck is moving with the velocity of 72 km/h. When the
driver applies brakes, the truck is stopped in 2 seconds. Calculate the
distance covered and retardation of the truck. If the mass of the truck is 5000
kg, calculate the force applied by the brakes to stop the truck.
26.Write one difference between action and reaction. A bus is
moving with the velocity of 60 km/h. By seeing a baby 11m ahead the driver
applied the brakes and the retardation produced is 13.88m/se. Calculate the
distance covered by the bus and time taken to stop the bus.
27.Prove that
(i)v2 = u2 + 2as
s=ut+1/2at2
Unit - Test
Unit 2: (Force)
Time: 40 min. F.M.: 22
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer
all the questions.)
समूह 'क'
(Group 'A') 1x6=6
1.Define IN force
2.On which factor does the inertia of a body depend? Write.
3. What is
velocity? Write down its sl unit.
4.What is acceleration? Write down its unit in SI system.
5 State
Newton's first law of motion.
6.What is balanced force ? Write with one example
समूह 'ख' (Group
'B') 3 x2 =6
7.Write any two differences between speed and acceleration
8.A soldier is running very fast. Can he stop immediately when
he gets command to stop? Why?
9. Why do fruits fall down when the branch is shaken?
समूह 'ग' (Group
'C') 2x3=6
10.A vehicle is moving with the velocity of 25m/s. If the
vehicle is stopped within 5 seconds by applying brakes, calculate the
retardation. If the mass of the vehicle is 1000kg, how much force is to be
applied to stop it?
11. Mention
any three points that should be remembered while solving numerical problen is
related to motion.
समूह 'घ' (Group 'D') 1x4
27.Prove that
(i)v2 = u2 + 2as
ii)s=ut+1/2at2
The End
Lesson :
3 (Machine )
Machine : The instruments that make our work easier ,faster and more convenient are known as
machine . They are 2 types :
1.)Complex
machine :The instruments whose structure are very complex and make our work easier ,faster, and more convenient are known as
complex machine .For example : Fan, bicycle, bus ,truck
etc.
2.)simple machine : The instruments which is very simple in structure and make our work easier ,faster and more convenient are known as simple machine .For example : scissor ,beam balance, bottle opener etc.

Advantages of simple machine :
i)It increase the rate of doing work .
ii)It multiplies the applied force .
iii)It help to change the direction of force .i.e Pulley
iv)It helps to do our work safe .
v)It help to
transfer force from one point to another point.
Some
terminology related to simple machine :
Effort: The force applied
in the simple machine in order to do useful work
is called effort .It is denoted by E and S.I. unit is Newton(N).
Load:-The force
exerted by machine on the resistance after application
of effort is called load .It is denoted by L and S.I. unit is Newton(N).
Fulcrum :The fixed point or axis of simple machine that help to
move or rotates freely the machine is called
fulcrum .
Load distance and effort distance : The distance covered by load is called load distance .It is
denoted by L.d.
and S.I. unit is metre (m)
The distance travelled by effort while moving the effort is called effort distance .It is denoted by L.d. and S.I. unit is metre(m).
Input work :The work
done by applied force on the machine is called
input work .It S.I. unit is Joule (J) .It is
always more than that of out put work because it is not
affected by friction .
Input work =Effort ×Effort distance
Out put
work =The work done by machine on the
load is called out put work (useful work).It S.I. unit is
Joule (J). It is always less than that of input work ,because it is affected by friction .
Out put work =Load ×Load distance
Mechanical advantage :-The ratio of load to the applied effort
is called mechanical advantage .It have no unit
.It measures the times by which a machine multiplies
the effort. It is denoted by MA. It is always less than that of velocity
ratio because it is affected by friction.
Mechanical advantage (MA) =Load/Effort
1.)The mechanical advantage of simple machine
is 5 .What does it mean ?
Ans. It means that work become 5 times easier if machine is used .
Velocity ratio :-The ratio of distance moved by effort to the distance moved by load
is known as velocity ratio .It have no unit .It measure the extent to which the speed of doing work increases by
using the machine .It is always more than that of mechanical advantage because it is not effected by friction .
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= distance covered by effort /distance covered by load
1.)The velocity ratio of simple machine is 5 .what does
it mean ?
Ans. It means that the distance covered by effort is 5 times more than that of distance covered by load .
Efficiency :-The percentage ratio of output work to the to the input work is known as
efficiency . or
The percentage ratio of
mechanical to velocity ratio is known as efficiency .It is affected by friction so it is always
less than that of 100%.It can be increased by applying
grease or oil between the movable part of a machine ,by making smooth surface ,by using ball bearing wheelers and
rollers .
Efficiency (
Efficiency (
Factors affecting efficiency :
i)Frictional force
ii)Gravitational force
iii)Weight of machine
Perfect or ideal machine :-The theoretical machines whose efficiency is 100% are called perfect machine
or ideal machine In ideal machine .There are not wastages of input
work due to friction .In ideal machine
Out
put work = in put work
Real machine or practical machine :-The machine in
which efficiency is always less than that of 100%
or out put work is always less than that of input work is called real or practical machine .
Principle of simple machine :-It states that if there is no friction in simple machine output work is always equal to input work in the simple
machine .
Output work = Input work
L×L d = E × E d
1.)A
machine has 70% efficiency .what does
this means ?
Ans. It means that 70% input work is converted
into out put work and remaining 30% of
input work is wasted due to friction
in the machine .
Types of simple machine :- There are 6 types of simple machine :
1)Lever
2)pulley 3) Wheel and axle 4) Inclined plane 5)Screw
6) Wedge
1)Lever : A rigid bar or
straight rod which can move freely around a fixed i.e.
fulcrum is known as lever . The
velocity ratio of lever can be increased
by reducing load distance . They are 3 types
.
i)First class of liver
:-for example : Beam balance , scissors
, sea saw
ii)Second class of lever :For example :Bottle
opener ,wheel barrow Lemon squeezer ,nut cracker etc.
iii)Third class of lever :For example : Fishing rod , Sugar tongs ,broom forceps, hair plucker etc.
Principle of lever :- in balanced condition the product of load and load arm is equal to the product of effort and effort arm is known as the principle of lever .
Load ×load arm =Effort ×Effort arm
2.Pulley :A simple machine
like a circular disc having a groove on its circumference over which a rope passes is called pulley .In a pulley an
effort is applied at one end of the rope and the load to be lifted to the other
end of the rope .It help to make our work easier
,faster by changing the direction of force .
i.)Single fixed pulley : It cannot magnify applied force but change the direction of
applied force .in this pulley distance covered by load
is equal to the distance covered by effort , its V.R. is always 1
ii.)Single movable pulley :-It can magnify
applied force but not change the direction of force
.In this pulley effort distance is always twice to the
load distance so its V.R. is always 2 .
The velocity ratio of combined pulley = N. of pulley used in system .
Velocity ratio of
pulley (V.R.) =No . of pulley used in system (Except single movable pulley )
Or
No .of rope of segments that support the load
3.)Wheel and axle :-A simple machine having two co –axial cylinder of different diameter fitted in common axis and rotate together is called wheel and axle .In wheel and axle bigger cylinder is called wheel and smaller cylinder is axle .The load is lifted to the axle and effort is applied to the wheel .It also can magnify the applied force .For example :Sterring of vehicles .
V.R. =2π R/2π r
V.R. =R/r
1.)Wheel
and axle is called continuous lever ,why ?
Ans. In wheel and axle just like lever force
is applied in wheel and load is lifted in axle and rotates continuously
until the load reaches the required height , therefore wheel and axle is called
continuous lever .
4.) Inclined plane :-A simple machine having a smooth ,rigid
flat surface ,inclined at an angle to the horizontal plane is called
inclined plane .for example :stairs ,turning road in
hilly region .Its mechanical advantage is always grater than one so,It make work easy and
faster by magnifying force
because in inclined plane length of inclined plane is always more than
that of height of inclined plane .
Principle of inclined plane :-In inclined plane when its length is increased by keeping its height constant its mechanical advantages increases but when its height is increased by keeping its length constant its mechanical advantages decreases so it is always used by increasing its length by keeping height constant .
Velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)= Length of inclined plane (l) or
distance covered by effort/Height of inclined plane (h) or distance covered by
effort
1.)6 km
long road in the western slope and 4 km long road in eastern slope of a
mountain are constructed to reach the peak .Which one of them is easier to
climb the mountain with a bicycle and why ?
Ans. Through 6 km long road in the western slope is easier to climb
the mountain with a bicycle ,because according to principle of inclined plane
if the length of inclined increases the mechanical
advantage also increase i.e. less effort
is required to climb the mountain .
5.)Screw :-A simple machine which is made by wrapping
an inclined plane spirally around a cylindrical rod is called screw .It
consist of mainly 2 parts i.e. i)Thread :The winding edge of screw is called
thread .
ii)Pitch
:The distance between two successive
threads is called pitch .For example : Jack screw ,
Nail driller etc.
Velocity ratio of screw (V.R.)=: Effort distance(Circumference circular part of screw)/Load distance (Pitch of the screw)
V.R.
=2rp Where r = radius of circular part of screw , P =
pitch of the screw .
6.)Wedge:- A simple machine which is triangular shape tool with at least one slanting side ending in a sharp edge is called wedge .For example :Knife, axe etc.
Moment of force :-The turning effect of force is
called moment of force .It is equal to the product of force and perpendicular
distance from the force to the fulcrum . Its S.I. unit is
Nm(Newton meter)
Moment of force = Force (F)
×Perpendicular distance from the force to the fulcrum (d)
Clockwise
moment :-If a body rotates
clockwise under the application of force the moment is called clockwise moment
.
Anticlockwise moment :-If a body
rotates anticlockwise under the application of force ,the moment is called
anticlockwise moment .
Law of moment :-If a body is at equilibrium state ,the total
clockwise moment is equal to the total anticlockwise moment is known as
law of moment .
Mathematically
Total clockwise moment = Total anticlockwise moment
Reason
:
1.)Why
is a longer a spanner (wrench) is used
to open a rusted knot or big knot ,?
Ans. A longer spanner has greater moment arm as result it multiplies the
force and produce greater moment ,whereas big not or rusted knot requires more
moment to be opened .Therefore ,a long spanner is used to open a rusted or big nut .
2.)The
probability of breaking a branch of tree is more when a person moves a long it
towards its end .why?
Ans. When a person moves towards end of branch
the moment arm is increased as result larger moment is produced by the
person on the branch .Therefore the probability of breaking a branch of tree is more when a
person moves along it toward its end .
3.)The
probability of breaking a taller tree is
greater than shorter tree at the time of storm ,why ?
Ans. The taller tree has greater moment arm
as result it multiplies the force applied by storm and produce greater moment
than that of shorter tree .Therefore the probability of breaking a branch of
tree is more than shorter tree at time of storm .
Numerical problems :
Mechanical
advantage (M.A,)= Load /Effort
Velocity ratio
(V.R.) =Load distance /Effort distance
Velocity ratio of
pulley (V.R.)=N. of pulley used in system (Except single movable pulley ) or
N. of rope segments
that support load
Velocity ratio of wheel and axle (V.R.)= Radius of wheel(R)/Radius
of axle(r)
Moment =Force ×Perpendicular
distance from the force to the fulcrum .
Law of moment
=Total clockwise moment=Total anticlockwise moment
In uplifting 450N load with the help of 1m long lever takes 150 N effort. What will be the efficiency of a machine if the fulcrum is kept 25 cm far from the load .
Here ,Given
Load (L) =450N
Effort (E)=150N
Load distance(Ld)=25cm
Effort distance (Ed)=75 cm
Efficiency (
According to the formula
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)= Load /Effort
=450/150=3
According to formula
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= Effort distance /Load distance
= 75/25
We know that
Efficiency (ጎ
=3/3× 100 %
Efficiency (
2.)A 600n
load is raised by an effort of 200N by using a 1m long lever .If the load is 20
cm from the fulcrum .What is the M.A. ,V.R. and efficiency of the machine ? (M.A.=3,V.R.=4
,Efficiency =75%)
3.) What is
the efficiency ,if an effort of 150N is applied to raise a load of 200N using
two pulley system ?
Ans.
Here, Given
Load(L)= 200N
Effort(E)=150N
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= 2 (Since the
number of pulley =2)
Efficiency (
Now, according to formula
Mechanical advantage(M.A.)= Load/Effort
=200/150=1.33
Again ,Efficiency (
؞The
efficiency of given pulley system is 66.5%
4.)A movable
pulley has efficiency of 75% .What is effort necessary to lift a load of 500N.
Ans. Given,
Efficiency (
Load(L)=500N
Velocity ratio (V.R.)=2
(Since V.R. of movable is 2)
Effort (E)=?
Now, according to formula
Efficiency (
75% = ×M.A./2100%
Or 100 M.A. =75 ×2
Or M.A. = 75x2/100=1.5
Again, M.A.= Load /Effort
Or 1.5 =
Or Effort =500/1.5
؞Effort =333.33N
5.)If a
pulley system with efficiency 80% has mechanical advantage 4 .how many pulleys
are there in the system ?What is the effort necessary to lift the load 1000N ?
Ans.
Given,
Efficiency(
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)=4
Load(L)=1000N
Number of pulley (V.R)=?
Effort (E) =?
Now, according to formula
Efficiency (
80% =4/V.R.×100%
Or 80 V.R. =4×100
Or V.R. =4x100/80=5
؞Number pulley (V.R.) =5
Again ,M.A. =Load /Effort
Or M.A. =1000/Effort
Effort =1000/4=250
؞Effort =250 N
6.)What
effort is needed to balance a load of 800N in a wheel and axle with efficiency
80% .If radius of the wheel is 8cm and that of axle is 2 cm ?
Ans. given
Load(L)=800N
Efficiency (
Radius of wheel (R) =8cm
Radius of axle (r) =2 cm
Velocity ratio (V.R.) =?
Effort (E) =?
Now, according to formula
Velocity ratio (V.R.) = R/r
=8/2 =4
Again ,Efficiency (
Or 80% =M.A./4×100%
Or 100 M.A. =80×4
Or M.A. =80x4/100 =3.2
؞M.A. =3.2
Again, M.A.= Load/Effort
Or 3.2 =800/Effort
Or Effort =800/3.2=250
؞Effort =250N
7.)In a wheel
and axle ,the radius of wheel is 70 cm and that of axle is 5cm .If an effort of
50N is needed to lift a load of 500N what is the efficiency of machine ?(V.R.
=14, M.A. =10, Efficiency =71.43%)
8.)Study the given diagram and calculate M.A. ,V.R,
and efficiency of the inclined plane .
Given,Load (L)= 500N
Effort (E)=250N
Effort distance or length (l)=15m
Load distance or height (h)= 5m
M.A.=?
V.R.=?
Efficiency(
Now,According to formula
Mechanical advantage (M.A.)= Load /Effort
= 500/250=2
؞ mechanical advantage (M.A.)=2
Again, Velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)= l/h
Or =15/5 =3
؞ velocity ratio of inclined plane (V.R.)=3
Again, Efficiency (ጎ
Or
؞Efficiency (ጎ
8.) An effort of 20N is required to unscrew a joined
nut by using a 20cm long spanner .Calculate the moment produced .
Ans.given,
Effort (E)= 20N
Length of spanner =20cm
=20/100 = 0.2m
Moment(M)=?
Now,we know that
Moment(M)= Effort ×Effort arm
Or = 20 ×0.2 =4
؞ Moment produced (M)= 4Nm
Questions for Practice
Unit -Machine
Group
'A' (1mark Each)
1.Define simple machine.
2.What is mechanical advantage?
3.How is the mechanical advantage of a machine calculated?
Write.
4.What is velocity ratio? Write down is formula.
5.What is efficiency?
6.Write down the formula to
calculate the efficiency formula.
7.Define input work and output work.
8.What is a pulley? Why is it used?
9.What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a simple
machine?
10.What is an inclined plane? Why is It used ?
11.What is velocity ratio of an inclined plane? Write.
12.What is a wheel and axle? Why is it used?
13.Write down the formula to calculate the velocity ratio of wheel
and axle..
14.What is moment?
15.State the law of moment.
Group 'B' (2 Marks
Each)
1.What is meant by mechanical advantage of a machine is 3? Velocity
ratio has no unit. Why?
2.What is meant by the velocity ratio of a machine is 2? The
efficiency of a machine is always less than 100%, why?
3.The efficiency of a machine can be increased by applying oil
or grease. Why?
4.The probability of breaking a tree branch increases while
moving towards the tip of the branch. Give reason.
5.Small spanner is made to open a small nut and long spanner is
made to open a big nut. Why?
Group 'C'
(3 Marks Each)
1.Write down two
advantages of using simple machines. What is a perfect machine? Why is it
impossible to get a perfect machine in practice?
2.How can we increase the efficiency of a simple machine? Give
any two methods. Write any two applications of simple machine.
3.What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a simple
machine? How can the efficiency of a simple machine be increased? Write.
4.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever. Justify
this statement.
5.What is moment? Write down its formula and Sl unit.
6.What are two factors that affect the turning effect of force
(moment)? No one machine has 100% efficiency. Justify this statement.
Group 'D' (4 Marks
Each)
1.A simple machine of velocity ratio 20 is used to lift a load
of 600N by applying an effort of 40N. Calculate the mechanical advantage and
efficiency of the machine.
2. Draw a
neat and labeled diagram of each of the given simple machines.
1)Lever ii) Pulley
iii)Wedge iv) wheel and axle
3.A 20cm long spanner is used to open a rusted nut of a bicycle.
If the effort is 60N, calculate the moment produced. Write any two differences
between ideal machine and practical machine.
Unit - Test
Unit 2: (Force)
Time: 40 min. F.M.: 22
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer
all the questions.)
समूह 'क' (Group
'A') 1x6=6
1.Define simple machine.
2.What is mechanical advantage?
3.How is the mechanical advantage of a machine calculated?
Write.
4.What is velocity ratio? Write down is formula.
5.What is efficiency?
6.Write down the formula to
calculate the efficiency formula.
समूह 'ख' (Group
'B') 2x3 =6
7.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever? Justify
this statement.
8.Probability of breaking a tree branch increases on moving
towards the tip of the branch. Explain it on the basis of law of moment.
9.What is meant by the velocity ratio of a machine is 2? The
efficiency of a machine is always less than 100%, why?
समूह 'ग' (Group
'C') 2x3=6
10.Write any three utilities of simple machines.
11.Wheel and axle is called an advanced form of a lever. Justify
this statement.
समूह 'घ' (Group
'D') 1x4
12.A simple machine of velocity ratio 20 is used to lift a load
of 600N by applying an effort of 40N. Calculate the mechanical advantage and
efficiency of the machine.
The End
Unit :- 4 Work ,Energy and Power
Work :The
product of force and displacement of a body in
the direction of applied force is called work
.Its S.I: unit is Juole (J) C.G.S. unit is erg(dynes cm) .It is a scalar
quantity .
Work(w) = Force (F) ×Displacement(d)
Or W = F × d
Relation between
Joule and erg :
Juole
=Nm
1juole =105dynes ×100cm
(We know that 1N =105 ,1m =100cm)
0r 1 Juole =105 dynes ×102cm
Or 1 Juole = 107 dynes cm
Or 1 Juole =107 erg (We know that erg = dynes cm)
Therefore
1 J = 107 erg is the required the relationship between
Juole and erg
1 Juole
work :-When an object is displaced through a distance of
one metre by applying one Newton force is known as 1 Juole work .
1 Juole work = 1N × 1m
Types of work :- They are two types :-
i)Work done
against friction
:-If
a work is done by pulling or pushing an
object horizontally on the earth’s
surface ,the done is called work against friction .For
example : Sliding a box n the ground , pushing a cart
on the road, close or open the door etc.
Work against friction (w) =F× d
Work against gravity (W)= m×g×h
Where m=mass of an object , g = acceleration due to gravity ,h =height of object
The total amount of consumed energy = Total amount of work done
Types
of energy :-There are various form of energy .Some of them major form of energy are :
i)Mechanical
energy a)Kinetic energy b)Potential energy
ii)Chemical
energy iii)Electrical energy
iv)Heat
energy v)Light energy
vi)Sound
energy vii)Magnetic energy
viii)Atomic
energy
i)Mechanical
energy :The
energy possessed by the bodies due to their position or
configuration or motion is called mechanical energy .It is two types :
a)Kinetic
energy
:The
energy possessed by body due to result of motion of
object is called kinetic energy .For example .Moving
bullets ,running water, moving buses etc.
Kinetic energy (K.E.) = 1/2 mv2
Where m= mass of object , v = velocity of a body
Initial
velocity =u
Applied
force =F
Displacement
after applied force =s
And
final velocity =v
Now
from definition of work
Work done (W)= F×s
![]() Or W
= m.a .s (i) ( We know F =m.a )
Or W
= m.a .s (i) ( We know F =m.a )
From
equation of motion
V2 = u2 +
2as
V2
= 0 + 2a.s (we know u =0 m/s)
![]() Or s = V2/2a (ii)
Or s = V2/2a (ii)
Putting
the value of eqn (ii) in equation eqn (i)
W = m. a.V2/2a
Or
W = m. v2/2
0r W = 1/2mv2
Therefore
kinetic energy (K.E.) =1/2mv2 ( we know
K.E. = W)
b)Potential
energy :
The energy possessed by the bodies due to its position
or change in its shape is called potential energy .For example :Energy
possessed by the compressed spring ,energy possessed by
a stone kept on the roof ,Water stored in dam, foot lifted to kick a football etc .
Potential energy (P.E.)= m×g×h
Where m= mass of an object, g=acceleration due to gravity , h=height of height
ii)
Electrical energy
:The
energy possessed by the object due flow of electron
is called electrical energy .For example Telephone
,radio, television ,heater etc.are operated
by electrical energy .
iii) Heat
energy
:The
energy possessed by the object due to the sum total
kinetic energy of an object is called heat energy .for example :The heat
is used to cook food, boil water,run steam engine
iv)Light
energy :-The
energy possessed by the object due to extremely hot by
radiation is called light energy .for example :It help us to sensation of vision ,preparation of food to plant ,to
increase rate of chemical reaction
etc .
v)Sound
energy :-The
energy possessed by the bodies due to vibration of body
is called sound energy .For example :It help us for sensation of hearing ,to form electrical bell ,etc.
vi)Magnetic energy : The energy possessed by the magnet is called magnetic energy .For example: Electric bell, television, loudspeaker etc are operated by using magnetic energy .
vii)Chemical
energy :The
energy which can be obtained from chemicals,
foods, and chemical reaction is called chemical energy .For example: for
example :Enegy contained in battery ,bread ,coal ,petrol
etc.
viii)Nuclear energy or
atomic energy :The energy obtained from atomic reaction or nucleus of atom or nuclear reaction
is called Nuclear energy .For example: The energy
released during the explosion of atom bomb or hydrogen bomb etc.
Transformation of energy :-The process of conversion of one
form energy into another types of energy is known as transformation of energy.
ii)Electric motor = Electrical energy ⟶ Kinetic energy
iii)
Dynamo =Kinetic
energy ⟶ Electrical energy
iv)Microphone =Sound
energy ⟶ Electrical energy
v)Headphone =Electrical energy ⟶ Sound energy
vi)Hydropower station =Potential energy ⟶ Kinetic energy ⟶ electrical energy
vii)Steam engine =Heat energy ⟶ Kinetic energy
viii)Solar battery = light energy ⟶ Electrical energy
ix)Battery = chemical energy ⟶ electrical energy
Principle
of transformation or conservation of energy :-The energy
can neither be created nor be destroyed but it
can be converted from one form to another form hence total energy always remains
constant or conserved .This is known as principle of
transformation of energy or conservation of energy .
1.)Name the
devices which changes
i)Chemical
energy into electrical energy =A battery or cell
ii)Chemical
energy into heat energy = A kerosene heater
iii)
mechanical energy into electrical energy =A dynamo or
generator
iv)Light
energy into electrical energy =Solar panel
v)Sound
energy into electrical energy = A microphone
vi)Electrical
energy into mechanical energy =A electrical motor
vii)Solar
energy into electrical energy = Solar battery
viii)Electrical
energy into light energy = Electrical bulb
2.) What
kinds of energy is possessed by the following .
i)A
compressed spring = potential energy
ii)Water
in a river = Kinetic energy
iii)A
stretched rubber or catapult = Potential energy
iv)
A red hot iron ball = heat and electro magnetic energy
v)cell
or battery = Chemical energy
vi)The
food we eat = chemical energy
Vii)
The sun light = Heat and light energy (Electro
magnetic energy )
Viii)
A magnetic field = Magnetic energy
ix)
A man climbing a hill = Potential and kinetic energy
x) A flying bird = Potential and kinetic energy
Power :- The rate of doing work is called power . Its S.I. unit is Watt (J/S) .It is scalar quantity
.
Power (P) = work(w)/time taken (t)
Or
P= w/t
One
watt power :- When one joule work done in one second
,the power is one watt power .
Or
The rate of doing one joule work in
one second time is called one watt power .
Horse
power (H.P.) : The unit which is to measure the the power of engines is called horse power .It is denoted by H.P.
1 H.P. = 746 watt
1.)A person is standing on the road . He is carrying a load on his head
? What is the amount of work done by him ?
Ans. A person
does not work i.e. W =0 j , because there is no
displacement of an object i.e. d or S = 0 m ,but
work done is calculated numerically by using formula by using formula work done (w) = Force ×displacement (d).
2.)What differences is
felt in catching a fast moving cricket ball and a fast moving table tennis ball ,why?
Ans .A fast
moving cricket ball hurt more than a fast moving tennis ball .it is because a cricket ball does more work due to more mass and
possess more kinetic energy than that of table
tennis ball .
Numerical problems
W
= F×d
F or W(weight ) = m×g
Work
against friction (W)= F×d
Work against gravity (W)= m×g×h
Total
amount of consumed energy = Total amount of work done
Kinetic energy (K.E.) = ½ mv2
Potential
energy (P.E) =m×g×h
P =W/t
1.)Sanu carries an object 20m away against the
friction of 500N .Calculate the work .
Ans. Given
,Weight (w or F) = 500N
Distance
(d)= 20m
Work
(W)= ?
We
know that
W = F×d
Or W = 500 × 20 =
10000 Juole
2.)How much work is done
when an iron ball of 50 kg mass is raised 4 m upward ?
Given
, mass (m)= 50kg
Height
(h)= 4m
Work
(W) =?
We
know that
W =m×g×h
Or w = 50 ×9.8×4
= 1960
Therefore work (w) = 1960 juole
3.)Calculate the potential
energy stored in a stone of 80kg kept at the height of 15 m. What is the
potential energy when the stone is kept on the earth’s surface ?
Given
, mass of stone (m)= 80kg
Height
(h)= 15 m
Potential
energy (P.E.) = ?
We
know that
P.E. = m×g×h
Or P.E. = 80×9.8×15 =11,760
Therefore Potential energy at height (P.E.)= 11,760 Juole
Again
Potential at the surface of earth (P.E.)= m×g×h
Or
P.E. = 80 ×9.8×0 ( we know h = 0 m on the earth surface)
Therefore
, potential energy on the earth surface (P.E.)= 0 juole
4.)A bullet of mass 50kg
is flying with the velocity of 200 km/hr .Calculate the kinetic energy of the bullet .
Ans.Given
,mass of bullet (m)= 50 kg
Velocity
of the bullet (v)= 200 km/hr =200x1000/60x60=55.55
=
55.55m/s
Kinetic
energy of bullet (K.E.)= ?
We
know that ,
K.E. = ½ mv2
Or K.E. = ½ 50 ×55.55×55.55
=77145.06
Therefore kinetic energy (K.E.)= 77145.06 juole
5.)A crane lift a car of 1500kg at height of 5m in 12 seconds
. calculate the power of the cranes .
Ans.Given ,
mass of car (m)= 1500kg
Height (h)= 5m
Time
taken (t)= 12 second
Power (P) = ?
We know that
P = w/t
Or P = mxgxh/t
Or P = 15x9.8x5/12 =6125
Therefore
, the power of the crane (P)= 6125 watt .
6.)A crane lift a load of 6000N at the height of 20m in 5 seconds .
Calculate the power of crane in horse power .
Ans. Given ,load (w)= 6000N
Height
(h)= 20m
Time
taken (t)= 5 Second
Power
(P)=?
We
know that
P =mxgxh/t
Or P = wxh/t ( we know w
= mg )
Or P =6000x2/5 =24000
Therefore the power of crane (P)= 24000 watt
And
the power of crane in horse power (H.P) = 24000/746
=
32.17 horse power (H.P.)
7.)What do you mean by the
statement that the power of the bulb is 60 watt ?
Ans. It means that bulb convert 60 joules of electrical energy into light and heat energy in one second . (we know 60 watt =60 j/s)
Unit -5
Light
Causes of refraction
Denser and rarer medium :The medium
in which the velocity of light is less or having more density in comparison to given other medium is called denser medium .For example : In
comparison to air and glass ,glass is denser medium to that of air
Incident ray :The path of the ray of light in the
first medium is called incident ray .
Point of incidence :-The point
where an incident ray strike on another or second medium is called the of
incidence .
Normal:-A line drawn perpendicular to the
boundary surface between two media is called a normal .
Angle of incidence :-The angle
which makes the incidence ray with the normal is called angle of incidence .
Refracted ray :-A ray of light which bends or deviates from
its original path when passing second medium is called refracted ray .
Angle of refraction :-The angle
which the refracted ray makes with the normal is called angle of refraction .

Laws of reflection of light :
1.)When
the ray of light travel from rarer medium to denser medium ,it bends towards
normal or i>r
2.)When
the ray of light travel from denser medium to rarer medium, it bends away from
the normal or i<r
3.)The
incident ray ,refracted ray and the normal line in the same plane and same
point .
4.)The
ratio of the sine angle of incidence(sine i) to
the sine angle of refraction(sine r) is a constant for a given pair of
media and this constant is called
refractive index of the medium .It is also called Snell’s law .
Refractive
index( μ ) =
Sine i /Sine r
Or
Refractive
index (μ ) =Speed of light in air or vaccum or air(c)/Speed of light at that medium(v)
Or
Refractive
index (μ ) =1/sine ic
Or Refractive
index (μ) =Real depth /Apparent depth
Factors
affecting refractive index:
i)The
nature of the medium
ii)The
wave length or colour of light
iii)Physical
condition i.e. density, temperature etc.
Consequences of
refraction of light :
i)A
star appear twinkling in the sky .
ii)A
pond appear shallow than its actual
depth .
iii)An
object placed in a denser medium when viewed from a rarer medium , appear to be
at lesser depth .
iv)An
object placed in a rarer medium hen viewed from a denser medium appear to be
greater distance that of real distance .
v)A
coin kept in vessel and not visible when seen from just below the edge of the
vessel but can be seen from the same
position when water is poured into the vessel .
1.)Why does a
pond appear shallow than its actual depth ?
Ans.
The ray of light coming from the bottom of pond get refracted and bend away
from the normal ,when refracted rays comes in our eyes give the apparent
position of the bottom of pond , therefore the pond appear shallow than its
actual depth .
2.)A stick partially dipped in water seems to be bent ,Why ?
Ans.
3.)A man standing in a pond sees a fish in the pond and tries to
thrust a spear into it. he will succeed or not .Explain with reason .
Ans.
He
will not succeed , because the ray of light coming from the fish get refracted
and bend away from the normal ,when refracted rays comes in our eyes give
apparent position of the fish .
Critical angle and Total internal reflection :
Fig. C
Critical angel :-The angle incidence in denser medium for
which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 900 is called critical angle .It is denoted by ic ..
Critical
angle (ic ) = 1/density of medium(d)
i)The
ray of light must passes from denser medium to rarer medium .
ii)
Angle of refraction in rarer medium should be 900 .
When the ray of light travel from denser medium to rarer medium it bends away from the normal .If angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle then there is no reflection of light into the rarer medium and the rays are reflected back into the denser medium or same medium .This phenomenon of reflection of light is known as total internal reflection of light .
Condition
of total internal reflection of light :
i)The
ray of light must passes from denser medium to rarer medium .
ii)Angle
of incidence should be greater than critical angle .
Consequences
of total reflection of light :-
i)Diamond
sparkle with great brilliancy .
ii)During
very hot weather mirage is observed on the hot desert of on the hot coal far
road .
iii)
Air bubbles shine inside water .
1.)Why does
diamond sparkle with great brilliancy ?
Ans.
The critical angle for diamond is 240 .When the ray of light inter
into diamond they are incident always greater than that of critical .As result
the ray of light undergoes total internal reflection multiple times due to this
light comes out of diamond only at few points causing the emergent rays to be
very bright ,Therefore diamond sparkle with great brilliancy .
2.)Air
bubbles shine inside water ,why?
Ans.
The critical angle of water is 490 .When the ray of light inter into
air bubble they are incident always greater than that of critical angle .As
result the of light undergoes total internal reflection ,due to this air bubble
shine inside the water .
Mirage :-
The
apparent image of water which is seen in pitched road or desert during hot
sunny days is called mirage .It is an optical illusion which can be observed
generally in hot desert coal tarred road ,when inverted image of distant object
is seen along with object in the pitch road or desert during hot sunny days .It
is caused due total internal reflection
of light in upward direction .
Light pipe :-
The bending pipe made up a bundle of optical or glass fibers through which light can pass in a curved line due to total reflection of light is called light pipe .It is used in endoscope. Doctors use the endoscope to examine internal part of our body i.e. food pipe ,stomach etc.
Optical fiber :-A
cylindrical wave made of transparent glass or plastic which pass light waves
along its length by total internal reflection is called optical fiber .It consist of 3 layers :
i)Core :-A
place in the centre of fiber through which light travel is called core .
ii)Cladding
:- The outer optical materials that reflect the light back into the core is
called cladding .
iii)Coating :-The plastic buffer coating that protect the fiber is
called coating .
ii)Cladding :- The outer optical materials that reflect the light back into the core is called cladding .
iii)Coating :-The plastic buffer coating that protect the fiber is called coating .
i)It is used in long distance communication .
ii)It is used in military application i.e. aircraft ,ships, tanks etc.
iii)It is used in medical imaging i.e. endoscopes ,laproscopes etc.
Dispersion of light (White light ):-
In seven colours of light red colour have largest wave length highest velocity and lowest angle of deviation and violet colour have smallest wave length lowest velocity and largest angle of deviation .
Causes of dispersion of light :-The
dispersion of light occurs due to the different in angle of deviation of
different colours of light when passing through a glass prism , because when the white light ray
enters a denser medium the velocity of light decreases and the different colours
of light bend by different angles.
1.)Refraction
from a prism disperse light but refraction from a glass slab does not
.Explain with reason .
Ans.
A prism is triangular in shape , so when seven colours consisting white light are incident on first surface they
are bent towards the base .Then when they passes from glass to air or from
second surface refract further from base .This increase the angle between rays
and separate from each other .Therefore prism disperse white light into
different colours of light .
But ,the glass slab is rectangular in shape or
consist of two prism joined at the diagonally so the rays of light get
dispersed in first prism and combine in second prism to form white light , so
glass slab can not disperses white light.
2.)Rainbow is seen when it is raining and sun rays pass through it
.Why ?
Ans.
When the raining stops ,a large number of tiny droplets of water are in the
atmosphere .The water droplets act as small prism .So when white light rays
from the sun into the atmosphere ,they are dispersed by the tiny droplets of
water into seven colours .The seven colours of light appears in the form of a
band and a rainbow is formed in the sky .
3.)Sun seems
to be red during sun set and sunrise ,why ?
Ans. During
sun set and sunrise ,sun rays travel greater distance through the atmosphere .The
blue colour ,due to its high scattering capacity get scattered away and cannot
reach to eyes but red colour having very low scattering capacity and reach our
eyes .Therefore the sun appears red during sun set and rise .
Ans. The
light from sun has to travel a long distance of earth in atmosphere before
reaching the earth .The light get scattered in different direction by air
molecules present in its path. But the
blue colour due to its high scattering capacity get scattered the most
.Therefore the sky appears in blue colours .
Electromagnetic wave :-The wave which are not
affected by electric and magnetic field and do not need material medium for
propagation are called electromagnetic wave .For example :i)Gamma ray ii)X
ray iii)Ultra violet radiation iv)
Visible light v)Infra red radiation vii)Micro wave viii)Radio wave .
ii)They do not need medium for their propagation .
iii)The electromagnetic wave are produced by accelerated charge .
iv)In electromagnetic wave electric and magnetic field vectors are at right angle to each other and to the direction of propagation. So electromagnetic wave are transverse wave .
v)The electromagnetic being charge less are not deflected by electric and magnetic filed .
Description of electromagnetic wave:
i)Gamma ray
Sources : Radioactive substances ,
Properties :Causes of fluorescence, easily penetrate thick metallic sheet .It have shortest wave length and higher frequency .
Sources :All heated bodies ,sun.
Sources :Produced by electric devices i.e crystal oscillators
Sources :Oscillating circuit .
Numerical
problems
Refractive
index (μ
Or
Refractive
index(μ )=Speed of light in vaccum or air /Speed of light at that medium
Or
Refractive
index (μ) =Real depth /Apparent depth
Or
Refractive
index (μ)= 1/Sin c
Given ,
Angle of incidence (i)= 370
Angle of refraction (r) =240
Refractive index(μ )=Sin i /Sin r
or =0.6/0.4 =1.5
Therefore refractive index of glass =1.5
2.)A ray of
light travelling in air is incident in a medium .If the angle of incidence is
600 and angle of refraction in medium is 450 .What is the
refractive index of the medium (Ans.
refractive index =1.22)
3.)A ray of
light enters liquid medium at angle of incidence 450 and angle of
refraction in liquid is 300 .Calculate the refractive index of
liquid .( Ans.Refractive index =1.4)
4.)Light travel
through water with a speed of 2.25 ×108 m/s.What is the refractive
index of water .Given the speedf of light in vacuum is 3×108 m/s.
Speed
of light in vacuum (c)=3×108 m/s
Speed
of light in water (v) =2.25 ×108 m/s
Refractive
index (μ
) = ?
We
know that
Refractive
index(μ) =c/v
Or = 3 ×108 /2.25×108 =1.33
Therefore
refractive of water =1.33
Refractive index(μ) =c/v
Or = 3 ×108 /2.25×108 =1.33
Therefore refractive of water =1.33
5.)The
velocity of light in air is 3×108 m/s.What is the velocity of light
when it travels through glass ?
Refractive index of the glass is 1.5 .(Ans. Velocity of light in glass =2×108
m/s )
6.)The
refractive index of diamond is 2.42 .What is the speed of light in diamond ?The velocity of light in air is 3×108
m/s. (Ans. The speed of light in diamond =1.24×108 m/s )
7.)The real
depth of coin placed in a beaker is 10 m and it appears at the depth of 8m
.Calculate the refractive index of water .
Real
depth =10m
Apparent
depth =8m
Refractive
index of water =?
We
know that
Refractive
index (μ) =Real deapth /Apparent depth
Or = 10 /8 = 1.25
Refractive
index of water = 1.25
8.)Water in certain pond appear to be 2m deep .If the refractive
index of water is 4/3 .Calculate the real depth of water ? ( Ans. Real depth of
water =2.66m)
Unit : 6
Sound
Sound: A form of energy which is
produced due to the vibration of a material of medium
is known sound.
Source of sound:-An object that produced sound is called source of sound.eg
Process of transmission of sound:-
Wave:-A
periodic disturbance that carries energy away
from an object through a medium during motion is
called wave.
2.Longitudinal wave
1.Transverse wave :-A
wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate up
and down perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave is
called transverse wave. For example: All electromagnetic
waves are transverse wave i.e.
:Infra red ,Gamma ray, Ultra violet ray,
light wave, wave on the surface of water.
Trough:-In
transverse wave the maximum displacement of
particle is called trough.
Wave length:-The distance
between two trough or two crest is called wave
length. Its S.I. unit is meter & denoted
2.Longitudinal wave:-A
wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate along
the direction of propagation of the wave is called longitudinal wave
.These waves are also called mechanical wave because they requires materials
medium i.e.: solid, liquid, or gas for its
propagation. For example: Sound wave, wave on stretched
spring.
Wave length:-The distance between two successive compression or rarefaction is
called wave length. Its S.I. unit is meter(m)
&denoted by lymda(ƛ).
Frequency:-The
number of complete wave produced in per second
is called frequency. Its S.I. unit hertz(Hz) &
denoted by f.
Wave velocity or sound velocity :The
distance travelled by the sound wave in per second is sound velocity. Its S.I.
unit is m/s.
V=ƛ×f
Types of sound on the basis of frequency:-There are three types of sound.
1.Sub sonic or infrasonic sound:-The
sound that have frequency less than 20 Hz is called infrasonic sound. This
sound is not audible to normal human ear but audible for animals. For
example: The sound produce by earthquake ,volcano eruption, whale and elephant.
2.Audible sound:-The
sound that have frequency between 20Hz to 20kHz is called audible sound. This
sound is audible for normal human ear. For example :The sound produced by human
vocal ,radio.

Uses of ultra sound:-
2.It is also used to study the healthy condition and posture of embryo in condition of pregnancy.
3.It is used in faithometer or SONAR to measure the depth of sea or ocean.
Reflection of sound:-When the sound wave produced
surface i.e. wall ,rocks. hill.etc then return and go back to the same medium is called reflection of sound. The application of reflection of sound is Eco, reverberation.
Eco:-The
repetition of sound due to reflection of sound

Conditions
necessary for the Eco:
Eco:-The repetition of sound due to reflection of sound
1.The source of sound and surface of
reflection should be required.
2.The distance between source of sound and
surface of reflection must be more than 17 m.
Reverberation:-The
prolongation of sound due to mixing of several reflected sound and original
sound is called reverberation. For example: The sound produced by hall, cinema
hall, musical studio etc.
Conditions
necessary for reverberation:
1.The source of sound and surface of
reflection should be required.
2.The distance between source of sound and
surface of reflection must be less than 17 m.
Intensity of sound:-The amount of sound energy carried by sound wave per unit area per unit time is called intensity of sound. Its S.I. unit is decibel (db).The sound wave having intensity up to 80 db is the safe limit of sound but having more than 120 db is harmful for our ear and our body.
Factors affecting intensity of sound:
1.Amplitude: Intensity ∞ amplitude
2.Distance of listener from the
source:Intensity∞1/Distance of listener
from the source.
3.Density of medium: Intensity sound
∞density of medium.
4.Area o vibration of surface: intensity of
sound ∞ area of vibration.
5.Frequency of sound: Intensity of sound
∞frequency of sound.
Pitch of sound:-The sharpness of sound is known as pitch of sound. It differs according to the frequency of sound. It can not be measured but can be felt.
Noise:-The sound which
produces unpleasant effect on listeners is called a noise.
Noise pollution:-Any
unwanted sound at a wrong place at a wrong time is called noise pollution.
Effects
of noise pollution:-
1.It causes of annoyance(irritation)
2.It increase blood pressure in human
being.
3.It increase nerve disorder and headache.
4.It produces unnecessary mental stress.
Control measure of noise pollution:-
1.It can be controlled by minimize running
loudspeaker, radio,& other musical instruments system.
2.It can be controlled by using silencers
with automobiles and machines.
3.It can be controlled by banning the air
horns.
4.The level of noise pollution can be
reduced by plantation along the road side.
Relation between velocity ,wave length ,and
frequency
We know that
wave length ‘ ƛ’ is
the distance travelled by a wave when a particles of the medium complete
one vibration
The particle takes time T equal to time
period to complete one vibration .
Let V be the velocity of wave
V = Distance travelled by the wave(ƛ ) /time taken(T)
Therefore , V=ƛ/T (but f= 1/T)
Now , V = ƛ ×f
Or
velocity sound = wave length × frequency
wave length ‘ ƛ’ is the distance travelled by a wave when a particles of the medium complete one vibration
The particle takes time T equal to time period to complete one vibration .
Let V be the velocity of wave
V = Distance travelled by the wave(ƛ ) /time taken(T)
Therefore , V=ƛ/T (but f= 1/T)
Now , V = ƛ ×f
Or velocity sound = wave length × frequency
Numerical problems
Velocity or speed of sound (v)= wave length (ƛ) × frequency (f)
Frequency
(f)= 1/T
1.)If a radio station
transmit at 219 m wave length and 1370 KHz, calculate the velocity of waves .
Given ,
Wave length (ƛ) = 219 m
Frequency (f) =1370 KHz = 1370 ×1000 = 1370000 Hz
Wave velocity (v)=?
We know that
Velocity of sound (V)= ƛ× f
Or
v = 219×1370000
Or
= 300030000 m/S
؞ velocity of wave (V) =3.00 ×10 8 m/s
2. What are the
shortest and the longest wave length of the sound that the human ears can hear
? Speed of sound in air is 330 m/s and the audible range of frequency is 20 Hz
to 20 KHz .
Given ,
Lower frequency (fL) =20 Hz
Upper frequency (fu) 20
KHz =20×1000 =20000Hz
Speed of sound (v) = 330 m/s
We know that
Velocity of sound (v) = ƛ × f
Or ƛL
= v/fS
Therefore
the longest wave
length of audible sound (ƛL)
=16.5 m
Again ,
We
known that ,the shortest wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =V/fL
Or
ƛs =0.0165 m
Therefore ,the shortest
wave length of audible sound (ƛs) =0.0165 m
3.The frequency of sound wave is 200 Hz
.What is its time period ?
Given ,
frequency of sound (f) = 200 Hz
Time period (T) =?
We know that
Time period (T) = 1/f
Or
T = 1/ 200 = 0.005
Therefore , time period (T) = 0.005 sec
4.A boy hears an echo of his own voice from
a distant hill after 1 s .The speed of sound is 340 m/s .What is the distance of hill from the boy ?
Given ,
Speed of sound (v)= 340 m/s
Time taken of hearing echo (t)= 1 s/2
=0.5 sec
Distance of the hill from the boy (d) =?
We know that
V= d /t
Or distance (d) = v × t
Or d
= 340 ×0.5 = 170
The distance of boy from the hill (d) = 170
m
5.A source of wave
produces 20 crest and 20 troughs in 0.2s .Find the frequency of the wave .
Given ,
We know that
A
complete wave consist of a crest
and a trough
؞
20 crest and 20 trough = 20 waves
؞ 1 complete wave produces = 0.2/20 = 0.01
sec
Again, we know that
Frequency (f) =1/T
Or f = 1
/0.01 = 100 Hz
Therefore frequency of wave (f) = 100 Hz
Unit :- 7 (seven )
Types of electricity : They are 2
types :
2.Current electricity :The rate of charge through conductor is called
electricity .
1Ampere =1 coulomb /sec
1 coulomb = 6 x 1018 electrons
1 ampere = 1000 milli ampere (mA)
1 Ampere =1000000 micro ampere (
)
A)
1mega Ampere = 1000000 A
One ampere current :When one
coulomb charge( 6x1018 electrons) flow through a conductor in one second then current flow the conductor is called one
ampere current .
= 1C/s or 1A
Hydroelectricity :The electricity generated by rotating turbine with
help of water is called hydro-electricity .In hydro-electricity there will be no substance that is ejected to the
air and causes of pollution ,So hydro- electricity is called pollution
electricity .
Electric circuit :A conducting path made by connecting electric source ,load , and switch with conducting wire is called electric circuit .
Types of electric circuit :They are two types :
i.)Closed circuit :The circuit in
which the loads are functioning due to continuous flow of current
through the circuit is called closed circuit .
.Symbol of some electric appliances :
Conductor :The substance
through which electricity can flow easily are called conductor. For example
:Aluminum, Copper , Iron, etc.
Insulator :The substance through which current electricity can not pass are called insulator or non conductors .For example :Plastic, dry wood , dry air Rubber etc.
Conventional current :The old direction of current from +positive to –Negative terminal of cell or circuit is called conventional current .The conventional current direction is traditionally accepted .It is still used in circuit diagram .
Direction of real current :The actual flow of electrons from negative terminal to positive terminal of cell or circuit is called real direction of current ,but conventional current direction is still used in circuit diagram .
Ammeter : A
instrument which is used to measure current in a circuit is called Ammeter .It
is always connected in series with resistance
in the circuit, because an ammeter is a very low
resistance device and total current flowing in the circuit should be
passed through it 
Voltmeter :A instrument which is
used to measure potential differences or electromotive force of the electric
circuit is called voltmeter .It is always connected in parallel with resistance
in the circuit in such way that its positive terminal is connected to the
positive and negative terminal is connected to its negative terminal of
electric sources because a voltmeter is a very high
resistance device so when it is connected
parallel with load the net resistance of the circuit does not change
.
Potential difference (P.d.):The work done against the
electrical field while flowing a unit of charge from lower potential to higher
potential is called potential difference .It S.I. unit is volt .It is a
measurement of work done in taking a unit charge
from one point to another point .It is measured in closed circuit .P.d. is always less than that of electromotive force .

Electromotive force (E.m.f.) : The total amount of energy supplied by the cell to make the flow of unit charge in an electric circuit is called electromotive force (E.m.f.) .Its S.I. unit is also volt .It help to measure the total amount of energy supplied by electric source to carry a unit of charge through a circuit .It is measured in open circuit .E.m.f is more than that of p.d .because because every cell has internal resistance as well as conductor so some portion of energy provided by the e.m.f is wasted to overcome .
Resistance :The
property of conductor i.e. wire by which the conductor oppose the flow of
current through it is called resistance .Its Symbol is R and its S. I. unit is oham (Ω
)
Resistor :The substance
that oppose the flow of current through it is known as resistor .For example
:Nichrome, Tungesten , manganin etc.
i)Good conductor :The
substance that have high concentration of free
electrons are called good conductor of electricity .They have very less resistance .For example :Copper ,Aluminum, Lead ,Silver
etc.
i)Nature of conductors :Different substance have different concentration of free electrons, so
resistance of conductors depends on the nature of conductor .For example:
a)Good conductor have very less resistance i.e .
Copper ,Aluminum ,
b)Semi conductors have more resistance i.e. Nichrome, tungsten
l
ii)Thick
of conductor :Resistance of conductors is inversely proportional to the thickness of
the conductors .
R∝ 1/A
iv)Temperature
of conductors :Resistance of
conductors is directly proportional the temperature of the conductors . i.e R∝ Temperature
v)The
resistance of conductors also depend upon the shape and size of conductor .For example In straight
wire and coil wire coil wire have more resistance.
a)Good conductor have very less resistance i.e . Copper ,Aluminum ,
b)Semi conductors have more resistance i.e. Nichrome, tungsten
ii)Thick of conductor :Resistance of conductors is inversely proportional to the thickness of the conductors . R∝ 1/A
iv)Temperature of conductors :Resistance of conductors is directly proportional the temperature of the conductors . i.e R∝ Temperature
v)The resistance of conductors also depend upon the shape and size of conductor .For example In straight wire and coil wire coil wire have more resistance.
Or V =R I (Where R is resistance )
؞ V = R I proved
One Oham’s resistance : When a potential difference of 1 volt is applied
across the ends of the conductor due flow of one 1 ampere current ,then resistance is called one Oham’s
Result
of experimental verification of Oham’s
law
|
N. of cell |
Reading of voltmeter (p.d) |
Reading of Ammeter |
R=V/I |
|
1 2 3 4 |
1.5 3.00 4.5 6.00 |
0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 |
5 5 5 5 |
Resistor :The substance which oppose the flow of current
through it is called resistor .for example :Nichrome ,Tungsten
Combination or connection of
resistor :They are connected by two ways:
I.)Series combination of
resistor or load :The combination of resistor in which resistors are
joined end to end in such way that same current passes through each of them is
called series connection of resistor .
Total resistance (T)= R1+R2+R3+…………Rn
ii.)Parallel combination of
resistor or load :The
connection of resistor in which each resistor are joined
across same potential difference is called parallel connection of resistor .
Total
resistance (1/R) =1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3 ………1/Rn
Electric power : The rate of doing work of electrical device at which it convert electrical energy into other form of energy is called electrical power .Its S.I. unit is watt .
Electric power (P)= Current (I) x Voltage (V)
Or P = Ix V
Magnet : The
substance which has ability to attract
magnetic substance towards its is called magnet 
Types of magnet :
They are 2 types :

2. Artificial magnet :Man made magnet are called artificial magnet . For example : Bar magnet
i.)If a magnet is freely suspended ,it always points
in North (N) and south (S) direction .
ii.)Like poles of magnet are repel eachother and unlike poles of magnet attract each other.
iii.)A magnet has two poles i.e N and S poles .
iv) A magnetic materials gets magnetized due to presence of a magnet is
called magnetic induction .
Magnetism :The property of magnet due which it attract magnetic
substance is called magnetism .
Properties of magnetic lines :
i.)They start from N- pole and end on S- pole of
magnet .
ii.) They never intersect each other .
iii) They are closed and continuous curve .
Terrestrial magnetism : The magnetic properties of earth is terrestrial magnetism .
Magnetic poles of earth : The place of earth where the freely suspended magnet needle become
exactly vertical that place of earth is
called magnetic poles of earth .For example : The magnetic
south pole is situated in the northern
part of Canada and the magnetic north
pole is situated at south Victoria land or in the corner of Antarctica .
ii.)Presence of magnetic properties in iron ores .
iii.)
Formation of angle of dip and
angle of dip and angle of declination .
iv)Formation of Neutral point in the magnetic field of bar magnet .
Geographical axis : A straight line
passing through the geographical poles of earth is called geographical axis or
polar axis .
Angle of declination :The angle made by intersection of the line joining the magnetic north
–south and the line joining the geographical north –south at a place is called
the angle of declination of that place. Its maximum value is less than 900 and minimum value is 00 .and
in Kathmandu is 22.It is measured by magnetic
compass
ii.)It
is used in finding the direction when travelling
in Aero planes in night .
1.)Angle
of declination in Kathmandu valley is 220 E. What does it mean ?
Ans. It means that the north pole of a horizontal
compass needle will point 220 east to the geographical north and south direction .

Angle of dip or inclination : The angle made by the dip needle or by the direction of the earth’s
magnetic field at particular place with the horizontal surface of the earth is
called dip at that place . It is measured dip circle
.The value of angle of dip at equator is 00 and
poles is 900 and Kathmandu is 420 .
1.)Why the value of angle of
dip is zero at equator ?
Ans. The effect of the earth’s magnetic north pole and
south pole are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction in equator
therefore the value of angle of dip is zero at equator .
Ans. The attraction effect of south magnetic pole of
earth is zero at north magnetic pole and attraction effect of north magnetic
pole of earth is zero at south magnetic pole of earth as result dip needle set
perpendicular to the horizontal axis and
makes 90 0at pole therefore the angle of dip is 900 at
poles .






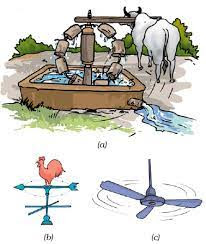





















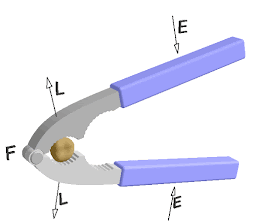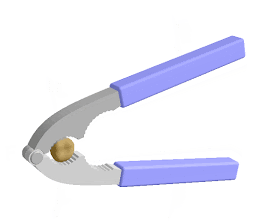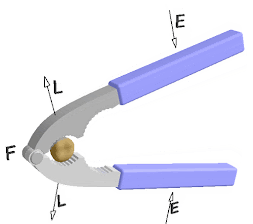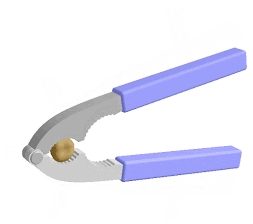
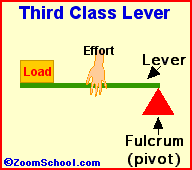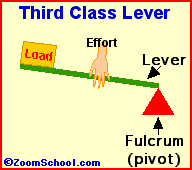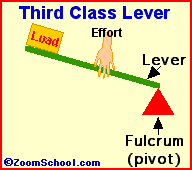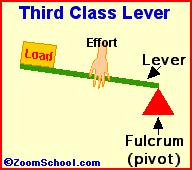































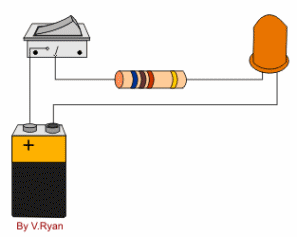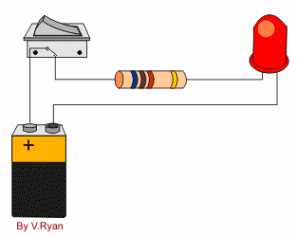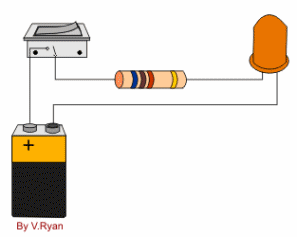

















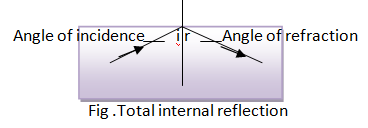

























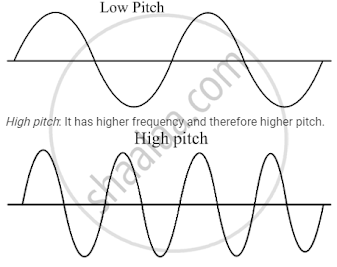







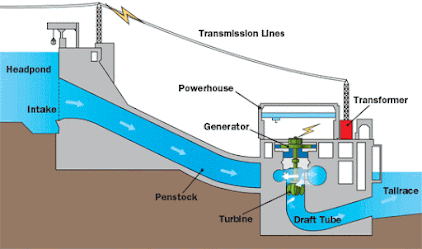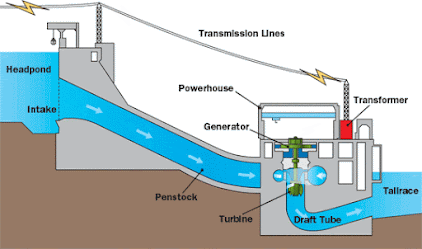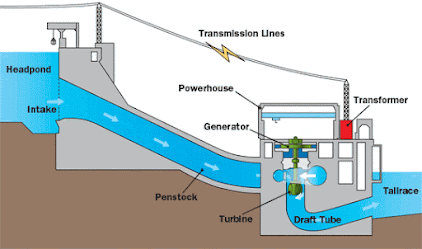


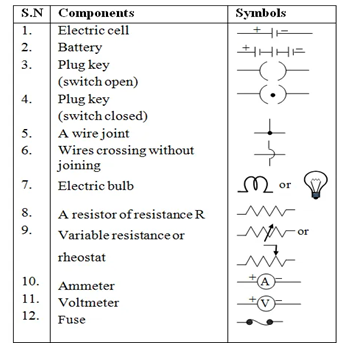
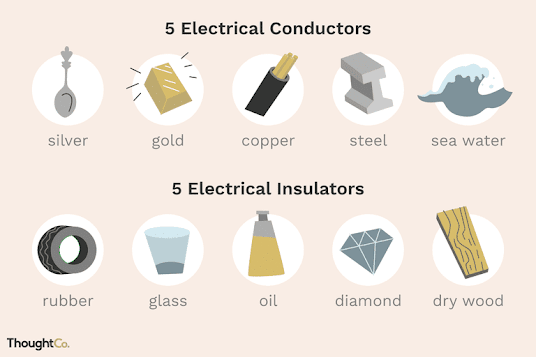











Eumaxindia is a leading auto rickshaw advertising agency in Chennai. We provide best Auto rickshaw branding all over the Chennai.
ReplyDeleteAuto Rickshaw Branding in Chennai