"Chemistry" Grade- 9 (New Course)

Unit -14
Atomic Structure and
Chemical Bond
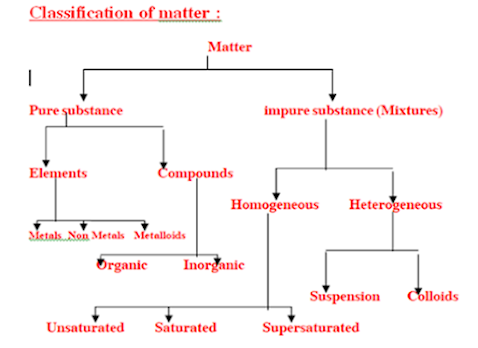
On the basis of chemical and physical properties elements are divided into 3 types :They are :i) Metal i.e. Iron ,gold , silver etc.
iii.)They can neither created nor destroyed .
iv) They can not be further divided .
iv)It is the smallest unit of an element .
v)Except hydrogen all atoms are made up of electron, proton, and neutron.
vi)Except atoms of inert gases ,all other atoms do not exist independently .
i)Molecules is smallest particles of an element or compound which can exist freely in nature .
ii) They are chemically decomposible .
iii)In molecule atoms are bonded together by chemical bond .

Sub –atomic particle :According to Lord Earnest Rutherford an is made of three smallest particles i.e. Proton ,neutron, and electron are called subatomic particles .
Atomic weight :The sum of number of protons and number of electrons in an atoms of element is called atomic mass . For example :atomic mass of He =2+2 =4 ,carbon =6+6=12 ,Nitrogen =7+7=14
Atomic
number and atomic weight :
|
Atomic N. or Proton or electron |
Name of element |
Symbol |
N. of Neutrons |
Atomic mass or weight |
|
1 |
Hydrogen |
H |
0 |
1 |
|
2 |
Helium |
He |
2 |
4 |
|
3 |
Lithium |
Li |
4 |
7 |
|
4 |
Berelium |
Be |
5 |
9 |
|
5 |
Boron |
B |
6 |
11 |
|
6 |
Carbon |
C |
6 |
12 |
|
7 |
Nitrogen |
N |
7 |
14 |
|
8 |
Oxygen |
O |
8 |
16 |
|
9 |
Fluorine |
F |
10 |
19 |
|
10 |
Neon |
Ne |
10 |
20 |
|
11 |
Sodium |
Na |
12 |
23 |
|
12 |
Magnesium |
Mg |
12 |
24 |
|
13 |
Almunium |
Al |
14 |
27 |
|
14 |
Silicon |
Si |
14 |
28 |
|
15 |
Phosphorus |
P |
16 |
31 |
|
16 |
Sulphur |
S |
16 |
32 |
|
17 |
Chlorine |
Cl |
18 |
35 |
|
18 |
Argon |
Ar |
22 |
40 |
|
19 |
Potassium |
K |
20 |
39 |
|
20 |
Calcium |
Ca |
20 |
40 |
Ans. It means that the combing capacity of Al is 3 i.e.It can donate electrons to other during compound formation .
i)Electropositive radical or Basic radical :The radical which have the capacity of losing electrons and carry positive charge are called electropositive radical .For example Mg++ ,(NH4)
Ammonium (NH4) = + 5-4 = +1
ii)Electronegative radical or acidic radical :The radical which have the capacity of gaining electrons and carry negative charge are called electronegative radical .For example :O-- -- (SO4)
Carbonate (CO3) = +4-6 = -2
Bicarbonate (HCO3) = +1+4 -6 = -1
Sulphate (SO4) = +6-8 =2
Bisulphate (HSO4) =+1+6 -8 = -1
Nitrate (NO3) = +5-6 = -1
Hydroxide (OH) = -2+1 = -1
Valency chart :
|
S.N. |
Name of Elements |
Symbol |
Valency |
|
|
Electro Positive |
Electro Negative |
|||
|
1 |
Hydrogen or hydride |
H |
|
1 |
|
2 |
Potassium |
K |
|
1 |
|
3 |
Sodium |
Na |
|
1 |
|
4 |
Silver |
Ag |
|
1 |
|
5 |
Gold-I(Aurous) |
Au |
|
1 |
|
6 |
Copper –I (Coprous) |
Cu |
|
1 |
|
7 |
Mercury –I(Mercurous) |
Hg |
|
1 |
|
8 |
Ammonium |
(NH4) |
|
1 |
|
9 |
Bicarbonate |
|
(HCO3) |
1 |
|
10 |
Bisulphate |
|
(HSO4) |
1 |
|
11 |
Hydroxide |
|
(OH) |
1 |
|
12 |
Bisulphite |
|
(HSO3) |
1 |
|
13 |
Nitrite |
|
(NO2) |
1 |
|
14 |
Nitrate |
|
(NO3) |
1 |
|
15 |
Chlorate |
|
(ClO3) |
1 |
|
16 |
Chlorite |
|
(ClO2) |
1 |
|
17 |
Chlorine or chloride |
|
Cl |
1 |
|
18 |
Bromine or bromide |
|
Br |
1 |
|
19 |
Fluorine or fluoride |
|
F |
1 |
|
20 |
Iodine or iodide |
|
I |
1 |
|
21 |
Cyanide |
|
CN |
1 |
|
22 |
Bisulphite |
|
(HSO3) |
1 |
|
23 |
Barium |
Ba |
|
2 |
|
24 |
Calcium |
Ca |
|
2 |
|
25 |
Magnesium |
Mg |
|
2 |
|
26 |
Nickel |
Ni |
|
2 |
|
27 |
Zinc |
Zn |
|
2 |
|
28 |
Coppper –II(Cupric) |
Cu |
|
2 |
|
29 |
Iron –II(Ferrous) |
Fe |
|
2 |
|
30 |
Mercury –II(Mercuric) |
Hg |
|
2 |
|
31 |
Lead –II (Plumbous) |
Pb |
|
2 |
|
32 |
Magnanese |
Mn |
|
2 |
|
33 |
Tin-II(Stannous) |
Sn |
|
2 |
|
34 |
Iron –II(Ferrous) |
Fe |
|
2 |
|
35 |
Oxygen or oxide |
|
O |
2 |
|
36 |
Sulpher or Sulphide |
|
S |
2 |
|
37 |
Peroxide |
|
H2O2 |
2 |
|
38 |
Carbonate |
|
(CO3) |
2 |
|
39 |
Sulphate |
|
(SO4) |
2 |
|
40 |
Sulphite |
|
(SO3) |
2 |
|
41 |
Chromate |
|
(CrO3) |
2 |
|
42 |
Dichromate |
|
(Cr2O7) |
2 |
|
43 |
Silicate |
|
(SiO3) |
2 |
|
44 |
Stanate |
|
(SnO3) |
2 |
|
45 |
Aluminium |
Al |
|
3 |
|
46 |
Gold –III (Auric) |
Au |
|
3 |
|
47 |
Iron-III (Ferric) |
Fe |
|
3 |
|
48 |
Chromium |
Cr |
|
3 |
|
49 |
Nitrogen or Nitride |
|
N |
3 |
|
50 |
Phosphrous or phosphide |
|
P |
3 |
|
51 |
Phosphate |
|
(PO4) |
3 |
|
52 |
Lead –IV (Plumbic) |
Pb |
|
4 |
|
53 |
Tin-IV(Stanic) |
Sn |
|
4 |
|
54 |
Sulpher or sulphide |
S |
|
4 |
|
55 |
Silicon |
Si |
|
4 |
|
56 |
Carbon or carbide |
C |
|
4 |
|
57 |
Nitrogen or nitride |
N |
|
5 |
|
58 |
Phosphrous |
P |
|
5 |
|
59 |
Sulpher |
S |
|
6 |
i)Compounds are formed by the combination of two or more elements in definite proportion by weight .
ii)They are formed by chemical reaction .
iii)Properties of compound are different from the properties of their constituents due to chemical reaction and chemical change .
iv)Compound are chemically pure substance .
v)Element of compound can be separated by chemical method.
Types of compound : They are two types :
1.)Electrovalent compound :-The compound which is formed by transfer of valence electrons between two atoms is called electrovalent compounds or ionic compounds .These compounds contains electrovalent bonds .They are formed generally from the combination of Metal and non metal .These compound can be electrolyzed .For example: Sodium chloride(NaCl ), Potassium chloride (MgO ) ,Magnesium oxide (CaCl2) etc.
i)Electrovalent or ionic compounds have high melting point .
i)Na –e- → Na+ ion
atom
ii)Cl +e- → Cl- ion
atom
iii) Na+ + Cl- → Na+Cl- (NaCl)
Sodium Chlorine (Sodium chloride
ion ion
i)Mg - 2e- → Mg++ ion
atom
ii)O + 2e- → O- - ion
atom
iii)Mg++ + O- - → Mg++O—(MgO)
ion ion
Atom
ii)2Cl +2e- → 2Cl- ion
Atom
iii)Ca++ + 2Cl- → Ca++2Cl- (CaCl2)
Ion ion
i)Covalent compound have less melting and boiling point as compared to electrovalent compound .
ii)They are insoluble in water but soluble in organic compound .
iv) They have fixed geometrical shape .
Atom Atom
2H + O → H– O – O (H2O)
Hydrogen Oxygen Water
Atom Ato
C + 4H → H – C –H
N + 3H → H– N–H
Nitrogen Hydrogen Ammonia
Atom Atom
2)Covalent bond or molecular bond
3)Co ordinate covalent bond
1)Electrovalent bond or ionic bond :The bond which is formed by the transfer of valence electrons between atoms is called electrovalent bond or ionic bond .For example : bond between NaCl ,MgCl2 ,K 2O etc
iii) Triple covalent bond :in covalent bond if three electrons are contributed by each atom is called triple covalent bond .It is denoted by ≡
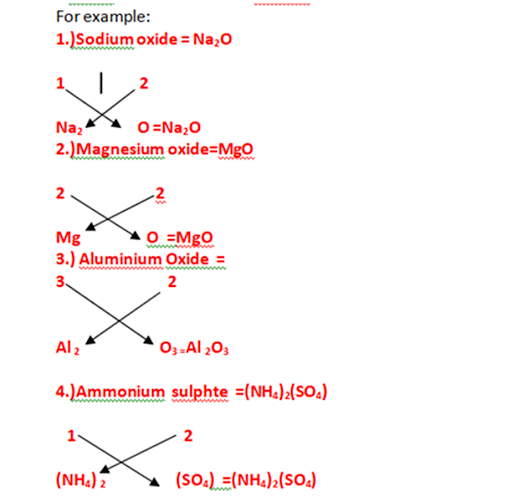
ii)NH4
ii)Write the valency of each atom at top of its symbol .
iii)Divide the valency numbers by highest common factor then inter change the valency of symbol .
iv)Write the inter changed valency number to the lower of the symbol .
Name of compounds Molecular formula
Water = H2O
Carbondixide = CO2
Carbonmonoxide = CO
Ammonia = NH3
Castic soda = Na(OH)
Castic Potash = K(OH)
Methene = CH4
Calcium carbonate or limestone =Ca(CO3)
Lime water = Ca(OH)2
Lime = CaO
Hydrochloric acid =HCl
Sulphuric acid H2(SO4)
Nitric acid =H(NO3)
Carbonic acid =H2(CO3)
Acetic acid =CH3COOH
Carbon sulphide =CS2
Nitric oxide =NO
Hydrogen peroxide =H2O2
Iron oxide (rust) =Fe2O3
Manganese dioxide =MnO2
Silica(Silicon oxide ) =SiO2
Urea =NH2-CO-NH2
Diatomic elements =H2,O2,N2,Cl2,Br2,I2,F2,
i)K- shell = 2n2
= 2 x12 =2 electrons.
ii)L- shell = 2n2
=2x 22 = 8 electrons
iii) M -Shell = 2n2
= 2x 32 =18 electrons
Name of shell Number of shell
K = 1
L = 2
M = 3
N= 4
O = 5
P = 6
Q = 7

Differences
between shell and sub shell .
|
Shell |
Sub shell |
|
i)A circular path on which electrons revolute
around the nucleus is called shell . ii) It is denoted by K,L,M,N,O,P,Q |
i)A part of shell is known as sub shell .ii) It
is denoted by s,p,d,f |
Difference
between orbit and orbital
|
Orbit |
Orbital |
|
i)A circular path on which electrons revolute
around the nucleus is called shell . ii)All orbit are circular and disc like . |
i)The region around nucleus in which
probability of finding the electrons maximum is called orbital. ii)Different orbital have shape and half filled
or full filled orbital more stable than other . |

Non Metal= Valence electros:5,6,7 for example :Cl, O, Br
Metalloid = valence electrons :4 ,For example :Si, Ge, As, Te
Inert gas : valence electrons :8 For example :Ne ,Ar, Kr ,xe, Ra
N. of group : Total valence electrons i.e. IA ,IIA ,IIIA group
N. of period =: N. of shell
Valency :valence electron 1=1 ,2 =2,3=3,4=4,5=3,6=2,7=1,and 8=0 valency
i)Write the electronic of Na, and O .
ii)Write name the group of Na and O ?
iii) Write name the period of Na,and O ?
iv)Write valency of Na and O?
v)Which one is metal and Non metal ?
i)Na =11
1s2 ,2s2 ,2p6, 3s1
K K L
ii) O=9
1s2, 2s2, 2p4
K L
ii)Na =IA group
O= VIA group
iii)Na =3rd period
O =2nd period
iv) Na =1 valency
O = 2 valency
v)Na =metal
O = Non metal
The nucleus of any atom is composed of protons and neutrons. But ,When the ratio of protons and neutrons in the nucleus is 1, (n0/p+ =1) or more than 1, (n0/p+ >1) the nucleus is unstable. These elements are trying to move from unstable state to stable state by emission powerful radiation. This is called Nuclear Stability or radioactive emission. (Rediodharmi utsarjan) Generally, the nucleus of elements with high atomic number i.e.more than 80 is unstable.
Radioactive elements
The unstable atoms emit powerful radioactive
radiation called alpha (a), beta (B) and gamma
( ) to achieve stability. These types of elements
are called radioactive elements.
Or
The element that can emit radioactive radiation is called radioactive element. Examples
of radioactive elements are uranium,
plutonium, thorium etc.
The process of emitting radioactive radiations from radioactive elements is called radioactive emission.
The process of spontaneous emission of powerful alpha (ᾳ), beta (ꞵ) and gamma (y) radiations from the radioactive elements is called radioactive emission.
i)Alpha (ᾳ) radiation
ii)Beta (ꞵ) radiation
iii)Gamma (y) radiation
The particles that consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus are alpha particles (ᾳ). A nucleus with too many protons causes repulsion between these like charges. To reduce this repulsion, the nucleus emits an a-particle. Examples of this can be seen in the decay of americium (Am) to neptunium (Np). An alpha particle always has a charge of +2, due the presence of two protons. Alpha-particles have very low penetration ,the outside layer of the human skin can block these particles.
The electron or positron produced from the nucleus is called beta particle. A nucleus with too many neutrons causes of conversion of neutrons into electrons called beta particle.
It may have positive or negative charge. It has more penetration power than alpha particle. The process production of electron from the nucleus is called beta decay.
An
An
An extremely high-frequency radioactive radiation consisting of high-energy photons is called Gamma radiation or gamma ray.It is also called electromagnetic waves. Gamma decay reactions occur if the energy of the radioisotope's nucleus is too high, and the resulting atomic number and the atomic mass remains unchanged during the course of reaction.
It was first discovered by a French chemist and physicist, Paul Villard in 1900. It was named gamma ray by Rutherford in 1903. Gamma radiation has no mass or charge. This type of radiation is able to penetrate most common substances, including metals.
1 H1 = Free proton or protium ,

4 1H1 2He4 +2 1e0+2 0v0+20ɤ0

i)It is used by developed countries to produce electricity.
ii)It is used to purify drinking water, food, medical equipment, etc.
iii) Nuclear energy is also used to treat various types of diseases like cancer.
iv)It is used for making Nuclear Bomb.

.
i)Reactant :The substance which takes part in chemical are called reactants .They are always written in the left side of the chemical equation .
Chemical equation : The symbolic
representation of the chemical reaction by writing the symbol and formula is
called chemical equation. For example:
2)Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
3)Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen
chloride
4)Zinc +Chloride → Zinc
Chloride
5)Nitrogen + Hydrogen → Ammonia
6)Iron + Oxygen → Iron oxide
7)Magnesium +Nitrogen → Magnesium
Nitride
8)Carbon dioxide +Water → Carbonic
acid
9)Aluminum + Oxygen → Aluminum oxide
10)Aluminum + Chlorine →
Aluminum Chloride
11)Ammonia +Hydrochloric acid → Ammonium
chloride
12)Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitric
oxide
13)Calcium oxide + Water → Calcium
hydroxide
14)Sodium
oxide +Water → Sodium
hydroxide
Na2O
+H2O →
2Na(OH)
15)Magnesium oxide +Water → Magnesium
hydroxide
17)Water → Hydrogen +
Oxygen
18)Potassium chlorate → Potassium
chloride + Oxygen
19)Calcium carbonate → Calcium oxide
+Carbon dioxide
20)Magnesium oxide → Magnesium
+Oxygen
21)Hydrogen peroxide → Water
+ Oxygen
22)Calcium bicarbonate → Calcium
carbonate +Carbon dioxide +Water
23)Magnesium bicarbonate → Magnesium
carbonate +Carbon dioxide +Water
24)Zinc +Sulphuric acid → Zinc
sulphate +Hydrogen
25)Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen
26)Potassium + Nitric acid → Potassium
Nitrate + Hydrogen
27)Iron + Copper Sulphate → Iron Sulphate +Copper
28)Aluminum + Hydrochloric acid → Aluminum chloride
+Hydrogen
29)Magnesium + Copper Sulphate →
Magnesium Sulphate + Copper
30)Sodium + Water → Sodium
hydroxide + Hydrogen
31)Magnesium+ Water → Magnesium hydroxide
+Hydrogen
32)Zinc +Silver Nitrate →
Zinc Nitrate +Silver
33)Calcium +Water → Calcium hydroxide
+Hydrogen
34)Aluminum +Sulphuric acid → Aluminum
Sulphate+ Hydrogen
35)Copper +Silver Nitrate →
Copper Nitrate +Silver
36)Calcium Carbonate +Hydrochloric acid → Calcium
Chloride +Carbon dioxide +water
37)Sodium Hydroxide +Hydrochloric acid → Sodium Chloride + Water
38)Sodium Oxide +Hydrochloric acid →
Sodium Chloride
+Water
39)Calcium Oxide +Sulphuric acid → Calcium Sulphate
+Water
40)Magnesium Oxide +Hydrochloric acid →
Magnesium Chloride +Water
41)Potassium Hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid →
Potassium Chloride +Water
1.)Exothermic reaction : The reaction in which heat is released to the surrounding is called exothermic reaction. For example :
ii)2K(ClO3) +Heat → 2KCl + 3O2
Advantages or information can be obtained from of balanced chemical reaction : Following information can be obtained from balanced chemical equation :
ii)Names of reactants and product
iii)Molecular formula or symbols of reactants and products
i.It helps plants in preparation of food during photosynthesis.
iii. Many medicine ,drugs, paints, fertilizer, etc. are manufacture by using chemical reaction.
ii)Negative Catalyst :A catalyst which decrease the rate of chemical reaction is called negative catalyst .i.e. Glycerin acts as negative catalyst in decomposition of hydrogen peroxide .
Characteristics of catalyst:
i.Catalyst do not take part in chemical reaction between reactants but they increase or decrease rate of chemical reactions.
ii. Catalysts remain chemically unchanged without being consumed during reaction.
Unit :- 16
1)Introduction: The symbol of hydrogen gas is H, atomic N. 1, atomic mass 1a.m.u. ,molecular formula H2, and valency is 1 .It was discovered by Henry Cavendish .It is generally found in volcanic eruption ,petroleum and organic substances i.e. hydrocarbon.

i)By electrolysis of water :Hydrogen gas can be prepared from decomposition of water by electrolysis .

i.)Apparatus required :Wolf bottle ,Thistle funnel ,delivery tube, gas jar, beehive self, heating apparatus.
Reaction
:
Zinc + dil. Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen gas
Zn
+ H2(SO4) → Zn (SO4) +H2
Zinc + dil. Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen gas
Zn + H2(SO4) → Zn (SO4) +H2
iii)Pure Zinc is not used for the prepartion of gas as it reacts very slowly with dil. H2(SO4) .Impurities increase the rate of reaction.
When a burning splinter is introduced in a gas jar containing if splinter goes out while the gas burns a the mouth of the gas jar with pop sound and gas is hydrogen gas.

Physical properties :
i)It is colourless ,odourless, and test less gas .
ii)It is the lightest gas .i.e. 22.2 liters of H2 gas of wt only 2 gm .
iii)It is insoluble in water .
iv)It has no effect on an indicator .
Chemical properties:
i)When Hydrogen gas is burn in air ,water is obtained .
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
ii)When Hydrogen react with halogens i.e. Cl2, Br2,I2,F2,etc. and their respective halides are formed .
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
H2 + Br2 → 2HBr Hydrogen halides
H2 +I2 → 2HI
iii)When hydrogen react with Nitrogen at high temperature and high pressure Ammonia gas is obtained .This process is Haber’s process .
N2 +3H2 → 2NH3
iv)When hydrogen combine with vegetable oil ,vegetable ghee is obtained .This process is known as hydrogenation .
i)It is used in manufacture of ammonia ,which is used making fertilizer .
1.)Introduction :The symbol of oxygen is O,atomic N. 8,atomic weight 16 a.m.u., molecular formula O2, and valency is 2 .It was first prepared by Joseph Priestley.It was named oxygen by Lavoisier
i)By Metal oxide :When metal oxide are heated and O2 gas is produced .
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
2Ag2O → 4Ag + O2
ii)By electrolysis of water :- Oxygen gas can be produced from decomposition of water by electrolysis method .
Reaction at cathode :
H+ + e- → H
4H → 2 H2
Reaction at anode :
(OH)- → (OH) + e –
4(OH) → H2O +O2
A)By heating method :
i)Apparatus required :Hard glass test tube, delivery tube , gas jar, beehive self, heating apparatus.
Potassium chlorate → Potassium chloride + Oxygen
2K(ClO3) → 2KCl +3O 2
i)The apparatus should made air tight.
ii)The manganese dioxide used as catalyst should be in pure form.
iii)The gas jar should be completely filled with water.
iv) Heat should be provided continuously with low flame strength.
b)Without heating method :
i)Apparatus required : Conical flask, thistle funnel, delivery tube ,Gas jar, Beehive self,

iii)Reaction
:
Hydrogen peroxide → MnO2 water +
Oxygen
2H2O2 → MnO2 2H2O
+ O2
i)End of the thistle funnel should be dipped under acid layer.
Test of O2 gas :When burning splinter is introduced in a gas jar containing gas if gas burn more brightly and gas is Oxygen gas .because it is supporter of combustion.

Physical :
i)It is colourless, odour less, and test less gas .
ii)It is slightly soluble in water i.e. about 3%
iii)It is does not burn but support to burn i.e. supporter to combustion.
Chemical properties:
i)When oxygen is burn with hydrogen, water is obtained .
2 H2 + O2 → 2H2O
ii)When oxygen react with carbon dioxide is obtained .
C + O2 → CO2
iii)When Oxygen combine with Nitrogen during lighting discharge Nitric oxide is obtained .
iv) When oxygen react with metal their respective metal oxide or base is obtained .
2Na + O2 → Na2O
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO Metal oxide or base
K + O2 → K2O
Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 (rust)
I) It is used by living being for respiration .
i)Ozone layer play an important role to keep weather and temperature of the balanced .
i)Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCl3 ,CFCl12 andCFCL13): American scientist Thomas Miez is the inventor of CFCs .It is major causes of ozone layer depletion.
-CFCl3 → UV radiation CFCl2+Cl(Nascent Chlorine)
-It act as cooling agent as well as solvent.
iii)Chloroform(CHCl3)
Process of depletion of ozone layer: When the gases like CFCs,CO,CH3Br,oxides of nitrogen etc. reach into stratosphere ,they are decomposed by ultra violet radiation and chlorine is formed .This chlorine help to decompose ozone and depletion of ozone layer takes place.
Effects of depletion of ozone layer: Due to depletion of ozone layer more ultra violet radiation reach on earth’s surface ,that cause of following effects:
i-)Effects on health of human being: due to depletion of ozone layer in human being ultra violet rays causes of various diseases i.e. skin cancer ,breast cancer, blood cancer, Blindness ,damage to immune system, affect to DNA and causes of mutation.
Protection of ozone layer:
i)Reducing and controlling the emission of CFCs.
ii)Uses of nitrogen fertilizer should be reduced.
iv)Generating awareness about the ozone layer depletion in people.
1.Itroduction : The symbol of Nitrogen is N, atomic N.7,atomic weight 15 a.m.u., molecular formula N2, and valency is 2,and3 .It was discovered by Daniel Rutherford. It was named azote by Lavoisier, because it does not support for combustion and respiration .
i.)By heating of ammonia with copper oxide :When ammonia gas is prepared over heated copper oxide ,Nitrogen gas is obtained .
ii)By heating copper oxide in air :At first air is passed through lime water to eliminate CO2 ,then passed through conc. H2( SO4) to revolve moister and through cooper gauze to form CuO and from remaining as N2 gas is obtained .

Na(NO2) + (NH4)Cl → NaCl +2H2O +N2
i)End of the thistle funnel should be dipped under acid layer.
v)Test of N2 gas :If a burning splinter is introduced inside the gas jar then they neither combustible nor support for combustion and gas is N2.
A) Physical properties :
i)It is colourless ,odourless and test less gas .
ii)It is lighter than that of air .
iii)It is slightly soluble in water .
iv) It is neither combustible nor supporter of combustion .
B)Chemical properties :
i)When magnesium is react with Nitrogen ,magnesium Nitride is obtained .
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
ii)When Nitrogen is react with hydrogen under high temperature and high pressure ,ammonia gas is obtained .
N2 + 3 H2 →high pressure/temp 2NH3
iii)At high temperature during lighting when Nitrogen react with Oxygen Nitric Oxide is obtained .
N2 + O2 → lighting 2NO
i)It is used for making different fertilizer .
ii)It is used for making Nitric acid ,and ammonia gas .
Unit :- 17

Physical properties:
i)Most of metals are solid at ordinary temperature ,except mercury ,it is found in liquid state .
v)Metal posses ductile property (i.e. can be change into wires)except Na, K, Li.
vi)Metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity .

Chemical properties:
i)Non metals are generally found in all three states i.e. solid For example: Carbon ,liquid For example: Bromine ,gas For example :Hydrogen ,Oxygen, Nitrogen etc.
i)They are poor conductor of heat and electricity .
ii)They posses metallic luster .
metal less than metal .
Uses of metalloids :
i)Tellurium is used in manufacture of electric resistors, rubber, ceramics ,glass .
i)They are generally harder than their components .
iii)They are malleable and ductile .
1.)Roles of Zinc in human body :It is found in small amount inside the body of organism .i.e. in adult about 2-3 gm Zn is found in cell , tissue, bone, retina, and abdomen.
ii). Dairy products, meat, fish, egg etc.
i.Zn is needed for the body's defensive system to proper work
ii. Zn plays a role in cell division, cell growth. wound healing and breakdown of carbohydrates.
iv. Zn may reduce the risk of bacterial and viral infection and reduces the risk of becoming sick with common cold, pneumonia, diarrhoea.
v. Zn enhances pituitary hormone function.
vi. It helps in the synthesis of genetic material, DNA, protein etc. in the cell.
vii)It support the body to make healthy .
viii)It act as a cofactor for enzyme
ix)It help for physical functions in the bone ,kidney and
brain.
Effects due to deficiency or irregularity:
i. Hair loss
ii. Reduction in taste and smell
iii. Laziness/fatigue
iv. Diarrhoea and weight loss
v. Slow healing of wounds and cuts.
i.Common salt [NaCI] is the main source of sodium in human body.
ii. Sodium is also obtained from meat and egg.
1It helps to balance the amount of water and salts inside and outside the human body cells
2. It regulates the efficiency of nerves and muscles.
i.It causes disease called hyponatremia.
iii. It can cause vomiting, dizziness, unconsciousness and even death.
i.Foods like soyabean, vegetables and dairy products.
ii. Fruits like banana, avocado and young bamboo shoots.
i.Potassium maintains the water balance and osmotic pressure.
ii. Potassium maintains acid-base balance.
iii. Potassium helps to metabolize carbohydrates and proteins
Effects due to deficiency or irregularity of Potassium
i.It causes disease called hypokalemia.
ii. It causes high blood pressure, constipation, weakness in body and weakens the muscles.
3.Roles of Iron in human body : Iron is present in all cells in the human body and help carry oxygen to tissues to lungs.
i.Spinach, grains, broccoli, seeds of plants etc.
ii. Meat and fish
Functions:
i.Iron present in haemoglobin of blood helps in oxygen transport.
ii. DNA synthesis.
iii. It helps to improve immunity and regulates energy production.
1. It causes anaemia.
2. It causes fatigue and difficulty in respiration.
i)It is causes of depression .
ii)It is causes of memory loss .
iii)It is causes of heart attack .
iv)It is causes of skin discolouration
Sources:
i.Volcanoes,forest fire,fossils i.e. coal and petroleum.
ii.Fish and shellfish contaminated with methylmercury.
Harmful effect of Lead :
i)It is causes of anaemia.
ii)It is causes of hyper tension.
iii)It is causes of headache and stomach pain.
iv)It is also may lead to coma and death .
Sources:
i) Lead based paint, contaminated soil.
Organic
chemistry :The branch of chemistry concerned with the compounds of carbon is called
organic chemistry .
Inorganic
chemistry: The branch of chemistry concerned with the compound of elements
other than carbon is called inorganic compound .
|
Organic compound |
Inorganic compound |
|
i.)The
compounds of carbon other than oxides of carbon
,carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbides are called organic
compounds . ii.)Organic
compounds having low melting and boiling points
. iii.)Organic compounds burn easily .i.e. Ghee, alcohol iv)These
are formed by covalent bond. v.)Organic
compounds are insoluble in water . |
i.)The
compounds other than compounds of carbon except
oxides of carbon, carbonates ,bicarbonates ,and carbides are
called inorganic compounds. ii.)Inorganic
compounds having high melting and boiling points iii)Inorganic
compounds do not burn easily . i.e. salt iv)These
are formed by electrovalent bond. v)Inorganic
compounds are soluble in water . |
Sources of carbon :
iii.)It is found in the form of carbonate, and bicarbonate compounds .
iv)It is found in natural hydrocarbon i.e. coal ,Petroleum, and natural gas .
Nature of carbon : Carbon atoms has 4 valence electrons to their valence shell ,so it can loss or gain 4 electrons to become stable but the size of the carbon atom is smaller,so effective nuclear charge is strong and strongly hold valence electrons .Hence It can neither loss nor can gain electrons and can not form electrovalent bond .Therefore it form 4 covalent bond by sharing its 4 valence electrons with other atoms .


Physical properties of carbon :
i)It is found in solid state and non metal .
ii.)It is insoluble in water .
iii)It show allotropic properties .
Chemical properties :
i)When carbon burn with sufficient oxygen ,carbon dioxide is obtained but with insufficient oxygen carbon monoxide is obtained.
C+O2 → sufficient CO2
2C + O2 → insufficient 2CO
ii)When carbon react with steam at high temperature ,carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas or water gas
C + H2O → CO+H2
i.)Carbon is used as fuel .
ii.)Charcoal is used for purifying drinking water ,decolourlizing sugar .
iii)Lamp black is used in the printers ,manufacture of polish,black paints .etc .
Types of hydrocarbon :They are two types :
A.)Saturated hydrocarbon :The hydrocarbon in which carbon-carbon atoms combines with single covalent bond are called saturated hydrocarbon .Its IUPAC(International union pure applied chemistry ) name is alkane For example :
i.Food: Food stuffs contains organic compounds i.e. cabohydrates ,protiens,fat, vitamins,etc. Are essential for healthy growth and development.
Unit :-19
Potassium(K) and Calcium(Ca). They help in growth and development of plants .
1)Organic fertilizers: The fertilizers which are obtained from dead and decomposed parts of animals and plants or their waste product are called organic fertilizer . There are also two types of organic fertilizers :-
i)Green organic fertilizers :The organic fertilizer which are prepared by cutting green plants and later which are decomposed under soil are called green organic fertilizer or green manure .These types of fertilizer mainly provides nitrogen to the plants in form of nitrates .
ii)Animal organic fertilizer :-The organic fertilizer which are prepared from dead and decayed parts of animals due to the action of bacteria and enzymes in their body are called animal organic fertilizer .It do not contain nitrogen ,phosphorus and potash but can control weeds and increases the moisture-holding capacity of the soil and increases air penetration in the soil.
i.)It help to Balances the soil ecosystem
ii)It help plant to make health naturally
iii)They’are all-natural .
iv)It increase the fertility of soil.
v)It does not affect the quality of soil.
vi)It controls environmental pollution.
vii)Prevents from over-fertilization
Disadvantages of organic fertilizers:
i)It requires more time to be prepared. so effectiveness is limited seasonally.
ii)It is insoluble in water and it is difficult to transport from one place to another place .
iii) Nutrients ratio is always unknown .
Advantages of chemical or inorganic fertilizers :
i)Inorganic fertilizer increase the fertility of the soil.
ii)They have special types of nutrients .
iii)They can transport easily .
iv)They are water soluble ,so plants can absorb easily .
Disadvantages of inorganic or chemical fertilizers :
i)Inorganic fertilizer pollute the environments.
ii)Inorganic fertilizers increase the fertility of the soil.
Considering factors or precaution while using chemical fertilizers :
i)Before the use of chemical fertilizers, we must test the acidic or basic nature of soil.
ii)At the time of using chemical fertilizers ,we must cover our mouth and nose .
iii)we must control the flow of chemical fertilizers in sources of water .
iv)Chemicals fertilizers should be used scientifically ,in term of proper dose and time ,because excessive use of fertilizer can harm plants instead of better growth .
1.)Nitrogeneous fertilizer :The chemical fertilizer that supply nitrogen to plants are known as nitrogeneous fertilizer For example :
i)Urea (NH2CONH2)
ii)Ammonium suplhate (NH4)2(SO4)
iii)Ammonium nitrate (NH4)(NO3)
Functions of Nitrogen :
i)It help in rapid growth in plants .
ii)It help to increase yield of growth .
iii)Sufficient nitrogen help for high rate of photosynthesis .
iv)It help in the formation of chlorophyll ,carbohydrate, and protoplasm .
Deficiency of Nitrogen :
i)Due to lack of nitrogen plants will be shorter ,leaves may be smaller and maturity of plants may be delayed too .
ii)Shortage of nitrogen will causes of yellowing of leaves .
iii) Due to lack of nitrogen rate of photosynthesis will decreases and less branching in plants .
2.)Phosphatic fertilizer :The fertilizers that supply phosphorus to the plants are called phosphatic fertilizers .For example :
i)Calcium super phosphate
ii)Triple super phosphate
iii)Bone metal .
Functions of Phosphorus :
i)It help in early maturity in plants .
Deficiency of phosphorus :
i)Due to lack of phosphorus flowering may be delayed .
ii)Due to lack of phosphorus rate of cell division decreases .
iii)Due to lack of phosphorus reduces diseases resistant power of the plants .
3.)Potash fertilizers :The fertilizers that supply potassium to plants are known potash fertilizers .For example :
i)Potassium chloride (KCl)
ii)Potassium sulphate K2(SO4)
iii)Potassium carbonate K 2(CO3)
iv) Potassium Nitrate K (NO3)
Functions of potassium :
i)It help in the utilization of nitrogen and help in protein synthesis .
ii)It help for making healthy roots and shoots .
iii)It also help to increase resist against diseases
iv)It help to regulates the opening and closing of stomata .
Deficiency of potassium :
i)Lack of potassium causes of poor resistance for diseases.
ii)Lack of potassium causes of weak roots and shoots.
iii)Lacks of potassium causes of losing of leaves .
1.)Organic insecticides :The insecticide which are containing carbon are called organic insecticides. It also contains hydrogen ,oxygen, chlorine and, phosphorous. On the basis of chlorine, phosphorous, and carbomate organic insecticides are also divided into 3 types :
ii)BHC =Benzene Hexa chloride
iii)Dieldrin
iv)Aldrin
B)Organo-Phosphorous :The organic insecticide which contains phosphorous as principle elements is called Ogano-phosphorous .For example :i)Malathion ii)Parathion
C)Carbomate :The organic insecticide which contains amino group(NH2) as principle element is called carbomate .For example :i)Baygon ii)Turmic
2.)Inorganic insecticide :The insecticides which are made up from minerals or inorganic compound is called inorganic insecticides. For example :i)Lead arsenate ii)Calcium arsenate iii)Lime sulpher iv)Floride
It is used to protect fruits ,vegetables ,cotton etc.
Advantages of insecticides :
i)They are used to control or kill harmful insects .
ii)They also help to control diseases.
Disadvantages of insecticides:
i)Insecticides kill harmful insecticide as well as useful insecticide .
ii)They are non bio-degradable so causes of soil,air and water pollution .
Precautions in using insecticides :
i.)Make globes and aprons should be used while using insecticides.
































Comments
Post a Comment