Physics -Grade -8
Physics
Grade
- 8 (Physics)
Unit Topics
1 Measurement
2 Force and Velocity
3 Machine
4 Pressure
5 Work ,Energy
and Power
6 Heat
7 Light
8 Sound
9 Magnetism
10 Electricity
Specification Grid
Division of 15 marks in Knowledge(K)
,Understanding(Un), Ability(A), and Higher Ability
|
Areas |
S.N. |
Units |
N.Of Ques. |
N.of Sub. Ques. |
Full marks |
K-30% |
U-40% |
Ap-20% |
HA-10% |
|
Physics |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
Measurement Force and Velocity Machine Pressure Work, Energy and Power Heat Light Sound Magnetism Electricity |
5 |
10 |
25 |
7.5 |
10 |
5 |
2.5 |
|
Total |
5 |
|
5 |
10 |
25 |
7.5 |
10 |
5 |
2.5 |
Note:
१) जम्मा १५ वटा मुख्य प्रश्नहरु हुनेछन् र प्रत्येक प्रश्नको दुईवटा उपप्रश्नहरु हुनेछन् । प्रत्येक मुख्य प्रश्नको अकंभार ५ र उपप्रश्नको अंकभार २ वा ३ हुनेछ ।
२)प्रश्न पत्र निर्माण गर्दा सवै एकाइहरुलाई समेट्नु पर्नेछ ।
३) प्रश्न निर्माण गर्दा ज्ञान, वोध, प्रयोग, र उच्च तह का प्रश्नहरु निर्माण गर्नु पर्छ ।
K= Knowledge ,U
=Understanding , A =Ability ,HA =Higher
Ability
Scholastic Areas :-Grading on 9 points Scale
|
S.N. |
Marks range |
Grade |
Attributes |
Grade
Points |
Remarks |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
90 to 100 80 to below 90 70 to below 80 60 to below 70 50 to below 60 40 to below 50 40 to below 50 30 to below 40 0 to below 20 |
A+ A B+ B C+ C D+ D E |
Outstanding Excellent Very good Good Satisfactory Acceptable Partially Acceptable Insufficient Very insufficient |
4.0 3.6 3.2 2.8 2.4 2.0 1.6 1.2 0.8 |
The minimum qualifying grade in all subjects under scholastic Domain Is C
|
Unit : One(1)
Physical quantity: The quantity which can be measured is called physical quantity .For example :distance, mass, length, volume, time etc.
Non-physical quantity:The quantity which can not be measured is called non physical quantity. For example: love, anger, sadness ,joy etc.
Types of physical quantity:They are two types.
i.)Fundamental quantity: The physical quantities which does not depend upon other physical quantities is called fundamental physical quantity. for example: Mass ,length ,time ,current, temperature, luminuous intensity, amount of substance are the seven fundamental physical quantities .
ii)Derived quantity: The quantity which depend upon fundamental quantities or produced from fundamental quantities is known as derived quantities .For example: speed ,velocity, acceleration, work, power, etc.
Measurement: The process of comparing an unknown quantity with a known standard quantity is called measurement.
Unit: The known or standard quantity of the same kind with which a physical quantity is compared for measuring is called unit .For example: meter(m),kilogram(Kg),second(s) etc.
Types of unit :They are two types :
i.)Fundamental unit :The unit which does not depend upon other unit is called fundamental unit. Or The unit of fundamental quantities are called fundamental unit. For example: There are seven basicfundamental unit:
S.N. | Fundamental quantities | Fundamental units(S.I. unit) | symbol |
1 2. 3 4 5. 6 7. | Length Mass Time Temperature Electric current Luminous intensity Amount of substance | Meter Kilogram Second Kelvin Ampere Candela mole | M Kg S K A Cd mol |
1.)What is the S.I. unit of length ?Why is it called fundamental unit?
Ans. The S.I. unit of length is meter .
The unit of mass is called fundamental unit because it does not depend on other unit .
2.)Why is the unit of mass is called fundamental unit?
Ans. The unit of mass i.e.kg is called fundamental unit because it does not depend on other unit .
Or The unit of derived quantities called derived unit .For example:
S.N | Derived quantity | Derived unit(S.I unit) | Fundamental unit involved | Fomula |
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6.
7. 8. 9.
10. | Area Volume Acceleration Force Density Pressure Work/Energy Moment Power Frequency | m2 m3 m/s2 Newton(N) Kg/m3
pascal(Pa) or N/m2 Joule(J) N.m Watt or J/S
Hertz(Hz) | m.m m.m.m. m.s-2 Kg.m.s-2 Kg.m-3 Kg.m-1s-2 Kg.m2.s-2 Kg.m.s-1 Kg.m2s1 1.s-2 | A=l×b V=l×b×h a= v-u/t F=m×a D=m/v P=F/A
W=F×d Moment=F×d P=W/t
F= v/λ |
1.)What is the S.I. unit of velocity ?Why is it called derived unit ?
Ans.The s.I. unit of velocity is m/s. The unit of velocity i.e.m/s is derived by combination of fundamental unit i.e. m and s, so it is called derived unit.
2.)What is the S.I.unit of pressure? Why is it called derived unit ?
Ans. The S.I. unit of pressure is Pascal(Pa).
We know that, P=F/A
Or P=mxa /lxb
Or P =kg.ms-2 /m2
Or Pressure( P) =kg.m-1.s-2
Therefore ,the unit of pressure i.e. Pa is called derived unit because it is derived combination of fundamental unit i.e. Kg .m and s , so it is called derived unit.
Types of of system of unit :The combination of fundamental unit is called system of unit :There are mainly four types of system of unit :
i)MKS system of unit :The system of unit in which the unit of length is metre (m),unit of mass is kilogram (Kg) and unit of time is second (S) is MKS system of unit .It is also called metric system .
ii)CGS system of unit :The system of unit in which the unit of length is centi metre (cm) ,unit of mass is called gram(gm) and unit of time is called second is called CGS system .It is also called French system of measurement .
iii)FPS system of unit :The system of unit in which the unit of length is foot (ft) ,unit of mass is pound (lb) and unit of time is called second is called FPS system of unit .It is also called British system of measurement .
iv)SI ( systemse international de unit or system of international unit )system of unit: The internationally standardrised unit of measurement is called SI system of unit .
Advantages of SI system :
i)It help to make the measurement simple and more reliable .
ii)It is help to bring uniformity in measurement and to take the actual measurement .
iii)It is an international system of unit of measurement .
Advantages of measurement :
i)It is used in comparision ,buying ,selling different types of goods .
ii)It is used in construction purpose and household activities i.e. cooking, washing etc.
iii)It help to carry different scientific experiment .
iv)It required for global understanding of the quantity of a substance .
v)It is required to make law and rule about the quantity of the substance .
Mass :The total quantity of the matter contained in an object is called mass .Its SI unit is Kg and measurement by beam balance .It is constant place to place .The mass of an object depends on the number of atoms contained in an object and mass of an object

One kilogram mass :The mass of the platinum –iridium block kept at the international Bureau of weight and measurement in France is called one kilogram .
Note:
1000 milligram (mg) =1 gram (g)
1000 Gram (g) = 1 kilogram (kg)
100 Kilogram (Kg) =1 Quintal
1000 Kilogram (Kg) =1 Tonne
1.The of amount of force gravity acting on a body is called weight.
2.It is a derived quantity.
3.Its SI unit is N.
4.It is measurement by spring balance.
5.It is a vector quantity.
6.It is variable place to place.
Weight(W)=mg
Time :The interval between two events or works is called time .Its SI unit is second and measured by different types watch .
Zenith :When we stand straight ,the point in the sky directly above our head is called zenith of that place .
One solar day :The time taken by the earth to complete one rotation in its own axis is called one solar day .
One solar day = 24 hours or 86400 second .
One second time :The
Questions
forPractice
1.What is measurement? Write any two
differences between mass and weight.
[BLE
Kaski 2074]
2.What
is unit? Write two differences between fundamental unit and derived unit.[BLE
Kathmandu 2074]
3.Write
any two differences between mass and weight. [BLE Chitwan 2074
4.What is derived unit ? Write any two
differences between mass and weight.[DLE Kathmandu 2072]
5.What is derived unit ? Write any two
differences between weight and mass.[BLE Morang 2074, DLE Lalitpur 2072]
6. What is fundamental unit? Write any two
differences between mass and weight.[BLE Butwal 2074]
7.Define a physical quantity. Write any two
differences between mass and weight.[DLE Bhaktapur 2072]
8.What is meant by fundamental units ? Write
the fundamental units involved in acceleration and pressure.[DLE Morang
2072, DLE Jhapa 2072]
9.What is physical quantity ? Write two
differences between fundamental unit and derived unit.[DLE Sunsari 2072]
10.What is meant by S.I. system? Write any
two differences between fundamental unit and derived unit.
[DLE Makwanpur 2072]
11. What is mass? On which factors does it
depend?
[BLEKanchanpur 2074]
12.Write any two differences between
fundamental unit and derived unit. [DLE Kaski 2072) [DLE Banke 2072]
13.Write any two differences between mass and
weight. 14.What is fundamental unit ? Write any two
differences between mass and weight.[DLE Kallall 2072]
15.What
is one second ? Which units are used to measure mass and pressure in S.I.unit.[DLE
Kathmandu 2073]
16.Define
one solar day. Write any two importance of SI system. (BLE Bhaktapur 20717)
17.What is derived
unit? Why is the unit of velocity called derived unit? [BLE Sunsari 20741)
18.What
is physical quantity? Write any two differences between fundamental unit and
derived unit.[BLE Kailali 2074] ___
19.What
is measurement? Write the units of area and density in SI system.[DLE Lalitpur
2073]
20.Define fundamental unit. Write any two
differences between fundamental and derived units.[DLE Bhaktapur 2073]
31/
21.
Why is the unit of velocity called derived unit?[DLE Morang 2073]
22.What
is weight? Write its SI unit. Why is it called as derived unit? [DLE Sunsari
2073]
23.What is one second time? Define physical
quantity with an example.[DLE Parsa 2073]
24.Define
physical quantity. Write any two differences between mass and weight.[DLE
Kaski 2073]
25.
What is mass? Write two differences between fundamental and derived unit.[BLE
Lalitpur 2074, DLE Rupandehi 2073]
26.Define
physical quantity. Write any two differences between fundamental and derived
unit.[DLE Banke 2073)
27.What
is meant by fundamental unit? Write any two differences between weight and mass.[DLE
Kailali 2073]
Unit
- Test
Unit 1: नाप (Measurement)
Time:
36 min. F.M.: 20
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the
questions.)
1.a)What is measurement? Write the units of
area and density in SI system. (1+0.5+0.5)
(b) Define fundamental unit. Write any two
differences between fundamental and derived units.(1+2)
2. (a)What is one second time? Define physical
quantity with an example. (1+2)
(b)
Convert 25 days in second.(2) (Ans: 2160000 sec.)
3. (a) What is unit? Write any two differences
between mass and weight.(1+2)
(b)
What is mass? On which factors does it depend?(1+1)
4.
(a) What is MKS system? Which units are
used to measure mass and pressure in S.I.unit. (1+1)
(bWhat is a physical quantity? Describe in
brief, the importance of measurement in our daily life.(1+2)
The End
Velocity and Acceleration
Force :- A physical quantity which change the state of an object is called force. Its S.I. unit (N) and measured by spring balance . It is a vector quantity. Eg. Pulling force, Gravitational force etc.
Force(F)=Mass(m)×acceleration(a) or mass(m)×acceleration due to gravity (g)
1N force :-The force which when acting on a body of mass 1kg to produces 1m/s2 acceleration is called 1 N force .
1 N =105 dynes
Motion:-If a body change its position with respect to its surrounding as the passage of time is called motion .For example :A man walking on the road ,vehicles, bus ,etc.
Differences between uniform motion and non uniform motion
Uniform motion | Non –uniform motion |
i)The motion in which a body covers equal distance in equal interval time is known as uniform motion. ii)For example :The motion of planet ,satellite, watch etc. | i)The motion in which a body covers unequal distance in equal interval time is called non – uniform motion . ii)For example :The motion of vehicles ,flying birds, etc. |
Reference point or relative point :-The place from which a location is observed and measured is called reference point or the origin point .
Distance :The length of actual path travelled by the moving body in any direction depend upon the length of path is known as distance .It is scalar quantity .
Displacement: The distance covered by a body in a particular direction in a certain interval time is called displacement . It is a vector quantity .
Vector quantity :-The quantities which have both magnitude as well as direction is known as vector quantities .For examples : displacement, velocity, acceleration force etc.
Scalar quantity :The quantities which does not have direction but only magnitude is known as scalar quantity .For example: mass, volume ,speed , work ,energy etc .
Speed:The distance covered by a body per unit time is called speed .It S.I. unit is m/s .It is scalar quantity because it have only magnitude but not direction
Speed or average velocity =Distance covered (m)/Time taken(t)
Velocity :-The distance covered by a in a particular direction per unit time is called velocity .or
Displacement per unit time is called velocity .Its S.I. unit is m/s .It is a vector quantity because it have both magnitude as well as direction .
Non-uniform velocity :-if a body does not covers equal distance in equal interval time is known as non- uniform velocity .
1.)A student runs 5m/s .What does this mean ?
Ans. It means that he covers a distance of 5 meters in a per second
Relative velocity :The velocity of a body with respect to a relative point or relative point is called relative velocity .
Relative velocity in opposite direction :Velocity of one body + Velocity of another body
Relative velocity in same direction : Velocity of one body - Velocity of another body
Acceleration:-The rate of change of velocity per unit time is called acceleration .or
Velocity change in per unit time is acceleration .It S.I. unit is m/s2.It is vector quantity.
a =v-u /t Where, a = acceleration , V= final velocity , u =Initial velocity , t= time taken
Retardation :The decrease in velocity per unit time is known as retardation .so the negative acceleration is called retardation .for example : -10m/s2 ,It means that the retardation is 10m/s2 .Its S.I. unit is also m/s2.
Equation of motion:-The mathematical equation that show the relation between initial velocity (u),final velocity (v),acceleration (a),time taken(t), and distance covered by the object(s) is known as equation of motion .The equation of motion are
V=u+at 一 i
S=u+v/2×t 一 ii
S=ut +1/2 at2 一 iii
V2 =u2+2as 一 iv
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
Now,
According to definition of acceleration
a= v-u /t
or v-u =at
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance travelled =s
Now, average velocity = =u+v/2 (i)
Again ,distance covered =average velocity× time taken(t)
Suppose here ,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =S
Now average velocity ==u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average velocity ×time(t)
Or S = u+v/2×t (i)
Putting the value of v at equation (i)
Or S=(u+v+at/2) ×t ( we know that v=u +at )
Or S =(2u+at/2) ×t
Or S = (2u/2+at/2)×t
Or S =ut + at2/2
Suppose here,
Initial velocity of a body =u
Final velocity =v
Time taken =t
and distance covered =s
Now average velocity = u+v/2
Again ,distance covered (s)=average velocity ×time taken(t)
Or S = u+v/2×t (i)
Putting the value of t at equation (i)
Or S = u+v/2 × v-u/a ( we know that t = v-u/a)
Or S = v2-u2/2a
Or v2 –u2 =2as
Questions for Practice
Unit - 2 (Velocity and acceleration)
Questions Based on Knowledge (K)
1.
What is velocity ? Write its SI unit.
2.What
is average velocity?
3.What
is relative velocity?
4.What
is relative point ?
5.Define
acceleration.
6.What
is retardation ? Write its SI unit.
7.
What is meant by uniform motion ? Write with an example. Write down SI unit of
retardation.
Questions Based on Understanding (U)
8.Write
any two differences between acceleration and retardation.
9.Reference
point is required to calculate relative velocity, why?
10.Write
any two differences between vector quantity and scalar quantity.
11.The
object having uniform velocity has zero acceleration, why
12.Why
are velocity and acceleration called vector quantities? Questions Based on Ability (A)
13.Describe
relative motion with an example.
14.What
is meant by non-uniform motion ? Write with figure. which condition does
relative velocity become zero? Why
15.Write
down the interrelationship between distance covered, initial velocity and time
taken by a moving body.
Questions Based on Higher Ability (HA)
16.A
motorcycle covers a distance of 1.5 km in 1 minute and 5 km in 4 minutes.
Calculate the average velocity of the motorcycle.
(Ans:
21.66 m/s)
17. The mass of a stone is 2 kg. If it takes 6
seconds to reach the maximum height, calculate the initial velocity.
(Ans: 58.8 m/s)
18.A
bus is moving with the velocity of 60 km/h. By seeing a baby 11m ahead the
driver applied the brakes and the retardation produced is 13.88m/s“. Calculate
the distance covered by the bus and time taken to stop the bus.
(Ans:
9.99m, 1.2s)
Unit -
Test
Unit 2: गति र प्रवेग(Velocity and Acceleration)
Time: 36 min. F.M.: 20
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the
questions.)
1.a)What
type of object is called the object in motion ? Give one example of object in
motion. (2)
b)What
is the acceleration of a body moving with uniform velocity ? A bicycle cover a
distance of 15 metre in 5 seconds and 40 metre in 15 seconds. Calculate the
average velocity of the bicycle.(1+2)
2.(a)Write
any two differences between accleration and retardation. (2)
b)
A car is moving towards east with the velocity of 20 m/s and another is moving
towards west with the velocity of 15 m/s. If those cars start to move
simultaneously from the same place, calculate the distance covered by them in 2
minutes. Also, calculate the distance between them. (3) (Ans: 2400 m पूर्व, 1800 m पश्चिम)
3.a) Prove that: v2 = u- +2as ( 3)
(b) A car is moving with the velocity of 25
m/s. If the car comes to rest after 5
seconds, what is its retardation ? (2)
(Ans: 5 m/s)
4.
(a) Write down the formula to calculate the relative velocity of two vehicles
moving towards the same direction. Write any two differences between vector
quantity and scalar quantity. (1+2)
(b)
How much retardation should be produced to stop a truck moving with the
velocity of 72 km/h in 5 seconds? Calculate the distance covered by the truck
within that time. (Ans: 4m/s', 50 m)
(2)
The End
Unit -3
Machine
Machine : The instruments that make our work easier ,faster and more convenient are known as machine . They are 2 types :
1.)Complex machine :The instruments whose structure are very complex and make our work easier ,faster, and more convenient are known as complex machine .For example : Fan, bicycle, bus ,truck etc.
2.)simple machine : The instruments which is very simple in structure and make our work easier ,faster and more convenient are known as simple machine .For example : scissor ,beam balance, bottle opener etc.
Advantages of simple machine :
i)It increase the rate of doing work .
ii)It multiplies the applied force .
iii)It help to change the direction of force .i.e Pulley
iv)It helps to do our work safe .
v)It help to transfer force from one point to another point.
Some terminology related to simple machine :
Effort: The force applied in the simple machine in order to do useful work is called effort .It is denoted by E and S.I. unit is Newton(N).
Load:-The force exerted by machine on the resistance after application of effort is called load .It is denoted by L and S.I. unit is Newton(N).
Fulcrum :The fixed point or axis of simple machine that help to move or rotates freely the machine is called fulcrum .
Load distance and effort distance : The distance covered by load is called load distance .It is denoted by L.d. and S.I. unit is metre (m)
The distance travelled by effort while moving the effort is called effort distance .It is denoted by L.d. and S.I. unit is metre(m).
Input work :The work done by applied force on the machine is called input work .It S.I. unit is Joule (J) .It is always more than that of out put work because it is not affected by friction .
Input work =Effort ×Effort distance
Out put work =The work done by machine on the load is called out put work (useful work).It S.I. unit is Joule (J). It is always less than that of input work ,because it is affected by friction .
Out put work =Load ×Load distance
Mechanical advantage :-The ratio of load to the applied effort is called mechanical advantage .It have no unit .It measures the times by which a machine multiplies the effort. It is denoted by MA. It is always less than that of velocity ratio because it is affected by friction.
Mechanical advantage (MA) =Load/Effort
1.)The mechanical advantage of simple machine is 5 .What does it mean ?
Ans. It means that work become 5 times easier if machine is used .
Velocity ratio :-The ratio of distance moved by effort to the distance moved by load is known as velocity ratio .It have no unit .It measure the extent to which the speed of doing work increases by using the machine .It is always more than that of mechanical advantage because it is not effected by friction .
Velocity ratio (V.R.)= distance covered by effort /distance covered by load
1.)The velocity ratio of simple machine is 5 .what does it mean ?
Ans. It means that the distance covered by effort is 5 times more than that of distance covered by load .
Efficiency :-The percentage ratio of output work to the to the input work is known as efficiency . or
The percentage ratio of mechanical to velocity ratio is known as efficiency .It is affected by friction so it is always less than that of 100%.It can be increased by applying grease or oil between the movable part of a machine ,by making smooth surface ,by using ball bearing wheelers and rollers .
Efficiency (
Efficiency (
Factors affecting efficiency :
i)Frictional force
ii)Gravitational force
iii)Weight of machine
Perfect or ideal machine :-The theoretical machines whose efficiency is 100% are called perfect machine or ideal machine In ideal machine .There are not wastages of input work due to friction .In ideal machine
Out put work = in put work
Real machine or practical machine :-The machine in which efficiency is always less than that of 100% or out put work is always less than that of input work is called real or practical machine .
Principle of simple machine :-It states that if there is no friction in simple machine output work is always equal to input work in the simple machine .
Output work = Input work
L×L d = E × E d
1.)A machine has 70% efficiency .what does this means ?
Ans. It means that 70% input work is converted into out put work and remaining 30% of input work is wasted due to friction in the machine .
Types of simple machine :- There are 6 types of simple machine :
1)Lever 2)pulley 3) Wheel and axle 4) Inclined plane 5)Screw 6) Wedge
1)Lever : A rigid bar or straight rod which can move freely around a fixed i.e. fulcrum is known as lever . The velocity ratio of lever can be increased by reducing load distance . They are 3 types .
i)First class of liver :-for example : Beam balance , scissors , sea saw
ii)Second class of lever :For example :Bottle opener ,wheel barrow Lemon squeezer ,nut cracker etc.
iii)Third class of lever :For example : Fishing rod , Sugar tongs ,broom forceps, hair plucker etc.
Principle of lever :- in balanced condition the product of load and load arm is equal to the product of effort and effort arm is known as the principle of lever .
Load ×load arm =Effort ×Effort arm
Unit 3: यन्त्र(Machine)
Questions Based on Knowledge (K)
1.Write any two characteristics of
simple machine.
2. What is lever? Write down the
working principle of lever.
3.What is meant by the saying that the
velocity ratio of a simple machine is 3 ?
4.What is fulcrum ?
5.What is meant by the saying that the
mechanical advantage of a machine is 2
6.What is mechanical advantage
7.Define
efficiency.
Questions Based on Understanding (U)
8.The cutting edges of metal-cutting
scissors are made shorter but those of cloth-cutting scissors are made longer,
why?
9.It is easier to lift a load when
shifted towards wheel in a wheel barrow, why?
10.Write any two differences between
Velocity ratio and Efficiency.
11. It is impossible to get a perfect
machine in practical life, why?
Questions Based on Higher Ability (H)
12. Draw a neat
and labeled figure showing various parts of a typical lever
13.Write down the formula to calculate
mechanical advantage and efficiency.
14.Simple machines are widely used in
our daily life. Write down its reason. Write any three advantages of using
simple machines.
15.Ram of weight 500 N and Shyam of
weight 400 N are playing see-saw. If Ram is playing 1.5 m away from the
fulcrum, how far should Shyam sit from the fulcrum to balance Ram? (Ans: 1.87m
16.A load of 600 N is lifted using a
lever of 4 m by applying an effort of 200 N. If load distance is 1 m, calculate
mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of the lever.
(Ans: MA = 3, VR=4, n= 75%)
Unit - Test
Unit 3: यन्त्र(Machine)
Time: 36 min. F.M.: 20
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the
questions.)
1. (a) Define
simple machine with any two examples. What is called the ratio between effort
distance and load distance?(2+1)
(b)If the
load distance of a lever is 30 cm and effort distance is 60 cm, calculate the
amount of effort required to lift a load of 200 N. (2) (Ans: 100N)
2. (a) Write
any two differences between mechanical advantage and velocity ratio. (2)
b)What is
the meaning of the saying that the efficiency of a lever is 90% ? Ram of weight
500 N and Shyam of weight 400 N are playing see-saw. If Ram is playing 1.5 m
away from the fulcrum, how far should Shyam sit from the fulcrum to balance
Ram? (1+2) (Ans:
1.87 m)
3. (a) What is
efficienty of a simple machine? The cutting edges of metal-cutting scissors are made shorter but those of cloth-cutting scissors are made
longer. Why? (1+2)
(b) In
a simple machine, if the load distance is 20 cm and effort distance is 60 cm
calculate the velocity ratio. (2)
(Ans: 3)
4. (a)What is meant by the saying that the mechanical advantage of a
machine is 2? It is easier to
lift a load when shifted towards wheel in a wheel barrow. Why? (1+2)
(b) The
mechanical advantage of a simple machine is 2 and its velocity ratio is 3.
Calculate the efficiency of the machine. (2) (Ans: 66.66%)
The End
Pressure
Pressure:-The force acting normally on per unit area is called pressure .Its S.I. unit Pascal or N/m2.It is a scalar quantity.
Pressure (P)= Force(F)/Area(A)
P = F/ A
Difference between force and pressure
Force | Pressure |
1.)A physical quantity that change the state of an object. ii) its S.I. unit N iii) It is a vector quantity. iv) Force(F) =mass ×acceleration(a) or acceleration due to gravity(g) F =m× a or g | 1.)The force acting normally on per unit area is called pressure . ii) Its S.I. unit is pascal. iii) It is a scalar quantity. iv) Pressure (P)= Force(F)/Area(A) P = F/A |
1.)A man exerts more pressure when he stand with one foot than when he stand on two foots, why ?
Ans. The area of one foot is less than that of two foots so a man exert more pressure he stand with two foots than with one foot ,because we know that
P∞1/A .
2.)Basses and truck have broad and double wheeled tyeres, why?
Ans. The areas of broad or doubled tyeres is more so give more less pressure on road and easily can carry heavy load .Therefore busses and trucks have broad and doubled tieres, because we know that P∞1/A
3.The studs are made on the sole of football player’s boot ,why?
Ans. The studs of sole on the football players boot reduce the area of sole and give more pressure on the ground ,which prevent the player from falling and sliding .Therefore studs are made on the sole of football player’s boot, because we know that P∞1/A.
Liquid pressure:- The thrust exerted by a liquid per unit area is called liquid pressure .Its S.I. unit Pascal or N/m2.
Liquid Pressure (P) = d×g×h
Where d= density of liquid ,g = acceleration due to gravity , h = depth of liquid
Factor affecting liquid pressure:-
i)density of liquid(d)
ii)Acceleration due to gravity (g)
iii)depth of liquid (h)
General laws of liquids pressure:-
i)The pressure of liquid is directly proportional to the depth of liquid. P∞h
ii)At the same depth the pressure of the liquid is same in all direction .
iii)Pressure of liquid is directly proportional to density of liquid . P∞d
iv)The pressure of liquid does depend upon the shape and size of container .
v) The liquid finds its own level .
Prove that P=d×g×h
According to definition of pressure
P =F/A
Or P =m×g/ A ( F=mg )
Or P = d×v×g/ A (m=d×v)
Or P = d×g×A×h/ A (V =A xh)
1.)The speed of flow of water out of a tap of up floor is less than that of the down floor ,why ?
Ans. The depth of liquid column of down floor is more than that of up floor. Therefore speed of flow of water is more at tap of down floor than that of tap of up floor, because we know that P∞d .
2.)While the building a dam for water reservoir the base is made wide, why ?
Ans. The depth liquid column of base of dam of water reservoir is more than that of upper portion,so base liquid column give more upthrust than that of upper portion. Therefore base of dam of water reservoir is made wide .because we know that p∞h
3) On which factors does the pressure of liquid depend ?
Ans. The liquid pressure depend on following factors ie i) density of liquid(d) ii)Acceleration due to gravity(g) iii) depth of liquid(h)
Density :-Mass per unit volume is called density. Its S.I. unit is kg/m3 and C.G.S. unit is gm/cm3.
Density (d)= Mass(m)/Volume(v)
D = m
Example:- density of water =1000kg/m3 or 1gm/cm3
i)Convert 1000kg /m3 into gm/cm3
= 1000 ×1000 / 100×100×100
= 1gm/cm3
ii)Convert 1gm/cm3 into kg/m3
= 1×100×100×100/ 1000
=1000kg/m3
Relation between density of a body and floatation:-
i)When the density of an object is greater than that of density liquid then sink in the object.
ii)When the density of an object is less than that of density of the liquid then object float on the liquid .
iii)When the density of an object is equal to the density of the liquid then the object floats just inside the surface of the liquid.
Relative density :-(R.D.):-The ratio of the density of the substance to the density of the water at 4
Relative density (R.D.) =Density of the substance / Density of substance at 4
Atmospheric pressure:-The pressure exerted by atmospheric air per unit area on surface of earth is called atmospheric pressure. The weight of air itself is the cause of atmospheric pressure. Its S.I. unit is N/m2 or mmHg(millimeter mercury) and measured by help of Barometer.
Barometer .The atmospheric pressure at sea level i.e. 5N/m2 or 760mmHg, is also called standard atmospheric pressure.
Atmospheric pressure(p) = d×g×h Where d=density of air g= Acceleration due to gravity ,h=depth of air
Air pressure :-The pressure exerted by gas per unit area enclosed in vessel i.e. balloon, is called air pressure .
Uses of atmospherics pressure:-
1)It help for movement of air due to change in atmosphere .
2)We can fill ink inside pen ,medicine inside syringe ,air inside tube of bus ,car bike etc.
3)Water pump work by help of atmospheric pressure .
1.)When we go to higher altitude ,nose bleeding occurs ,why?
Ans. When we go to higher altitude depth of atmosphere decreases, so human blood pressure become more than that of atmospheric pressure due this blood vessel present inside nose ,ear feel more pressure and rupture .Therefore, when we go to higher altitude bleeding occurs .
2.)A air filled balloon at higher altitude brusts ,why ?
Ans. In air filled balloon at higher altitude ,the atmospheric pressure become less than that of air pressure inside balloon, so air filled balloon at higher altitude brusts ,because we know that atmospheric pressure decreases due increase of height .
Unit-
4 Pressure
Questions Based on Knowledge (K)
1.What is pressure ?
Write its SI unit.
2.Define atmospheric
pressure.
3.What is liquid
pressure?
4 Write two
characteristics of liquid.
5.What is relative
density ? Write down the formula to calculate the relative density.
6.What is the density
of a substance ? Write down the SI unit of density.
7.What is the value of
atmospheric pressure at sea level ?
(Ans: 760 mmHg)
8.Write down the
formula to calculate density of an object.
Questions
Based on Understanding (U)
9.Write any two
differences between Force and Pressure.
10.A tin can sinks
when it is heated with a lid closed and then poured cold water in it. Why?
11.The speed of water
at the tap of lower storey is more than that in the upper storey. Why?
12.The density of sand
is more than that of wood. Why?
13.Write any two
differences between Mass and Volume.
Questions Based on Ability
(A)
14.How is the density
of sand calcualted by using water ? Describe in brief.
a)How is it possible to fill medicine in a syringe ? Write.
b) A piece of plastic floats on water but a piece
of iron sinks. Why?
15.a) Why does air
blow from one place to another place.
b) Write
down the importance of atmospheric pressure.
Questions Based on Higher Ability (HA)
16.Describe an
experiment with a labelled figure to demostrate that liquid exerts pressure perpendicularly in all directions.
17. In a drum, a liquid of 2 m depth exerts a
pressure of 29400 Pa. If the value of acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2.
Calculate the density of the liquid.(Ans: 1500 kg/m')
18.The density of gold
is 19200 kg/m' and that of water is 1000 kg/m'. Calculate the relative density.(Ans: 19.2)
Unit - Test
Unit 4:(Pressure)
Time: 36 min. F.M.: 20
सबै प्रश्नहरूको उत्तर दिनुहोस् । (Answer all the questions.) MMM
1.a)What is pressure ? Write its SI unit.
Write down the formula to calculate liquid pressure. (2+1)
b)The weight of a body is 600 N and its
base area is 2 m2. Calculate the pressure exerted by the body on the ground. (2) (Ans: 300 Pa)
2.a) Why
does air blow from one place to another ? Write any two differences between
force and pressure. (1+2)
b.)Calculate the pressure exerted by
liquid at the bottom. (Ans: 29400 Pa)
3.a)Write down the formula to calculate the
density of a substance. A tin can sinks when it is heated with a lid closed and
then poured cold water in it. Why? (1+2)
b)The
mass of an ice block is 500 kg and its density of 920 kg/m'. Calculate the
volume of the ice block. (Ans: 0.543 m')
4.a)What
is relative density ? The speed of water at the tap of lower storey is more
than that in the upper storey. Why? (1+2)
b.)The density of wood is 800 kg/m' and
density of water is 1000 kg/m'. Calculate the relative density. (2) (Ans: 0.8)
The End
Work :The product of force and displacement of a body in the direction of applied force is called work .Its S.I: unit is Juole (J) C.G.S. unit is erg(dynes cm) .It is a scalar quantity .
Work(w) = Force (F) ×Displacement(d)
Or W = F × d
Relation between Joule and erg :
Juole =Nm
1 Juole work :-When an object is displaced through a distance of one metre by applying one Newton force is known as 1 Juole work .
1 Juole work = 1N × 1m
Types of work :- They are two types :-
i)Work done against friction :-If a work is done by pulling or pushing an object horizontally on the earth’s surface ,the done is called work against friction .For example : Sliding a box n the ground , pushing a cart on the road, close or open the door etc.
Work against friction (w) =F× d
ii)Work against the gravity :-If a work is done by lifting a body vertically upward from the earth’s surface ,the work done is called work against gravity .For example :Water is pulled from well, A load is lifted by crane etc.
Work against gravity (W)= m×g×h
Where m=mass of an object , g = acceleration due to gravity ,h =height of object
Energy :-The capacity of doing work is called energy .Its S.I. unit is Juole and C.G.S. unit is erg .
The total amount of consumed energy = Total amount of work done
Types of energy :-There are various form of energy .Some of them major form of energy are :
i)Mechanical energy a)Kinetic energy b)Potential energy
ii)Chemical energy iii)Electrical energy
iv)Heat energy v)Light energy
vi)Sound energy vii)Magnetic energy
viii)Atomic energy
i)Mechanical energy :The energy possessed by the bodies due to their position or configuration or motion is called mechanical energy .It is two types :
a)Kinetic energy :The energy possessed by body due to result of motion of object is called kinetic energy .For example .Moving bullets ,running water, moving buses etc.
Kinetic energy (K.E.) = 1/2 mv2
Where m= mass of object , v = velocity of a body
b)Potential energy : The energy possessed by the bodies due to its position or change in its shape is called potential energy .For example :Energy possessed by the compressed spring ,energy possessed by a stone kept on the roof ,Water stored in dam, foot lifted to kick a football etc .
Potential energy (P.E.)= m×g×h
Where m= mass of an object, g=acceleration due to gravity , h=height of height
ii) Electrical energy :The energy possessed by the object due flow of electron is called electrical energy .For example Telephone ,radio, television ,heater etc.are operated by electrical energy .
iii) Heat energy :The energy possessed by the object due to the sum total kinetic energy of an object is called heat energy .for example :The heat is used to cook food, boil water,run steam engine
iv)Light energy :-The energy possessed by the object due to extremely hot by radiation is called light energy .for example :It help us to sensation of vision ,preparation of food to plant ,to increase rate of chemical reaction etc .
v)Sound energy :-The energy possessed by the bodies due to vibration of body is called sound energy .For example :It help us for sensation of hearing ,to form electrical bell ,etc.
vi)Magnetic energy : The energy possessed by the magnet is called magnetic energy .For example: Electric bell, television, loudspeaker etc are operated by using magnetic energy .
vii)Chemical energy :The energy which can be obtained from chemicals, foods, and chemical reaction is called chemical energy .For example: for example :Enegy contained in battery ,bread ,coal ,petrol etc.
viii)Nuclear energy or atomic energy :The energy obtained from atomic reaction or nucleus of atom or nuclear reaction is called Nuclear energy .For example: The energy released during the explosion of atom bomb or hydrogen bomb etc.
Transformation of energy :-The process of conversion of one form energy into another types of energy is known as transformation of energy.
ii)Electric motor = Electrical energy ⟶ Kinetic energy
iii)
Dynamo =Kinetic energy ⟶ Electrical energy
iv)Microphone =Sound energy ⟶ Electrical energy
v)Headphone =Electrical energy ⟶ Sound energy
vi)Hydropower station =Potential energy ⟶ Kinetic energy ⟶ electrical energy
vii)Steam engine =Heat energy ⟶ Kinetic energy
viii)Solar battery = light energy ⟶ Electrical energy
ix)Battery = chemical energy ⟶ electrical energy
1.)Name the devices which changes
i)Chemical energy into electrical energy =A battery or cell
ii)Chemical energy into heat energy = A kerosene heater
iii) mechanical energy into electrical energy =A dynamo or generator
iv)Light energy into electrical energy =Solar panel
v)Sound energy into electrical energy = A microphone
vi)Electrical energy into mechanical energy =A electrical motor
vii)Solar energy into electrical energy = Solar battery
viii)Electrical energy into light energy = Electrical bulb
2.) What kinds of energy is possessed by the following .
i)A compressed spring = potential energy
ii)Water in a river = Kinetic energy
iii)A stretched rubber or catapult = Potential energy
iv) A red hot iron ball = heat and electro magnetic energy
v)cell or battery = Chemical energy
vi)The food we eat = chemical energy
Vii) The sun light = Heat and light energy (Electro magnetic energy )
Viii) A magnetic field = Magnetic energy
ix) A man climbing a hill = Potential and kinetic energy
x) A flying bird = Potential and kinetic energy
Power :- The rate of doing work is called power . Its S.I. unit is Watt (J/S) .It is scalar quantity .
Power (P) = work(w)/time taken (t)
Or
P= w/t
One watt power :- When one joule work done in one second ,the power is one watt power .
Or
The rate of doing one joule work in one second time is called one watt power .
Horse power (H.P.) : The unit which is to measure the the power of engines is called horse power .It is denoted by H.P.
1 H.P. = 746 watt
Relation between Energy, Work and Power:
Energy provides capacity of doing work, and the rate of doing work is power therefore Energy ,Work and power are inter related with each other .
Unit :- 6 Heat
Heat: The sum of kinetic energy of molecules of an object is called heat . Its S.I. unit is joule and C.G.S. unit is calorie and measured by calorimeter .It is transmitted from one place to another place. The quantity of heat present in an object depend on following two factors : i) Number of molecules ii) Kinetic energy of molecules.
1 calorie = 4.2 joules
Effects of heat : following are the effect of heat .
i)It change the state of matter .
ii)It change the temperature of an object .
iii)It change the size or volume of an object .
iv)It change the solubility of the substance .
v)It is the cause of chemical change in an object
Temperature :- The average kinetic energy of molecules of an object is called temperature .Its S.I. unit is is Kelvin (K) and measured by thermometer .It is not transmitted from one place to another place .
The temperature of an object depends directly on the average kinetic energy molecules .
Thermometer :- The instruments which is used to measure temperature is called thermometer.
Structure of thermometer :-
It consist of long glass tube having a fine capillary tube. The lower end of glass tube consist of
a bulb contains mercury or alcohol as thermometric
liquid .Its outer body consist of a scale is called thermo-metric scale .
On the basis of liquid filled inside bulb ,there are two types of
thermometer :
1)Mercury thermometer
2)Alcohol thermometer
Principle of thermometer :- The volume of liquid expands on
heating and contract on cooling is know as principle of thermometer .
Thermometric liquid :-The liquids which is filled in the bulb of thermometer to
measure temperature are called thermo metrics liquid .They are :
1)Mercury :- Causes used as thermo metric liquid :-
i)Mercury
is good conductor of heat .
ii)It
is shiny and opaque .
iii)It
is does not stick to the inner wall of capillary tube .
vi)The
freezing point of mercury is -39℃
2)Alcohol:- Causes used as thermo metric liquid :-
i)It
Is good conductor of heat .
ii)
It is does not stick to the inner wall of capillary tube .
iii)
It is cheaper than that of mercury .
iv)Its expansion rate is
six times more than that of mercury .v) vi)The freezing point of alcohol is -117℃
Calibration of thermometer :The graduation of
number in thermometer between the lower and upper fixed point is called the
calibration of the thermometer .The determination of upper and lower fixed point are required for
calibration of thermometer .
1)Determination of upper fixed
point :For
determination of upper fixed point a round bottom flask is taken with some
water and heated .Then bulb of thermometer is kept in round bottom flask with
help of glass tube .The bulb of thermometer should not be touched The level of
mercury or alcohol of thermometer increases due to heat and finally
become constant at fixed point is called upper point or boiling point of of water i.e.100℃ or 212℉
Types of thermometer :
There
are different types of thermometer :
1)Clinical thermometer :- A thermometer that is used to measure temperature of body is called is clinical
thermometer .The normal temperature of human body is 37℃ or 98.6
Construction :-It consist of two parts ie. Bulb and stem .The bulb is thin walled and filled with mercury .The stem is long and prismatic structure having capillary tube that help to magnify image of capillary tube and make bulb is called constriction that help to prevent back flow of raised mercury level .The stem of thermometer is calibrated with scale ie. 35℃ to 42℃ in Celsius scale and 94℉ to 108℉in Fahrenheit scale.
2)Laboratory thermometer or Ordinary thermometer :-The thermometer that is in lab. to measure temperature of materials is called is laboratory thermometer .Its bulb is filled with mercury or alcohol .It has temperature range from -10℃ to 110℃
3)Maximum-minimum thermometer :- A thermometer that is used to measure maximum –minimum temperature of 24 hours of certain place is known as maximum- minimum thermometer .
Construction:- It consist of U shaped glass tube
having bulb on their end .One side measure minimum
temperature filled with alcohol and other
side filled partially alcohol and mercury measure maximum
temperature .It consist of two metal index
at two side of tube that indicates max-min temperature .
Temperature scale :-There are 3 major types of temperature scale :
i)Celsius Scale or Degree centigrade scale(℃
ii)Degree Fahrenheit cale (℉
3)Kelvin scale :-The scale in which lower fixed point is 273K and upper fixed is 373K is
called Kelvin scale . In this scale the range between two points is divided into 100 equal parts and in Kelvin scale water freeze into ice at
273K and boil at 373 K.
The relation between different temperature scales :-
=C-0 /100 = F-32/180=K-273/100
Given
,
C=47
F=?
i)From relation between
centigrade and Fahrenheit
or
=C-0
/100 = F-32/180
or
47-0/100=F-32/180
or 100F
-32x100 =47x180
or 100F-3200
=8460
or 100F
=8460+3200
or 100F
=11660
or F
=11660/100
or F= 116.6
Therefore 47
Light: A form of energy which affects our eyes to produce the sensation of vision is called light .It is emitted from very hot objects in the from of radiation .
Types of object : On the basis of light they are two types :
Luminous object :-The object which can emit the light by themselves are called luminous object .For example :Sun ,Burning candle, Electric lamp e.tc.
Non luminous object :The object which do not produce or emit light themselves are called Non luminous object .For example :Moon , Earth ,Book, etc.
Ray of light :-A smallest path along which light energy travel in a given direction is called ray of light .It is represented by an arrowhead on straight line in which arrowhead gives the direction of propagation of light .
Beam of light :The collection of the several rays of light forming a certain pattern is called beam of light .They are 3 types :
i)Parallel beam of light :The beam of light in which all the rays are parallel to each other is called parallel beam of light .
ii)Convergent beam :The beam of light in which the rays of light meet at a point is called convergent beam .
iii)Divergent beam :The beam of light in which the rays of light scatter from a point is called a divergent beam .
Mirror:-An smooth surface which form an image due to reflection of light is called mirror .They are two types :
1)Plane mirror :The mirror which reflection of light occurs on smooth and flat surface is called plane mirror. It form virtual and erect image but laterally inverted and equal in size as that of object .
Lateral inversion : The process in which the left side of image is formed on the right side and right side of on the left side is called lateral inversion .
Uses of plane mirror :
i)It is used to see our face .
ii)It is used to make telescope and periscope .
iii)It is used in lab for various purpose .
2)Spherical mirror :-The mirror which reflection occurs on spherical and surface is called spherical mirror .They are two types :
i)Concave mirror | ii)Convex mirror |
i) ii)The mirror in which reflecting surface is curved inside and outside is silvered is called concave mirror . iii)It diverge the rays of light after reflection so it is called diverging mirror . | i) ii)The mirror which reflecting surface is curved outside and outside is silvered is called convex mirror . ii)It converge the rays of light after reflection so it is called converging mirror . |
Image :When the rays of light coming from object falls on mirror after reflection form a picture is called image .They are two types :
i)Real image | ii)Vertual image |
i)The image which can be obtained on screen is called real image . ii)It is always inverted and image is formed front of mirror . | i)The image which cannot be obtained on the screen is called virtual image . ii)It is always erect and image is formed behind the mirror . |
Parts of mirror :-
i)Principal axis :The line passing through pole of the mirror is called principle axis .It is denoted by P.
ii)Pole of the mirror :The central point of spherical mirror is pole of spherical mirror .It is denoted by P .In the mirror the distance are measured from pole .
iii)Principle focus: The point at which the rays of light converge or diverge after reflection is called principle focus .It is denoted by F.
iv)Focal length :The distance between the focus and poleof the mirror is called focal length .It is denoted by f .
v)Centre of curvature :The centre of that sphere of which the mirror forms a part is called centre of curvature .It is denoted by C .
Rules of drawing ray diagram in concave a mirror:
i)A ray of light parallel to the principle axis passes through the principle focus after reflection .
ii)A ray of light passing through the principle focus passes parallel to the principle axis after reflection .
iii)A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature pass along the same path after reflection .
Position and nature of image formed by concave mirror when object is kept at different position .
S.N. | Position of object | Position of image formed | Nature of image formed |
1
2
3
4
5
6 | At C or 2F
Beyond C
Between F and C At F
At infinity (∞) Between F and P | At C or 2F
Between F and C Beyond C
At infinity (∞) At F
Behind the mirror | Real ,inverted,and the same size Real, inverted, and smaller
Real ,inverted ,larger
Real,inverted,larger
Real ,invrted,smaller
Virtual ,erect and larger |
1.)Draw neat and labeled ray diagram showing the image and also write down the characteristics or nature of the image formed by the concave mirror .When object is placed
i)At C
Nature
i)The image is formed at C
ii)Image is real and inverted .
iii)The size of image is equal to the same size of the object .
ii)Beyond C
Nature
i)The image is formed between F and C
ii)Image is real and inverted .
iii)The size of image is smaller than that of the object .
iii)Between F and C
i)The is formed beyond C
ii) Image is real and inverted .
iii)The size of image is larger than that of object .
iv)At F
i)The image is formed at infinity .
ii)Image is real and inverted .
v)At infinity ( ∞ )
Nature
i)The image is formed at F
ii)Image is real and inverted .
iii)The size of image is smaller than that of object .
vi) Between F Focus ) and P (pole)
Nature
i)The image is formed behind the mirror .
ii)image is virtual and erect .
iii)The size of image is larger than that of object .
Rules for drawing ray diagram in a convex mirror .
i)A ray of light passing parallel to the principle axis appear to diverge from the principle focus
ii) A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature pass along the same path after reflection .
iii)A ray of coming from an object which strikes the pole of the mirror at certain angle ,reflect at the same angle .
Position and nature of image formed by convex mirror when object is kept at different position .
S.N. | Position of the object | Position of image formed | Nature of image formed . |
1 | At infinity ( ∞) | At F behind mirror | Virtual ,erect, and smaller |
2 3 4
5 6 | At C Beyond C Between F and C At F Between F (Focus) and p (pole) | Between P and F (behind the mirror .)
Between P and F (behind the mirror .) | Virtual ,erect and smaller
|
2.)Draw neat and labeled ray diagram showing the image and also write down the characteristics or nature of the image formed by the convex mirror .When object is placed
i)At infinity ( ∞ )
Nature
i)The image is formed at F behind the mirror .
ii)Image is virtual and erect .
iii)The size of image is smaller than that of object .
ii)At C
i)The image is formed between F and P behind the mirror .
ii)The image virtual and erect .
iii)The size of image smaller than that of object .
ii)Beyond C
i)The image is formed between F and P behind the mirror .
ii)The image virtual and erect .
iii)The size of image smaller than that of object .
Uses of concave mirror
i)It is used for making reflection of torch light and headlight of vehicles .
ii)It is used for saving and making cosmetic mirror.
iii)It is used for reflector of telescope .
iv) It is used for observing internal body organ .
Uses of convex mirror
i)it is used for making street light reflector to spread light in wider region .
ii)It is used for making view mirror in automobiles to view wide field .
Refraction of light : The bending of light from its original path when passing from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light .
Causes of refraction
The change in the velocity of light on going from one medium from another medium is causes of refraction of light .for example :The velocity of light in air is 3×105m/s but when it passes into water it change into 2.2×108 m/s and in glass it change into 2× 108 m/s.
Denser and rarer medium :The medium in which the velocity of light is less or having more density in comparison to given other medium is called denser medium .For example : In comparison to air and glass ,glass is denser medium to that of air
The medium in the velocity of light is more or having less density in comparison to given medium is called rarer medium .For example air is rarer medium to that of glass .
Incident ray :The path of the ray of light in the first medium is called incident ray .
Normal:-A line drawn perpendicular to the boundary surface between two media is called a normal .
Angle of incidence :-The angle which makes the incidence ray with the normal is called angle of incidence .
Refracted ray :-A ray of light which bends or deviates from its original path when passing second medium is called refracted ray .
Angle of refraction :-The angle which the refracted ray makes with the normal is called angle of refraction .
Laws of reflection of light :
1.)When the ray of light travel from rarer medium to denser medium ,it bends towards normal or i>r
2.)When the ray of light travel from denser medium to rarer medium,it bends away from the normal or i<r
3.)The incident ray ,refracted ray and the normal line in the same plane and same point .4.)The ratio of the sine angle of incidence(sine i) to the sine angle of refraction(sine r) is a constant for a given pair of media and this constant is called refractive index of the medium .It is also called Snell’s law .
1.)Why does a pond appear shallow than its actual depth ?
Ans. The ray of light coming from the bottom of pond get refracted and bend away from the normal ,when refracted rays comes in our eyes give the apparent position of the bottom of pond , therefore the pond appear shallow than its actual depth
2.)A stick partially dipped in water seems to be bent ,Why ?
Ans.

The ray of light coming from the dipped portion of stick get refracted and bends away from the normal , when refracted rays comes in our eyes give the apparent position of dipped portion of stick ,therefore stick partially dipped in water seems to be bent .
3.)A man standing in a pond sees a fish in the pond and tries to thrust a spear into it. he will succeed or not .Explain with reason .
He will not succeed , because the ray of light coming from the fish get refracted and bend away from the normal ,when refracted rays comes in our eyes give apparent position of the fish .
Sound : A form of energy which is produced by a vibrating body is called sound .It travel from one place to another place in the form of longitudinal wave .
Source of sound :The objects that produced sound are called source of sound .For example :Tuning pork ,Guitar ,Madal ,Basuri etc.
Properties of sound :
i)It is produced by a vibrating body .
ii)It requires a materials medium for propagation .It can not travel in vacuum or without medium .
iii)The speed of sound is different in different medium i.e.in solid 6000m/s in liquid 1500m/s and gas 332 m/s.
iv)It may be reflected or refracted like light .
Process of transmission of sound:-
Wave:-A periodic disturbance that carries energy away from an object through a medium during motion is called wave.
Types of wave:-There are two types waves:
1.Transverse wave
2.Longitudinal wave
1.Transverse wave :-A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate up and down perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave is called transverse wave. For example: All electromagnetic waves are transverse wave i.e. :Infra red ,Gamma ray, Ultra violet ray, light wave, wave on the surface of water.
2.Longitudinal wave:-A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate along the direction of propagation of the wave is called longitudinal wave .These waves are also called mechanical wave because they requires materials medium i.e.: solid, liquid, or gas for its propagation. For example: Sound wave, wave on stretched spring.
Compression:-In longitudinal wave the region in the space where the density of particles is high are called are called compression.
Rarefaction:-in longitudinal wave the region in the space where the density of particles is low are called rarefaction.
Wave length:-The distance between two successive compression or rarefaction is called wave length. Its S.I. unit is meter(m) &denoted by lymda(ƛ).
Frequency:-The number of complete wave produced in per second is called frequency. Its S.I. unit hertz(Hz) & denoted by f.
Wave velocity or sound velocity :The distance travelled by the sound wave in per second is sound velocity. Its S.I. unit is m/s.
Sound velocity (v)=wave length (ƛ)×frequency(f)
V=ƛ×f
Amplitude:-The maximum displacement of particles of the medium from its mean position is called amplitude. The wave of more amplitude has more energy and the wave of less amplitude has less energy.
Time period :-The time taken by a wave to travel complete one cycle or a complete wave is called time period .Its S.I. unit is second .
Time period (T)=
Reflection of sound: - The process of returning the sound in the same medium after striking in the surface is called reflection of sound.
Echo:-The repetition of sound caused due to its reflection is called on echo. . For example : Sound produced from mountains, jungle etc.
Conditions for echo:
i)The distance between source of sound and reflecting surface is more than 17 meter.
(ii)The source of sound and surface of reflection should be required .
Reverberation:-The prolongation sound by the mixing of the reflected sound with the original sound is called reverberation. For example :Sound produced from cinema hall ,New vacant room etc.
Conditions for reverberation are: (i) The distance between source of sound and reflecting surface should be less than 17 meter.
ii)The source of sound and reflection of surface should be required .
1)How can you predict if a dark room is vacant or not with the help of sound?
Ans. When we produce a sound in darkroom, if reverberation of sound is produced, then we know that the room is empty or vacant one. If no sound is reverberated or less reflection of sound is occurred, then we know that the room is not vacant
2.)Calculate the speed of a sound wave whose frequency is 15 KHZ and wave length is 0.022 metre.
Here,
Frequency (f) = 15kz = 15 x 1000 Hz
= 15000 Hz
Wavelength (a) = 0.022m
Speed of sound (v) =?
Now, We know that,
V=fx ʎ
= 0.022 x 15000 = 330m.
Hence the speed of wave is 330m.
3)Calculate the frequency of a sound wave whose speed is 350 m/s and wavelength is 35 metre.
Speed of wave (v) = 350 m/s
Wavelength (ʎ) = 35m
Frequency (f) =?
Now,
We know that, V=f x ʎ
Or 350 =f x35
Or f = 350/35 =10
Hence the frequency of a sound wave is 10Hz.
4)A person makes sound facing his mouth towards water of well and hears echo il 0.5 sec. Find the distance between the man and level of water.
Here, Time (t) = 0.5 sec. =0.5/2 =0.25m
Velocity (v) = 332 m/s
We know that
V =S/t
Or 332 =S/0.25
Or S =332 x0.25
Or S =83 m
Required distance =83 m
5)If a ship receives the echo sound 4 seconds after it is transmitted. What is the d. of the sea? The speed of sound in water is 1500m/S.
As given in question;
Velocity of sound (v) = 1500m/s
Time taken (t) = 4 sec. =4/2 =2 sec
Depth of sea (d) =?.
Using formula;
V= s/t
Or 1500=S/ 2
Or S=1500 x2
Or S =3000
. Hence, the depth of the sea is 3000 metere
Unit -9 Magnetism
.
Magnet : The substance which has ability to attract magnetic substance towards its is called magnet .
Types of magnet : They are 2 types :
1.Natural magnet : Naturally produced magnet are called natural magnet .For example : Lodstone ,Magnetites etc.
2. Artificial magnet :Man made magnet are called artificial magnet . For example : Bar magnet
Fig .Natural magnet (Load stone)
Magnetic substance :The substance which are attracted by magnet are called magnetic substance .For example :Iron (Soft magnetic substance ),cobalt , Nickel etc.
Magnetic substances are classified into three types :
i)Diamagnetic materials : The materials which are repelled by a magnet such as zinc. mercury, lead, sulfur, copper, silver, bismuth, wood etc., are known as diamagnetic materials
ii)Paramagnetic materials:The materials which are not strongly attracted to a magnet are known as paramagnetic material. For example: aluminium, tin magnesium etc.
iii)Ferromagnetic materials :The materials which are strongly attracted by a magnetic field or magnet is known as ferromagnetic material for eg: iron, steel , nickel, cobalt etc.
Properties of magnet :
i.)If a magnet is freely suspended ,it always points in North (N) and south (S) direction .
ii.)Like poles of magnet are repel each other and unlike poles of magnet attract each other.
iii.)A magnet has two poles i.e N and S poles .
iv) A magnetic materials gets magnetized due to presence of a magnet is called magnetic induction .
Magnetism :The property of magnet due which it attract magnetic substance is called magnetism .
Some terms related to magnet :
i)Magnetic poles :The two ends of a magnet where most of its magnetic power is concentrated are called magnetic poles .i.e. South pole (S) and North pole (N)
ii)Magnetic axis: An imaginary line joining the magnetic north and south poles of magnet is called magnetic axis.
iii)Magnetic length :The distance between one of the magnetic poles and the centre of the magnetic length is called magnetic length .
iv)Magnetic force :The force by which magnet attract magnetic substances is called magnetic force .
v)Magnetic field : The space around a magnet up to which it can attract or influences the magnet substance is called magnetic field .
vi)Magnetic lines of force: The curved lines of force are originated from N pole and terminate at S pole are called magnetic lines of force .
Properties of magnetic lines :
i.)They start from N- pole and end on S- pole of magnet .
ii.) They never intersect each other .
iii) They are closed and continuous curve .
Terrestrial magnetism : The magnetic properties of earth is terrestrial magnetism .
Molecular magnet :Each molecule of magnet or magnetic substances is an independent magnet ,which is called molecular magnet.
Molecular theory of magnetism: It state that , if molecular magnet are kept in row then the magnetic substance exhibit magnetic property but if they are kept haphazardly ,they do not exhibit magnetic property .
Fig. Magnetic substance Fig.magnet
Supporting evidences of molecular theory :
i)A magnet can be broken in small pieces each of which is a magnet .
ii)An iron can be changed into magnet by magnetized .
iii)A magnet gets demagnetized when it is hammered or heated .
iv)Two poles of magnet are equal in strength ,due free north and south poles .
Magnetic induction :The process by which a magnetic substances develops magnetic properties when it is kept near a magnet is called magnetic induction .
Magnetization: The process of make magnet is called magnetization .
Demagnetization :The process of losing magnetic property by a magnet is called demagnetization .Demagnetization takes place due to following ways :
i)Dropping regularly from table or height .
ii)Rubbing against diamagnetic materials .
iii)Bringing similar poles closer by force fully .
iv)Using it for making another magnet.
v)By passing A.C. current in the magnet .
Ways of conservation of magnetism :
i)A magnet should not be heated or it must be kept at distance from hot objects .
ii)A magnet should not be hammered .
iii)A magnet should not be dropped from certain height .
iv)A magnet should be kept in a magnetic keepers .
v)A magnet should be protected from rusting .
Electricity :-The energy which is possessed by a body due to flow of electrons in the body is called electrical energy or electricity
.There are two types of electricity :
1)Statics charge or electricity :The electricity which is possessed by due to flow of electrons in the conductors is called static electricity
Or
Accumulation of electric charge on the surface of an object is called static electricity . Statics charge originates when certain materials rubbed against each other .During the process of friction the electrons moves from one materials to another .So there are two types of electric charge :
i)Positive electric charge
ii)Negative electric charge
2.) Current electricity: The flow of electrons through a conductors is called current electricity .
There are two kinds of current electricity:
i)Direct current (DC): The electricity which is generated by Cell, and battery is called Direct current .
ii) Alternating current (AC).:The electricity which is generated by dynamo or generator is called alternating current .
Source of electricity :The instruments or devices that generate electricity are called source of electricity.Types of sources of electricity :They are two types:
1.)Cell 2.) Generator or dynamo
1.)Cell :An electrical device that convert Chemical energy into electrical energy is called cell.
Types of cells :They are also two types :
1.)Primary cell
2.)Secondary cell
1.)Primary cell :The cells that can not be recharged again and can not be used again and again are called primary cell .
For example :
Simple cell :A cell having two metallic plates dipped in acid solution to generate electricity is called simple .
It was invented by Italian scientist named Volta ,so it is also called Voltaic cell .
Structure :It is made up from a glass vessels containing dilute sulphuric acid as electrolyte in which electrodes made up zinc and copper are dipped .The copper rod is positively charged act as anode and zinc rod is negatively charged act as cathode .
FIg. simple cell
Defects of simple cell :There are two main defects in a simple cell :
a)Polarization : The defect of simple cell in which in which hydrogen gas formed during chemical reaction gets deposited on the surface of copper plate and stop the flow of electric current is called polarization .
Remedy of polarization :Polarization can be removed by cleaning the copper plate regularly with a brush or adding potassium dichromate (K2,Cr2,O7) or manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the solution of simple cell .
b)Local action :The impurities present in zinc plate i.e. carbon, iron etc. which causes to consume the zinc plate and resist the flow current in the external circuit and reduce the life span of cell .This defect of cell is called local action .
Remedy of local action :Local action can be removed by using pure zinc plate or by mercury coated zinc plate .
Dry cell :A cell which is made without using liquid and having paste of of chemical is called dry cell .
Structure :It is made up from zinc container act as negative electrode (Cathode )containing a carbon rod with a cap act as positive electrode(anode).It consist of mixture of zinc chloride and ammonium chloride in the form of paste act as electrolyte .It is surrounded by a moist mixture of manganese dioxide and powder of carbon help to remove polarization defect in the dry cell.
Fig. Dry cell
Uses :It is widely used in torch light, telephone, remote control ,toys, and electric bells etc.
2.)Secondary cell : The cells that can be recharged again and can be used again and again are called secondary cell .For example :Lead storage battery ,Cadmium storage cell .
Photo cell or solar cell :An electrical devices that convert directly solar energy into electrical energy is called photo cell or solar cell.
It consist of a thin layers of semiconductors in such way that potential differences is developed between them when sunlight falls over them and charge flows from high potential to low potential .It produce very less potential differences i.e. 0.4 v to 0.5 v at 60 milliampere ampere current .
2.)Generator or Dynamo :An electrical device that convert kinetic energy into electrical energy is called generator or dynamo .Generator produces large amount of energy and dynamo produce small amount of energy .It is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction .
Symbols used in electric circuit :
Household wiring system :
Domestic or household circuit : :-An A.C. circuit which is connected in house, factories ,industries is called domestic circuit .In household wiring load are always connected parallel .
It consist of following four types of wires:
Wires of house hold wiring :- it is 3 types.
i)Phase or live wire:-The wire which possess high potential is called live or phase wire .In house hold wiring red or brown wire are used for phase .It give electric shocks.
ii)Neutral wire :-The wire which possess zero potential is called Neutral wire .In house hold wiring black or blues wire are used for neutral wire. It does not give electric shocks.
iii) Earthing wire :-The Process of connecting the metallic body of an electric appliances to earth by conducting wire is called earthing wire. In house hold wiring green or green with yellow stripes are used for earthing wire .
Functions :-It save the electric appliances from being damage in case of short circuit and overloading .
Important rules for household wiring system :
i)Electric cables should not be laid in damp places .
ii)Separate fuse should be used in every room or floor.
iii)Fuse with proper capacity should be provided for each circuit.
iii)Power line and domestic line should be separated .
Advantages of parallel connection :
i)Each electric appliances in room can be separately switch off or on .
ii)It is easier to add any new point .
iii)It is easier to repair and check the electric appliances .
iv)When the fuse blows it only affect the single room .
Switch :An electrical device that can break an electrical circuit by diverting the current from one conductor to another conductor is called switch .
i)switch should be connected with the live wire because, it cut the supply the of electric current to electric appliances and prevent from the chance of electric shock when switch is turn off .
Fuse : A safety thin wire device made up an alloy of tin (63%) and lead (37%) having low melting point is called fuse .It is measured in ampere by using following formula .
Fuse (I) =Power(P)/Voltage(V)
The rating of fuse always selected slightly more than the current flowing in the circuit .
Functions of the fuse :-
i)It control the maximum limit of current passing through the circuit by melting itself .
ii)It prevent from the chances of electric shocks and broken of electric circuit due to overloading and short circuit by melting itself .
M.C.B.: (Main circuit breaker ):- An electrical device that is used to protect household wiring is called M.C.B. .It help to protect the house hold wiring from short circuit or over
loading.
Use of M.C.B.is better than fuse :
i)M.C.B. will automatically switch off the main supply ,if the current drawn exceeds the prescribed upper safe limit .but fuse wire melt and produces the break in the circuit .
ii)It can reset with the help of a flip over switch ,but it is difficulty to change the fuse .
Some electrical devices :
Electrical devices :A device that convert electrical energy into other form of energy or work is called electrical device .
1.)Electric lamp :An electrical device that convert electrical energy into light energy is called electric lamp .There are following major types of lamps:
a)Filament lamp : The electrical lamp in which filament is which filament is used to get lighting effect of electricity is called filament lamp. It convert only 10% of electrical energy into light energy and 90% into heat energy .Its life span is about 1000hours .It is cheap .
b) Fluorescent lamp :-The electrical lamp in which fluorescent power ( ie. Cadmium silicate ) is used to to get lighting effect of electricity is called fluorescent lamp. .It convert 30% electrical energy into light energy and 70% into heat energy .Its life span is about 3000 hours .It is expensive
c)CFLs (Compact fluorescent lamp) :A lamp that working system is similar to fluorescent and convert electrical energy into light energy is called CFSs.It produce more light energy than that of fluorescent lamp.
d)LEDs (Light emitting diodes)lamp:The lamp which consist of a special types of diodes instead of filament that emit light when connected with electricity is called LEDs .It convert five times more light energy than that of fluorescent lamp.
2)Heater :An electrical devices that convert electrical energy into heat energy is called heater .It is used to cook food ,boil water ,warming room .it is made up from heating element is called Nichrome. Nichrome is an alloy of chromium and Nickel .
3.)Electric bell : The bell that is operate with the help of electromagnet is called electric bell .It convert electrical energy into sound energy .It is used in house ,office ,school 
4.)Radio :.An audio electrical communication instrument is called radio .It convert electrical energy into sound energy and operated by battery or electricity .
5.)Television :An audio –visual communication instrument is called television .It convert electrical energy into light and sound energy and operated by electricity .
6.)Telephone and mobile :An electrical telecommunication device is called telephone and mobile .It is operated by electricity
7.)Computer :An electrical instrument that is used to operate E-mail, internet ,in the field of communication is called computer .It is also used to write book, store data, play music, and store vides .

























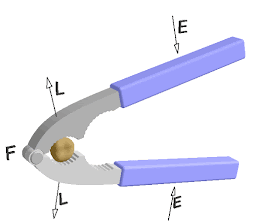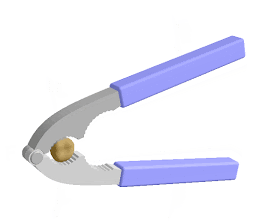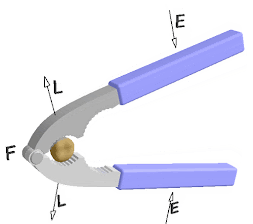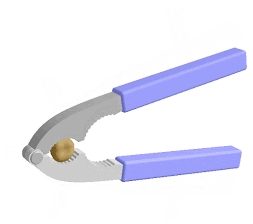
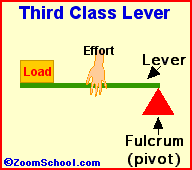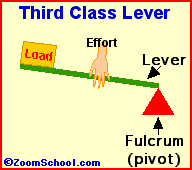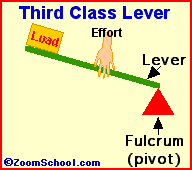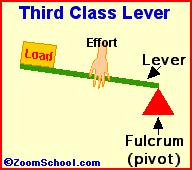

















































































































very useful sir
ReplyDelete