Chemistry Grade 10 (Science New Course)
Chemistry Grade - 10 (Science )
Unit Topics
14 Classification of Elements
15 Chemical Reaction
16 Some Gases (CO2, NH3)
17 Metal and Non Metals
18 Hydrocarbon and its Compounds 19 Chemicals used in Daily Life
Unit:-14 Classification of elements
Periodic table :A table in which elements are classified into various blocks ,periods, and groups on the basis of their similarities and dissimilarities is called periodic table .There are two types lines in the periodic table :
i)it help to remember the properties of elements, if its position in the periodic table is known .
ii)It makes the study of chemistry systematic and easy .
iii)It is used as teaching aids in chemistry in school and college .
A.)Mendeleev`s periodic table : The periodic table in which elements are arranged in the table with the increasing order of their atomic weight is called Mendeleev’s periodic table .It was formed by Demitri Mendeleev’s .
Mendeleev’s periodic law: It states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic weights .
i)Mendeleev’s periodic table divided the elements into horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns are called groups .
ii)It help to correct the incorrect atomic weights .
iii)Mendeleev’s left proper gaps in the periodic table for undiscovered elements .
iv)There are 8 groups numbered from I to vii.
v)Physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic weight .
Drawbacks of Mendeleev’s periodic table :
i)The position of hydrogen could not be explained by Mendeleev’s periodic table i.e. Hydrogen resembles metal as well halogens .
ii)There was not suitable place for lanthanides and actinides series in the Mendeleev’s periodic table .
iii)Copper ,Gold and silver and alkali metals both were placed in the same groups .
iv) Some elements having higher atomic weight but have been placed before element of lower atomic weights i.e. Ar having At.wt. 39.9 a.m.u. was placed before K having At. Wt. 39.1 a.m.u.
v)The properties like valency ,reactivity ,electro negativity, can not be explained in the terms of periods and groups .
Modern periodic table :The periodic table in which elements are arranged in the table with the increasing order of their atomic number is called Modern periodic table .It is also called long form periodic table .It was formed by Henry Moseley.
Modern periodic law: It states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number .
Characteristics of modern periodic table :
i)The elements are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number in the modern periodic table .
ii) There are seven periods i.e. horizontal rows in modern periodic table .
Period | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th |
N.of elements | 2 | 8 | 8 | 18 | 18 | 32 | 26 |
Form of Periods | Very short | Short | Short | Long | Long | Very long | Long But incomplet |
iii)In the modern periodic table there are 18 groups which are named by following two ways .
According to inter national pure applied chemistry (IUPAC) | |||||||||||||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
According to modern periodic table | |||||||||||||||||
IA | IIA | IIIB | IVB | VB | ViB | VIIB | VIII | VIII | VIII | IB | IIB | IIIB | IVB | VB | VIB | VIIB | 0 |
iv)The elements between group 3 and group 12 are placed between reactive metal and non metal .These elements are called transition metal .These element are also called d-block elements or these elements have variable valency .
v)There are separate place for Lanthanides and Actinides at the bottom of modern periodic table .These elements are also called f-block of elements .
Differences between Mendeleev's and Modern periodic table
Electronic
Configuration on basis of sub shell
2n2 rule
:The
rule that gives the maximum number of electrons present in the shell is called
2n2 rule .For example :
i)K-
shell = 2n2
ii)L-
shell = 2n2
iii)
M -Shell = 2n2
Name of
shell
Number of shell
K
= 1
Differences
between shell and sub shell .
|
Shell |
Sub
shell |
|
i)A circular
path on which electrons revolute around the nucleus is called shell . ii) It is
denoted by K,L,M,N,O,P,Q |
i)A part of
shell is known as sub shell .ii) It is denoted by s,p,d,f |
Difference
between orbit and orbital
|
Orbit |
Orbital |
|
i)A circular
path on which electrons revolute around the nucleus is called shell . ii)All orbit
are circular and disc like . |
i)The region
around nucleus in which probability of finding the electrons
maximum is called orbital. ii)Different
orbital have shape and half filled or full
filled orbital more stable than other . |
Valency
: The combine capacity of an elements with another elements is
known as velency .It is represented by 1,2,3,4,5,6 .
Valence
shell :The outer shell of an atom of the elements is called valence shell
.
ii)Atomic
size or radius
iii)Temperature
iv)Catalyst
Electronic configuration :The systematic distribution of electrons according of their
shell and sub shell is called electronic configuration.
Electronic
configuration formula :
Note
:
Metal
=Valence electrons :1,2,3 For example :Na, K
Non
Metal= Valence electros:5,6,7 for example :Cl,O, Br
Metalloid
= valence electrons :4 ,For example:Si, Ge, As, Te
Inert
gas: valence electrons: 8 For example:Ne ,Ar, Kr ,xe, Ra
N. of
group : Total valence electrons i.e. IA ,IIA ,IIIA group
N.
of period =: N. of shell
Valency :valence electron 1=1 ,2 =2,3=3,4=4,5=3,6=2,7=1,and 8=0 
For example :A element have 1 electron and B element
have electrons to their valence so A elements can loss easily 1 electrons than that of 2 electrons
of B elements therefore
A element is more reactive than that of B elements .
For example : A element have
7 electrons and B element have 6 electrons to their valence shell ,so A element easily gain 1 electrons than that
of 2 electrons of B elements to
complete their valency shell, therefore A element is more reactive than that of
B elements .
For
example : The atomic size of B element is larger than that of A element ,due larger atomic size of B element the nuclear
attraction to the valence shell is less than that of A element ,so B element can more easily loss 1 electron than that of 1
electron of A element , therefore B element is more reactive than
that of A element .
For example : The atomic
size of A element is smaller than that of B element ,due smaller atomic size of A element the nuclear attraction to
the valence shell is more than that of B element ,so
A element can more easily gain 1 electron than that of 1 electron of
B element , therefore B element is more reactive than that of A element .
Chemical
reactivity non metal ∝ valence electrons
Chemical
reactivity in group :The chemical reactivity of metal increases gradually while
moving from top to bottom in 1 to 14 group ,similarly the
chemical reactivity of non metals decreases gradually while moving from top to
bottom in 15 to 17 group due to increase of size of atom .
Chemical
reactivity of metal ∝ atomic size
Chemical
reactivity non metal ∝ 1/ size of atom
Classification
of elements in modern periodic table :
In
modern periodic table the elements are classified following ways :
A.)Metal
:The
elements which have 1 to 3 electrons to their valence shell are called metals .They can conduct
heat and electricity and also can develop electropositive charge by losing electrons
.
On
the basis of reactivity they are divided in following types :
i)Alkali
metal :The elements of IA group in modern periodic
table are called alkali metal , because they are dissolve in water to form metal hydroxide or alkali .
ii)Earth
alkaline metals :The elements of IIA group in modern periodic
table are called earth alkaline metals, because they are found in the form of oxide on the surface
of earth and react with water to produce
alkali .For
example : Mg (magnesium ) Ca (calcium ).
iii)Transition
elements : The elements of groups from IB to VIIB and VIII are called
transition elements.becausse they have tendency of reactivity between reactive elements and Nonmetal.They have variable valency. These elements are also
called d-block
of elements .
B.Non metal : The elements which have 4
to 8 electrons to their valence shell are
called Non metals .They are bad conductor heat and electricity and also
can develop electronegative charge by gaining electrons . For example :The elements of
VA,VIA,VIIA and 0 Group of elements i.e.O,Br,Cl,F,
i)Chalcogens
:The
elements of VIA group in modern periodic table are called chalcogens ,because
these elements are found combined with copper in nature .For example :O (oxygen), S (Sulphur
) etc .
This
group of elements are also called very reactive non metal because they
have 7
electrons to
their valence so they receive 1 electron very to complete their valence .
iii)Noble
gas or inert gas :The elements of 0 group in modern periodic table are called Noble
gas .because they have already 8 electrons to their valence
shell so they neither receive nor donate electrons to complete their valence
shell .For example :He (Helium), Ne (Neon) ,Ar (Argon ) etc.
f-block
of elements : : The elements of modern periodic table having last electron
in f-sub shell are called f-block of elements .This block is situated at the bottom of
modern periodic table .For example :
Atomic
size or radius : The distance between the outermost shell and the centre of nucleus of
that atom is
called atomic size.The Number of positive charge (Proton)present in the nucleus of an atom is called
nuclear charge .
Unit.:-15 Chemical reaction
Velency:-The combine capacity of element or radical to
another element or radial to form compound is called valency .
Radical :A radical is an atom or group of atoms
different element having positive or negative charge and act as single unit
during chemical reaction is called radical .They are two types :i)Electropositive radical or Basic radical :The radical which have the capacity of losing
electrons and carry positive charge are called electropositive radical .For
example Mg++ ,(NH4)
Ammonium (NH4)
= + 5-4
= +1
ii)Electronegative radical or acidic radical :The radical which have the capacity of gaining electrons and carry
negative charge are called electronegative radical .
Radical
Valency of elements Valency
of radicals
Carbonate (CO3)
= +4-6
= -2
Bicarbonate (HCO3)
= +1+4
-6
= -1
Sulphate (SO4)
= +6-8
=2
Bisulphate
(HSO4) =+1+6
-8
= -1
Nitrate
(NO3) = +5-6
= -1
Hydroxide
(OH) = -2+1
= -1
Valency Chart
|
S.N |
Name of Elements |
Symbol |
Valency |
|
|
Electro Positive |
Electro Negative |
|||
|
1 |
Hydrogen or hydride |
H |
|
1 |
|
2 |
Potassium |
K |
|
1 |
|
3 |
Sodium |
Na |
|
1 |
|
4 |
Silver |
Ag |
|
1 |
|
5 |
Gold-I(Aurous) |
Au |
|
1 |
|
6 |
Copper –I (Coprous) |
Cu |
|
1 |
|
7 |
Mercury –I(Mercurous) |
Hg |
|
1 |
|
8 |
Ammonium |
(NH4) |
|
1 |
|
9 |
Bicarbonate |
|
(HCO3) |
1 |
|
10 |
Bisulphate |
|
(HSO4) |
1 |
|
11 |
Hydroxide |
|
(OH) |
1 |
|
12 |
Nitrate |
|
(NO3) |
1 |
|
13 |
Nitrite |
|
(NO2) |
1 |
|
14 |
Chlorate |
|
(ClO3) |
1 |
|
15 |
Chlorite |
|
(ClO2) |
1 |
|
16 |
Chlorine or chloride |
|
Cl |
1 |
|
17 |
Bromine or bromide |
|
Br |
1 |
|
18 |
Fluorine or fluoride |
|
F |
1 |
|
19 |
Iodine or iodide |
|
I |
1 |
|
20 |
Cyanide |
|
CN |
1 |
|
21 |
Bisulphite |
|
(HSO3) |
1 |
|
22 |
Barium |
Ba |
|
2 |
|
23 |
Calcium |
Ca |
|
2 |
|
24 |
Magnesium |
Mg |
|
2 |
|
25 |
Nickel |
Ni |
|
2 |
|
26 |
Zinc |
Zn |
|
2 |
|
27 |
Coppper –II(Cupric) |
Cu |
|
2 |
|
28 |
Iron –II(Ferrous) |
Fe |
|
2 |
|
29 |
Mercury –II(Mercuric) |
Hg |
|
2 |
|
30 |
Lead –II (Plumbous) |
Pb |
|
2 |
|
31 |
Tin-II(Stannous) |
Sn |
|
2 |
|
32 |
Magnanese |
Mn |
|
2 |
|
33 |
Iron –II(Ferrous) |
Fe |
|
2 |
|
34 |
Oxygen or oxide |
|
O |
2 |
|
35 |
Sulpher or Sulphide |
|
S |
2 |
|
36 |
Peroxide |
|
O2 |
2 |
|
37 |
Carbonate |
|
(CO3) |
2 |
|
38 |
Sulphate |
|
(SO4) |
2 |
|
39 |
Sulphite |
|
(SO3) |
2 |
|
40 |
Chromate |
|
(CrO3) |
2 |
|
41 |
Dichromate |
|
(Cr2O7) |
2 |
|
42 |
Silicate |
|
(SiO3) |
2 |
|
43 |
Stanate |
|
(SnO3) |
2 |
|
44 |
Aluminium |
Al |
|
3 |
|
45 |
Nitrogen or Nitride |
|
N |
3 |
|
46 |
Phosphrous or phosphide |
|
P |
3 |
|
47 |
Chromium |
Cr |
|
3 |
|
48 |
Iron-III (Ferric) |
Fe |
|
3 |
|
49 |
Gold –III (Auric) |
Au |
|
3 |
|
50 |
Phosphate |
|
(PO4) |
3 |
|
51 |
Lead –IV (Plumbic) |
Pb |
|
4 |
|
52 |
Tin-IV(Stanic) |
Sn |
|
4 |
|
53 |
Sulpher or sulphide |
S |
|
4 |
|
54 |
Silicon |
Si |
|
4 |
|
55 |
Carbon or carbide |
C |
|
4 |
|
56 |
Nitrogen or nitride |
N |
|
5 |
|
57 |
Phosphrous |
P |
|
5 |
|
58 |
Sulpher |
S |
|
6 |
Molecular formula :The symbolic representation of molecules of
substance which show actual number of atoms present in the molecules is called
molecular formula or chemical formula .For example :i) Magnesium chloride =MgCl2,
Sodium sulphate =Na2(SO4 ) etc.
Ways of writing molecular
formula : This method is
called criss –cross method.
i)Write the symbols side
by side but electropositive is written first and then electronegative .
ii)Write the valency of
each atom at top of its symbol .
iii)Divide the valency
numbers by highest common factor then inter change the valency of symbol .
iv)Write the inter
changed valency number to the lower of the symbol .
For example:
Molecular formula of
some compounds :
Name of
compounds Molecular
formula
Water
=
H2O
Carbondixide
= CO2
Carbonmonoxide
= CO
Ammonia
= NH3
Castic soda
= Na(OH)
Castic Potash
= K(OH)
Methene
= CH4
Calcium carbonate or
limestone =Ca(CO3)
Lime water
= Ca(OH)2
Lime
= CaO
Hydrochloric acid
=HCl
Sulphuric acid
H2(SO4)
Nitric acid
=H(NO3)
Carbonic acid
=H2(CO3)
Acetic acid
=CH3COOH
Carbon sulphide
=CS2
Nitric
oxide
=NO
Hydrogen
peroxide =H2O2
Iron
oxide
(rust)
=Fe2O3
Manganese
dioxide =MnO2
Silica(Silicon oxide )
=SiO2
Urea
=NH2-CO-NH2
Diatomic elements =H2,O2,N2,Cl2,Br2,I2,F2,
Chemical reaction :-The
exchange ,combustion or decomposition that occurs in the molecules of
substances during a chemical change is called chemical reaction .
2H2 +O2 →
2 H2O
ii)Sodium +Oxygen
Sodium oxide
Na +O2
→
Na2O
Word equation :The chemical equation in
which the names of substance and products are expressed in the form of word is
called word equation . For example :
Types of chemical reactions :There are
4 types chemical reaction:
2)Magnesium
+ Oxygen → Magnesium
oxide
3)Hydrogen
+ Chlorine → Hydrogen
chloride
4)Zinc
+Chloride → Zinc Chloride
5)Nitrogen
+ Hydrogen → Ammonia
6)Iron + Oxygen → Iron oxide
7)Magnesium
+Nitrogen → Magnesium
Nitride
8)Carbon
dioxide +Water → Carbonic
acid
9)Aluminum + Oxygen
→ Aluminum oxide
10)Aluminum + Chlorine →
Aluminum Chloride
11)Ammonia
+Hydrochloric acid → Ammonium
chloride
12)Nitrogen
+ Oxygen → Nitric
oxide
13)Calcium
oxide + Water → Calcium
hydroxide
14)Sodium oxide +Water
→
Sodium hydroxide
Na2O +H2O
→
2Na(OH)
15)Magnesium
oxide +Water →
Magnesium hydroxide
2.)Decomposition
reaction :-The chemical reaction in which a compound split
or decompose into two or more elements or compound is called decomposition
reaction .For example:
2)Potassium
chlorate → Potassium
chloride + Oxygen
3)Calcium carbonate
→ Calcium oxide +Carbon dioxide
4)Magnesium oxide
→ Magnesium +Oxygen
5)Hydrogen
peroxide → Water + Oxygen
6)Calcium
bicarbonate → Calcium
carbonate +Carbon dioxide +Water
7)Magnesium
bicarbonate → Magnesium carbonate +Carbon dioxide +Water
8)Silver Bromide
→ Silver + Bromine
9)Potassium
Permanganate → Potassium manganate +Manganese dioxide
+Oxygen
10)Ammonium carbonate → Ammonia +Carbon dioxide +Water
3.Displacement reaction :The chemical reaction in which an element or radical of a compound
is displaced by another element or radical of compound is called displacement
reaction .For example :
2)Zinc + Hydrochloric
acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen
3)Potassium + Nitric
acid → Potassium Nitrate + Hydrogen
3)Iron + Copper
Sulphate → Iron Sulphate +Copper
4)Aluminum +
Hydrochloric acid → Aluminum chloride +Hydrogen
5)Magnesium + Copper
Sulphate → Magnesium Sulphate + Copper
6)Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
7)Magnesium+
Water → Magnesium hydroxide +Hydrogen
8)Zinc +Silver Nitrate → Zinc Nitrate +Silver
9)Calcium +Water
→ Calcium hydroxide +Hydrogen
10)Aluminum +Sulphuric
acid → Aluminum Sulphate+ Hydrogen
11)Copper +Silver
Nitrate →
Copper Nitrate +Silver
12)Ammonia
+Chlorine → Ammonium Chloride +Nitrogen
13)Calcium
Chloride +Silver Nitrate → Calcium
Nitrate +Silver Chloride
14)Calcium Carbonate
+Hydrochloric acid → Calcium Chloride +Carbon dioxide +water
15)Sodium
Chloride +Silver Nitrate → Sodium
Nitrate+ Silver Chloride
16)Calcium
Carbonate +Sulphuric acid → Calcium
Sulphate +Carbon dioxide +Water
17)Magnesium Sulphate
+Sodium Carbonate → Magnesium Carbonate
Mg(SO4)+Na2(CO3) → Mg(CO3)+Na2(SO4)
4)Acid –Base reaction :The Chemical reaction in
which an acid react with a base to form salt and water is called acid- base
reaction .In acid base reaction both acid and base loss their
properties during chemical reaction and form neutral substance salt and
water ,so it is also called Neutralization reaction .
i)Hydrochloric acid=HCl
ii)Sulphuric acid =H2(SO4)
iii)Nitric acid =H(NO3)
iv)Carbonic acid =H2(CO3)
Some bases :
i)Metal oxide ePdf = Mgo,Na2O,K2O,CaO
etc.
ii)Metal hydroxide ePdf =
Na(OH),K(OH),Ca(OH)2 etc.
1)Sodium Hydroxide +Hydrochloric
acid → Sodium Chloride + Water
2)Sodium Oxide +Hydrochloric
acid → Sodium Chloride +Water
3)Calcium Oxide +Sulphuric acid → Calcium Sulphate +Water
4)Magnesium
Oxide +Hydrochloric acid →
Magnesium Chloride +Water
5)Potassium
Hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Potassium
Chloride +Water
6)Sodium
Hydroxide +Sulphuric acid → Sodium
Sulphate +Water
7)Ammonium
Hydroxide +Sulphuric acid → Ammonium
Sulphate + Water
8)Magnesium
Hydroxide + Nitric acid →
Magnesium Nitrate + Water
Types of reaction
according to heat :There are two types of reaction according to
heat :
1.)Exothermic reaction : The reaction in which heat is released to the surrounding is
called exothermic reaction. For example :
ii)2K(ClO3)
→ 2KCl + 3O2
Some rules of what happens :
Reactants Product
i)Single
2 elements = Combination of element .i.e.
Na + Cl2
→
NaCl
Mg + O2
→
MgO
ii)Metal
+Water = Metal Hydroxide i.e.
Na+ H2O
→ Na(OH)
Ca +H2O
→ Ca(OH)2
iii)Metal
+Water = Metal Hydroxide +Hydrogen i.e.
Mg + 2H2O →
Mg(OH)2 +H2
Na+2 H2O →
Na(OH)2
+H2
iv)Acid+ Base = Salt + Water
HCl +Na(OH) → NaCl +H2O
H2(SO4) +Na2 O
→ Na2(SO4) +H2O
v)Carbonate
+ acid = Carbon dioxide + Water i.e.
Ca(CO3)+2HCl
= CaCl2 + CO2 +H2O
Balanced chemical equation
: The chemical
equation written by balancing the N. of atoms of element on both sides of
reactants and products is called balanced chemical equation .For example :
Advantages or information
can be obtained from of balanced chemical reaction : Following information can be obtained from balanced chemical
equation :
ii)Names of reactants
and produced
iii)Molecular
formula or symbols of reactants and products
iv)N. of atoms and
molecules of reactants and products .
Limitation of a balanced
chemical equation :The
information which can not show a balanced chemical equation are called
limitation of balanced chemical equation .They are as following :
ii)Concentration of
reactants .
iii)Duration of chemical
reaction .
iv)Conditions necessary for chemical reaction .
The rate of chemical reacton :The time taken from the start of a chemical reaction to its ends is called the rate of reaction .Different
chemicals react to each other a
different rates .For example :Chemical
reaction of rusting of iron occurs
very slowly,but reaction between sodium and woter occurs very fast to releases hydrogen .
Factors affecting chemical reaction or chemical change : Some of the Factors which affect the rate of the chemical reaction are called factors affecting chemical reactions.
2)Light :Light makes the reactants molecules more
reactive and help to
2 Ag(NO3) →
Light 2 NO2 + O2 +2Ag
3)Electricity :The
electrical energy help the ions to move to wards opposite. charged electrodes
that brings out a chemical change and increase the rate of reaction .
4)Direct Contact :Some active substance
react on coming in direct contact with other .i.e.
5)Pressure :Some
chemical reaction takes place by the application of pressure .i.e.
6.)Surface area :The rate of chemical
reaction is directly proportional to the surface area of the reacting molecules
,because there is more chances to contact and collision between reacting
particles .For example :During preparation of hydrogen gas if the granulated
zinc has more area the chemical reaction proceeds in faster rate .
ii)Negative Catalyst :A catalyst which
decrease the rate of chemical reaction is called negative catalyst .i.e.
Glycerin,Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) acts as negative
catalyst in decomposition of hydrogen peroxide .
Gram atomic weight : The atomic weight of an element expressed
in gram is known as gram atomic weight of that element .For example :The gram atomic weight of oxygen is 16 gm ,because
the atomic weight of oxygen is 16 .
=23 gm
K = 19+20
= 39 gm
Ca =20+20
= 40 gm
Gram molecular weight :The molecular weight of the substance is
expressed in gm is known as gram molecular weight of that substance .For
example :The gram molecular weight
of water is (H2O) is 18 gm because molecular wt of water is 18 .
1.)Find the molecular
weight of given compounds .
i)H2O
= 1x2+16
18 gm
ii)CaO
= 40+16
=56 gm
iii)Ca(CO3)
= 40+12+16x3
=40+12+48
=100gm
1mol: The gm atomic wt. or gram molecular of any
substance is known as 1 mol of that substance .
=1x2+16
=18 gm.
Mass of 1 mol of water
=Gram molecular wt. of water
= 18gm .
Therefore ,mass of 8 mol
of water =18x8
=144gm.
ii)Convert 5 gm of
Ca into mol .
Gram at. wt. of Ca =1
mol of Ca
40 gm of Ca = 1mol of Ca
1gm of Ca =1/40
؞5
gm of Ca =1/40 x 5
Unit :-16 Gases (Carbon dioxide (CO2), Ammonia (NH3)
A) Carbondioxide =CO2
1.Indtroduction :The molecular formula of carbon dioxide is CO2,molecular
weight is 44 a.m.u. Air contains about 0.03% of carbon dioxide by volume .Its molecular structure is
2.Methods of general
preparation of CO2 :
1.)When carbon is burn
in air with plenty of oxygen and carbon dioxide is obtained .
C +O2 → CO2
Carbon dioxide
ii.)When calcium
carbonate is heated strongly and carbon dioxide is obtained .
Ca(CO3) → CaO + CO2
Lime
stone Lime
iii)When fuel like
methane, ethane ,is burn in air carbon dioxide is obtained.
CH4 +
2O2 → CO2 +2 H2O
Methane
3.)Method of lab.
preparation CO2 gas :
i.)Apparatus required :Wolf bottle ,Thistle funnel ,delivery tube, gas jar, beehive self,
heating apparatus.
ii)Chemicals required: Lime stone (marble), hydrochloric acid
iii)Principle:- CO2 gas can be prepared by
treating pieces of calcium carbonate with dil. Hydrochloric acid .
Reaction :
Ca(CO3)
+ dil. HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Lime stone
iv)Precaution: a)The apparatus should be made air tight .
b)The end of thistle
funnel should be dipped into the acid in wolf bottle.
v)Test of CO2 :a) When a burning match stick is placed
near the mouth of gas jar containing CO2 .If match stick
extinguish the gas is CO2 gas ,because CO2 gas is non supporter
of combustion .
4.)Properties
1.)Physical properties :
i)It is colourless
,odourless and testless gas .
ii)It turns wet blue
litmus paper into red .
iii)It is heavier than
that of air .Therefore CO2 gas
can be collected down word displacement method of water or it is collected by upward displacement
of air .
iv)It dissolve in water
so, it is not collected in
water .
v)It is non supporter of
combustion .
Chemical properties :
i)When carbon dioxide is
treated with water carbonic acid is obtained .Therefore when blue litmus paper
is introduced inside gas gar containing CO2 it change in to red
colour due to formation of
carbonic acid.
CO2
+ H2O → H2(CO3)
ii)When carbon dioxide
is passed into lime water for long time in the beginning milky solution of insoluble calcium carbonate is
obtained
If when carbon dioxide
is passed continuously in the solution for long time the milky ness
disappear slowly due to the formation of
water soluble calcium bicarbonate .
a)Ca(OH)2
+ CO2 → Ca(CO3)
+H2O
Lime
water
Milky sol.
b)Ca(CO3)
+H2O →
Ca(HCO3)2
iii)When burning
magnesium ribbon is introduced into gas jar filled with CO2 ,white
colour of MgO is produced along with the formation of black spots of
carbon .
2Mg + CO2
→ 2Mg
O + C
Black
iv)When carbon dioxide
react with water in presence of chlorophyll, and sun light ,Glucose and oxygen
is obtained .
6CO2
+ 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Glucose
CO2 +
KOH → K2CO3 +H2O
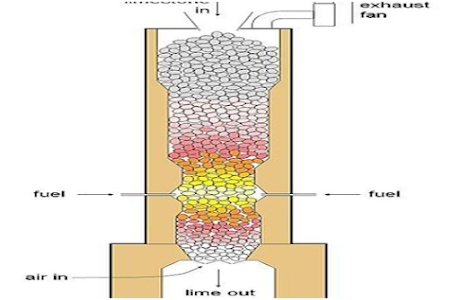
5.)Method of industrial
preparation of CO2 gas :
In industries carbon
dioxide gas is prepared in large scale by heating lime stone at very high
temp. in the furnace .In this process lime is also produced .
Ca(CO3) Heat
→ CaO +CO2
Lime stone
Lime
6.)Uses :
i)It is used by all
green plant during photosynthesis .
ii)It is used as fire extinguisher .
iii)It is used for
making dry ice to preserve meat, fruit etc. (A solid form of carbon dioxide which is obtained by cooling it about
-780C is called dry ice .
v)The mixture of oxygen((85%
to 90%) and carbondixide (10% to 15%) is called carbogen which is used to
provide artificial respiration because it increase the rate of respration .
Fire extinguisher :
Afire extinguisher is a metallic cylinder divided in to two section .The outer section is a metallic covering contains sodium bicarbonate =Na(HCO3) and inner section is made up a glass vessel filled with conc. Sulphuric acid =H2(SO4).When glass vessel is broken by pressing knob at the top of cylinder sulphuric acid gets mixed with sodium bicarbonate to form carbon dioxide .
2Na(HCO3) + H2(SO4) → Na2(SO4) +2H2O+ 2CO2
B.)Ammonia (NH3)
1.) Introduction :
La Voiser prepared first time ammonia gas .Its
molecular formula is NH3 ,molecular
weight is 17 a.m.u. and its molecular
structure is
Methods of general preparation of NH3 gas
:
i)When magnesium Nitrate is treated with water
and ammonia gas is formed .
Mg3N2 + 6H2O
→ 3Mg(OH)2 +2NH3
3.)Methods of lab
preparation of ammonia gas :
i) i.)Apparatus required :Round bottom flask ,delivery tube, gas jar, , heating
apparatus, lime tower
ii)Chemicals required: Ammonium chloride ,Calciumhydroxide.
iii)Principle:- NH3 gas can be prepared by
treating mixture of Ammonium Chloride and of calcium hydroxide .
iv)Reaction :
2(NH4)Cl
+ Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + H2O + 2NH3
Ammonia
Fig. Lab preparation of NH3 gas .
v)Precaution :
i)The apparatus
should made air tight.
ii)The should be
collected in gas jar by the downward displacement .
vi)Test of NH3 gas
:When a wet a red litmus
paper is introduced in to gas jar containing ammonia gas . It change into blue colour due to formation of Ammonium hydroxide
alkali .
4.)Method of industrial
preparation of NH3 gas : In industries ammonia is prepared by Hyber’s process .In this process ammonia gas is prepared by the direct
combination of Nitrogen and Hydrogen gas under high pressure and high
temperature in presence of Fe catalyst .
N2
+ 3H2 → 200atm/500C 2NH3
Ammonia
5.)Properties :
Physical properties :
i)It is colourless
,testless , but strong pungent odour .
ii)It is highly soluble
in water .
iii)It is lighter than
that of air .
iv)It turns wet red litmus paper into blue colour due to formation ammonium hydroxide
alkali.
Chemical properties .
i)When ammonia react
with water an alkali ammonium hydroxide is formed .
NH3
+ H2O → (NH4)(OH)
Alkali
ii) When ammonia react
with acid ,salt are formed .
NH3 +
HCl → (NH4)Cl
NH3 +
H(NO3) → NH4(NO3)
iii)When ammonia is
treated with carbon dioxide at high temperature at 1500 0C
under certain pressure urea is formed .
2NH3
+ CO2 → NH2 – CO – NH2 + H2O
Urea
iv.)When
ammonia gas is burn with oxygen water and Nitrogen gas is obtained
4NH3 + 3O2
→ 2 N2 + 6H2 O
v)When
ammonia gas is treated with Oxygen gas at high temp.in presence of Pt. at
catalyst Nitric oxide and water is obtained .
4NH3 + 5O2 →high temp/pt. 6H2O + 2NO
Vi
)When ammonia is sent in melt Sodium metal Sodamide and Hydrogen gas is
obtained .
2NH3 + Na →
2 NaNH2 + H2
6.)Uses :
i)It is used for
making chemical fertilizer .i.e.
urea, ammonium sulphate .
ii)It is used for
making plastic, washing
soda etc.
iii)It is used for making medicine .
iv)It is used for
develop blue print .
vi)It is used as
cleansing agent for oil,greeze etc.
1.)Lime tower is used in
lab preparation of ammonia gas ,why?
Ans. Lime tower help to
form dry ammonia gas ,because when ammonia gas comes out from lime tower ,it absorb water of ammonia gas due to water soluble properties of ammonia
.
2.)The mouth hard glass
test tube is slightly slanted during the preparation of ammonia gas ,why ?
Ans. When mixture of (NH4)Cl
and Ca(OH)2 is heated steam is formed and reach upper end of steam but when it liquefied
come back at the bottom of test .It
may cause cracking of test
tube ,so hard glass
test tube is slightly slanted to prevent of cracking .
Green house effect: The increase of temperature of earth by trapping the solar heat in earth by green house gases( i.e.CO2,N2O,CH4,CFCs and water vapour) is called green house effect
Effects of green house:
i)It causes the skin and eye cancer .
ii)It help spreading
diseases like malaria, filarial
,etc.
v)It causes the increase surface temperature of earth and living being can survive on earth
surface.
i)by reducing use of fossil fuels .
The temperature inside
the green house is always more than that of
outside it ,because glass or plastic allow inter sun radiation but
when strike on the ground it change into wave have less energy or longer wave
length that can not go out from the house and get reflected inside house
as result due to accumulation of more sun radiation the temperature of inside
the increases.
Uses or advantages : i)It is used to grow different crops in off seasons i.e. summer plant can be grow in winter season and the plant of terai can
be grow in mountain region.
Earth can be described as a natural greenhouse, because The
natural greenhouse effect is a process in which certain gases in Earth's
atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and water vapour,
trap heat from the Sun and warm this planet.
This process is essential for maintaining a
habitable temperature range on Earth,
allowing life to thrive.
i)CO2+ H2O
→ H2CO3(carbonic
acid)
ii)SO2 →oxidation SO3 + H2O →
H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid)
iii) 2NO2+2H2O
+O2
→ 4HNO3(Nitric
acid)
Effects of acid rain:
i)Acid rain damages the building and sculptural materials i.e.lime stone and marbles .
iii)It remove basic nutrients i.e. calcium from soil.
iv)It increase the acidity of soil that reduce the
fertility of soil.
v)it also damages the lot of crops ,plants etc.
Control measures of acid
rain :
1.We
should reduce the emission of oxides of
nitrogen and sulphur .
Unit: 17. Metal and Non
Metals
Minerals : Naturally
occurring, inorganic substances that have a specific
chemical composition and a crystalline structure is called Mineral .
They are the building blocks of rocks and are found in the Earth's crust.
Minerals are the composed of various
elements, such as oxygen, silicon, aluminium, iron,
calcium, and many others Elements.
1. Construction: Minerals like limestone, granite, and sand are used
in construction materials.
6. Health and Medicine: Minerals have important roles in human health. For
example: Calcium and phosphorus are crucial for bone
health. Iron is necessary for the production of haemoglobin
in red blood cells.
Naturally occurring minerals or rocks that contain sufficient quantity of metals
are called Ores They are the primary source of metals
and other valuable materials used in various industries. Therefore all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores.
For example :Haematite is the ore of iron, Bauxite is
the of Aluminium ,Copper pyrites is ores of the copper .
Metal :The elements
which have a tendency to loss electrons and form cat ion are called metal .For example :Mg, Na, Ca, Al etc.
Properties of metals:
Physical properties:
i)Most of metals
are solid at ordinary temperature ,except mercury ,it is found in liquid state .
ii)Most of metals
are generally hard ,except Na, K, Li, they are soft .
iii)Metal posses metallic luster (shining)
iv)Metals have
generally high density ,except Na, K ,Li.
v)Metal posses ductile property (i.e. can be change into wires)except Na, K, Li.
vi)Metals are generally
good conductors of heat and electricity .
vii)The boiling and
melting point of metals are
high ,except Na, K, Li.
viii)Metals atoms
generally contains 1,2,3,electrons to their valence shell .
ix)Metals are
generally electropositive in nature because loss their valence electrons.
x)Metals possess malleability (i.e. can be beaten in thin plate)
i)Non metals are
generally found in all three states i.e. solid For example:
Carbon ,liquid For example: Bromine ,gas For example :Hydrogen ,Oxygen, Nitrogen etc.
Ores of some Metals:
1.)Iron
Symbol =Fe (Ferrum)
Atomic number (At .N.)=26
Atomic weight (At. Wt.)=56
Valency :2 (Ferrous)
: 3 (Ferric)
Position in periodic
table :Transition metal ,d-block elements ,4rth periods .
Ores :
i)Haematite (Fe2O3)
: it is also called major ores of iron .
ii)Magnetite
(Fe3O4)
iii)Iron
carbonate (FeCO3)
iv)Siderite(FeCO3)
v)Limonite(2Fe2O3.3H2O)
vi)Iron pyrite (FeS2)
Physical properties :
i)It is shiny and grayish white metal .
ii)It is malleable and ductile .
iii)It is good conductor of heat and electricity
Uses :
i)It is used for
making different types of pipes
rods ,and cable wires .
ii)It is used for
making different types
instruments and weapons .
iii)It is used for
making building ,bridges ,and
means of transportation i.e. bus, trucks etc.
iv) It is used for
making different types of
household utensils .
v) It is used for making steels .
2.) Aluminium
Symbol =Al (Aluminium)
Atomic number (At .N.)=13
Atomic weight (At. Wt.)=27
Valency :3
Position in periodic
table : Group -IIIA ,P-block
elements ,3rth periods .
Ores :
i)Bauxite =Al2O3.2H2O
:It is also called major ores of Aluminium.
ii)Felspar
=K((AlSiO3.O8)
iii)Cryolite(Na3AlF6)
Physical properties :
i)It is shiny and silvery white metal .
ii)It is malleable and ductile .
iii)It is good conductor of heat and electricity
Uses :
i)It is used for making aluminium paint .
ii)It is used for making electric cable .
iii)It is used for making coins .
iv)Due to its malleable ,ductile and light properties it is used for making aeroplane .ship,car etc .
v)It is used for making household utensil .
3.)Copper
Symbol =Cu (Cuprum)
Atomic number (At .N.)=29
Atomic weight (At. Wt.)=63.57
Valency :1 (Cuprous )
=2(Cupric)
Position in periodic
table : Transition metal ,d-block
elements ,4rth periods .
Ores :
i)Copper pyrite or
chalcopyrite =CuFeS2: it is also called major ore of copper .
ii)Chalcocite or copper
glance =Cu2S
iii)Cuprite (Ruby copper )
iv)Malachite
v)Azurite
Physical properties :
i)It is shiny and reddish brown metal .
ii)It is malleable and ductile .
iii)It is good conductor of heat and electricity.
Uses:
i)It is used for making cables ,and electric appliances .
ii)It is used for making coins ,and brass .
iii)It is used for making household utensil.
iv)It is also used
for making insecticide and
pesticides .
4.)Silver
Symbol =Ag (Argentum)
Atomic number (At .N.)=47
Atomic weight (At. Wt.)=107.9
Valency :1
Position in
periodic table : Transition metal ,d-block elements ,5th periods .
Ores :
i)Argentite or silver
glance =Ag2S: It is also called major ore of silver .
ii)Silver copper glance =(AgCu)2S
iii)Horn silver (AgCl)
Physical
properties :
i)It is shiny white metal .
ii)It is malleable and ductile .
iii)It is good conductor of heat and electricity.
Uses:
It is used for making valuable household utensil .
ii)It is used for making coins and jewelry .
iii)it is used for making negative in photography .
iv)It is used
for silver plating .
4.)Gold
Symbol =Au (Aurum)
Atomic number
(At .N.)=79
Atomic weight
(At. Wt.)=197.2
Valency :1(Aurrous )
Position in periodic
table : Transition metal ,d-block
elements ,6th periods .
Ores :Gold is mostly found free state in nature due to less reactive nature ,so it is also called noble gas, but some important ores of gold are :
i)Alluvial soil
ii)Calaverite=AuTe2
Uses of gold :
i)It is used for making jewelry and coins .
ii)It is used for making medals .
iii)It is used for making status.
iv) It is used for gold plating .
Aquarejia :Mixture of 3 parts of Conc HCl and 1 parts of Conc H(NO3)is called aquarejia .It produce nascent
i)Iron :Lalitpur ,Bhojpur,chitwan, Pyuthan
ii)Copper =Udayapur ,Makwanpur
iii)Gold= Rapti river,Mustang ,Kathmandu
iv)Manesium =Udayapur
v)Lead =Lalitpur
vi)Bismuth =Makwanpur
vii)Cobalt :Palpa
viii)Calcium =Lalitpur ,Kathmandu
ix)Zinc =Lalitpur
Metallurgy :
The process
of extracting valuable minerals or other geological
materials from the Earth is called mining .
Types of
mining: There
are two main types of mining:
2.)Underground
mining: The mining which is
done by digging tunnels to reach
the minerals or materials is called under ground
mining. This type of mining is often used for minerals
that are found deeper underground, such as gold, diamonds, and copper etc.
General
steps of Metallurgy:
2.Crushing and Grinding: The process of converting a solid material into fine particles by rubbing or crushing is called grinding .In this step ores are break down into smaller pieces. This is done using powerful crushers and grinding mills, turning the ore into a fine powder.
3.Concentration: The process to separate the metal from the gangue, is called concentration. The powdered ore contains not just the desired metal but also unwanted impurities called gangue. So in this step the gangue are removed from metal by various techniques such as froth flotation, where the metal-rich particles stick to bubbles and float to the top, while the gangue sinks., magnetic separation where by help of magnetic method unmagnetic substance are removed.
4.Oxidation : The chemical reaction of a metal with oxygen, resulting in the formation of a metal oxide is called oxidation. It
is easy to extract metal from metal oxide so
oxidation is done after
concentration .it is done by two
methods:
a) Roasting and Calcination:
To prepare the metal for extraction, it's often heated
in a controlled environment. This process,
called roasting or calcination, To removes impurities and converts
the metal into a more suitable form for
reduction.
The process in which metal is
converted into its oxide by heating it below
its melting points in presence of excess of air is called roasting. For example: ZnS is
convert into ZnO by roasting .
5.Reduction:
The process of reducing metallic oxide into metal by removing oxygen is called reduction . Reducing agent such as coal, coke, natural gas, carbon monoxide are used as reducing agents, leaving behind the pure metal. For example: ZnO is reduced by using carbon, Ag2O and HgO is reduced by heating, Na, K, Ca, Mg ,Al oxide are by electrolysis method.
6.Refining: The
process of purifying about 90% a metal from their respective ores is called refining .The extracted metal may still contain some impurities,
so it undergoes further purification called refining. On the basis of the nature of
the metal to purified refining is done by two
methods :
a) Distillation:
The process of separating the components of a liquid mixture by
heating it to a boil and then condensing the
vapour into a liquid. The process is based on the different boiling points of the components of the mixture. if impurities or metals can be
evaporated by boiling. The liquid with the lowest boiling point will vaporize first, and the vapour will then condense
back into a liquid. This process can be repeated to further purify the liquid. 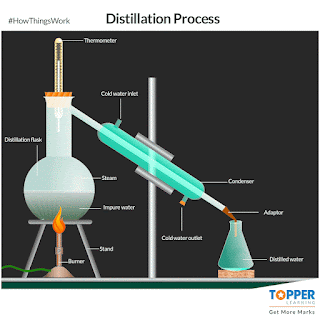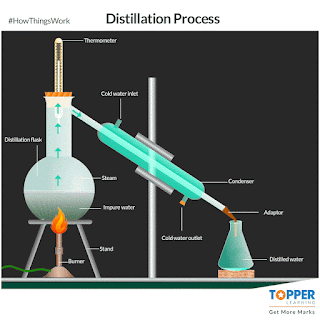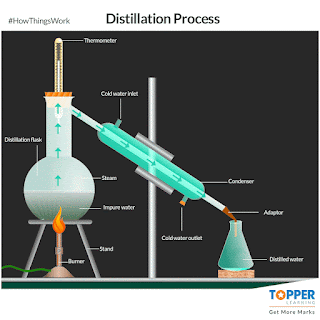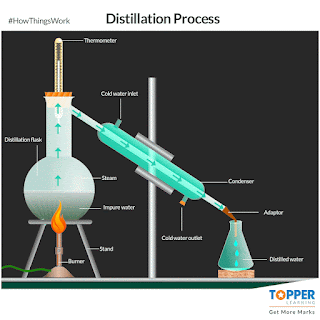
b.)Electro refining:
The process of purifying a metal by passing an electric current through a solution containing
the metal ions is called Electro refining . The impure metal is used as the anode,and cathode is a thin sheet of
pure metal. When the electric current is passed
through the solution, the metal ions are attracted to the
cathode and deposited
on it, while the impurities remain in the solution. This
process is used to purify a variety of metals, including copper, nickel, silver, and gold. It is a
very effective way to remove impurities from metals and produce high-purity
products.
7.Shaping and Forming: Finally, the
purified metal is ready to be shaped into various forms, such as sheets, wires,
or bars. This can be done through various processes like casting, rolling,
forging, or extrusion.
Unit -18 Hydrocarbon and its compounds
Organic chemistry :The branch of chemistry
concerned with the compounds of carbon is called organic chemistry .
Inorganic compound
i.)The compounds of carbon other than oxides of carbon ,carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbides are called organic compounds .
ii.)Organic compounds having low melting and boiling points .
iii.)Organic compounds burn easily .i.e. Ghee, alcohol
v.)Organic compounds are insoluble in water .
iii)Inorganic compounds do not burn easily . i.e. salt
iv)These are formed by electrovalent bond.
v)Inorganic compounds are soluble in water .
B.)Unsaturated hydrocarbon :The hydrocarbon in which carbon atoms combine with double or triple covalent bond is called unsaturated hydrocarbon.Its IUPAC (International union pure applied chemistry ) name is Alkene and Alkyne .
Alkene or Olefins :A hydrocarbon in which carbon –carbon atoms combine
with double covalent bond is called alkene or olefins .For example :
Alkyne or Acetylene : A hydrocarbon in which carbon –carbon atoms combine with triple covalent is called alkyne or acetylene .For example :
Catenation: The ability of carbon to combine with another carbon atoms to long chain of or ring of different size is called catenation .For example :
Allotropes
:The
property of a pure element having same composition but found in two or more than two forms in the
same state is called allotropes .For example :
Homologous series :A group of hydrocarbon
which contains the same functional group but has the different
CH2 group or length is called homologous
series For example : Homologous series of alkane i.e.
Methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
Pentane
Homologous series of Alkene i.e.
Ethene
Propene
Butene
Pentene
Hexene
Properties of homologous series :
i)All
members of homologous series can be represented by the same
general formula .
Ethyl
alcohol
Dimethyl ether
ii)CH3-O-C3H7 C2H5-O-C2H5
Methyl
propyl ether Diethyl ether
Properties of isomers :
i)Isomers
have same molecular formula .
iii)Isomers
have different physical and chemical properties .
Alkyl radical :The group of organic
compound which is formed by removing one hydrogen
atoms from alkane For example :![]() i)CH4⟶
-H
CH3+ (Methyl radical )
i)CH4⟶
-H
CH3+ (Methyl radical )![]() ii)C2H6 ⟶
-H C2H5+ (Ethyl
radical)
ii)C2H6 ⟶
-H C2H5+ (Ethyl
radical)
When alkyl
group combine with functional group and form different types organic compounds .For
example :
ii)C2H5-O-C2H5 (diethyl
ether )
Functional group: An atom or group of
atoms that determine the chemical properties of a hydrocarbon is
called a functional group . For example : i)Hydroxyl -(OH) =formed
alcohol ii)-O- Formed ether
Some important hydrocarbon and their uses ;
A)Methane =CH4
It is
saturated hydrocarbon and formed during decomposition of organic matter
i.e.vegetable ,animals matters .It is also called Marsh gas .It
is found in marshy or swamp areas and natural gas and petroleum mine .
i)It is
used as source of fuel .
ii) It is
used for making water gas and hydrogen gas .
iv) It is
used for making chloroform, carbon tetrachloride ,methyl alcohol.
B)Ethane =C2H6
It is
saturated hydrocarbon .It is found in natural gas ,coal and
petroleum mine .
i)It is
used as source of fuel .
C)Propane = C3H8
It is a
saturated hydrocarbon .It is found in natural gas ,and petroleum
mines .
Uses : i)It
is used as source of fuel .i.e. in lighter.
It is
saturated hydrocarbon .It is found in natural gas and petroleum
mine .
i)It is
used as source of fuel i.e. LPG (Liquefied petroleum
gas)
E) Alcohol: Organic compound having
hydroxyl group (OH) is called alcohol . For example : Methyl alcohol , Ethyl
alcohol etc .
2.)Di
hydric alcohol : The
alcohol which is formed replacement of two hydrogen atom of alkane by same number of
hydroxyl group is
called dihydric alcohol .For example :
3.)Tri hydric alcohol : The alcohol which is
formed replacement of three hydrogen atom of alkane by same number of
hydroxyl group is called tri hydric alcohol .For example :
Example
of some monohydric alcohol :
Some important alcohol :
Uses :i)It is used as fuel in sprit lamp (Produce
heat without smoke )
iii)It is
used to dissolve fat, oil paints ,varnish .
2.)Ethyl alcohol =C2H5OH :It
is also called real alcohol .
iii)It is
used for making medicine, soap, synthetic rubber etc.
iii)It is
used for making formalin which is used as a preservative for biological
specimen
Unit -19
Chemicals used in Daily Life
A. Food Preservatives :The materials or chemicals that can be added to food to prevent from spoilage(Sadna), deterioration(bigrina), discoloration(ranghin),
and and help to enhance flavour(swad bdhauna) are called Food preservatives .They help maintain the quality, freshness, and
safety of food .
The example of some common food preservatives are:
2.Sugar: Sugar can also inhibit bacterial growth by creating a
hypertonic environment,( by reducing the water
content of foods, which inhibits microbial growth)where bacteria
struggle to survive.
3.Vinegar: The acetic acid in vinegar inhibits the growth of bacteria and gives food a tangy flavor.
4.Citric acid: Citric acid is a
naturally occurring compound found in citrus fruits. It inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi.
5.Sulfur dioxide:
Sulfur dioxide is widely used as a preservative in dried fruits, fruit juices,
and wine. It helps prevent discoloration and inhibits
the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds.
6.Sodium benzoate:
Sodium benzoate is a common preservative used in acidic foods such as
carbonated drinks, fruit juices, and pickles. It inhibits
the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds.
7.Potassium sorbate: Potassium sorbate is used to inhibit the growth of molds, yeasts, and certain bacteria. It is commonly used in cheese, baked goods, and dried meat products.
8.Nitrites and nitrates:
Nitrites and nitrates are commonly used in cured meats (dry) like bacon, ham, and sausages.
They help prevent the growth of bacteria,
particularly Clostridium botulinum,
which can cause botulism(disease caused by
a toxin that attacks the body's nerves 
9.Probiotics: Live bacteria that can help to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
Types of food preservatives :A.:On the basis of amount uses :They are 2types :
1.First class- preservatives :The preservatives which can be used in any amount without exact measuring are called first class -preservatives .For example:salt,mustard oil,vinegar,honey etc.
2.Second class -preservatives:The preservatives which must be used in exact amounts as they are prescribed are called second class-preservatives.For example:sodium nitrate,potassium nitrate,sulphur dioxide,sodium benzoate, Potassium, Sorbate etc
B.: On the basis of sources :There are 3 types of food preservatives :1.Chemical food preservatives(Second): The chemical substances which are added to food products to extend their shelf life, inhibit the growth of microorganisms, and prevent spoilage are called Chemical food preservatives. These preservatives help maintain the quality, freshness, and safety of food by preventing the growth of bacteria, yeasts, molds, and other pathogens (an organism causing disease) .For example :
i.Sodium
Benzoate
ii.Potassium
Sorbate
iii.Sodium
Nitrite
iv.Sulfur
Dioxide
v.Propionic Acid and its salts (calcium propionate, sodium propionate): These preservatives are commonly used in bread and other baked goods to prevent the growth of molds and extend shelf life.
vi.Benzoic Acid and its salts (sodium benzoate, potassium benzoate): They are used in a wide range of products, including soft drinks, fruit juices, and pickles, to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds.
2.Natural Food preservatives (First) :
Natural food preservatives are the substances derived
from natural sources which are added to food products to extend to their shelf life, inhibit the growth of microorganisms, and prevent spoilage are called the shelf life of food products
are called natural preservatives .
i.Vinegar:
ii.Salt
iii.Sugar:
iv.Citric Acid:
v.Vitamin E (Tocopherol): Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant that can help delay the oxidation of fats and oils. It is often used in food products that contain oils.
vi..Clove Oil: Clove oil has strong antimicrobial properties and can be used as a natural food preservative. It is particularly effective against fungi and molds (fungi). Clove oil is used in some meat products and baked goods.
3.Induced ripening fruits foods preservatives : The process of accelerating the natural ripening of fruits using
various methods are called Induced ripening
fruits . There are certain substances and
techniques are used in to the induce ripening in fruits are called Induced ripening fruits foods preservatives .For example:
i.Ethylene Gas:
Ethylene is a natural plant hormone that regulates fruit
ripening. It is commonly used to induce ripening in fruits like
bananas, mangoes, and avocados. Fruits can be exposed to ethylene gas in controlled environments to speed up the ripening process.
ii.Calcium Carbide: Calcium carbide is a chemical compound that produces acetylene gas when it comes into contact with moisture. Acetylene gas has similar effects to ethylene and can be used to induce ripening in fruits.
Importance of food preservatives:
1.Preservatives help food to prevent
from spoilage caused by bacteria ,molds (large group of fungus), fungus and Yeasts .
1.High sodium product like pickle can
causes of higher blood pressure.
B.Introductions
and uses of chemicals used in cleansing:
1. Rittha :It is a herb, also known as soapnut or Indian soap berry, has a long
history of traditional use for cleansing purposes in various cultures.
Advantages:
i.Natural cleansing: Rittha contains saponins, natural
foaming agents that gently cleanse the skin and hair.
Advantages:
i.Mustard paste is used to clean
the hair, make the hair soft and strong.
The paste of wood ash is used in cleansing. It is mixed with a small amount of water to make a paste.
Advantages:
i.The paste of ash is used as an abrasive
cleaner.
ii.It is used to shines
metals, cleans dirty dishes and also removes stubborn dirt and oil.
Sajivan is a multipurpose plant that has been naturally produced
in various parts of Nepal. It has been used in various ways in
Nepal. This plant is not eaten by domestic animals.
Advantages:
i.it is used to make fences(khet
bari ko bsr) in the fields.
iii. Its juice is used to heal
burns, as an anti-cancer drug.
C.) Soap and Detergent
:
Soap :The sodium salt of long chain of fatty acid
having cleansing properties in water is
called soap . For example :i)Sodium stearate (C17H35COONa) ii)Sodium Oleate (C17H33COONa), iii) Sodium Palmitate (C17H31COONa)
It is prepared by
heating fat or oil with sodium hydroxide
solution .
The process of making
soap by hydrolysis of fat or oil with sodium hydroxide or alkali is called saponification
.
Detergents :Synthetic petrochemical obtained from hydrocarbon which is more soluble than soap is called detergent .It is more soluble and useful than that of salt .Detergent possess cleansing properties similar to the soap but they are not chemically soap therefore detergents are also called soapless soap .For example :i)Sodium lauryl sulphate ii) Alkyl benzene sulphonate iii)Sodium pyrophosphate .
Due to following reasons detergent is better than that of salts :
i)Detergent clean
more effectively in hard water than that of soap .
ii)It maintains its
cleansing power better than that of soap over long period of time .
iii)It is more
soluble in water than that soap .
iv) It also help to
save vegetable oil for human consumption .
Washing powder :A
synthetic powder having cleansing properties containing synthetic detergent about 15%-30% is called washing powder
|
Soap |
Detergent |
|
i)It is prepared from animals
fat or plants oil . ii)It is sodium salt of long chain of fatty acid . iii)It has weak cleansing properties . iv)it is very less soluble in hard water . v)It is bio-degradable . v)For example :Sodium stearate |
i)It is prepared from hydrocarbon of
petroleum . ii)It is sodium salt of long chain of
benzene sulphonic acid . iii)It is has strong cleansing properties . iv)It is soluble in hard water . v)It is non bio-degradable . vi) For example :Sodium lauryl sulphonate. |
1.Respiratory irritation: Many cleaning products, like bleach and ammonia, release fumes that can irritate the lungs, eyes, and throat. This can lead to coughing, wheezing, and asthma
2.Skin and eye damage: Direct contact with cleansing chemicals can cause skin burns, rashes, and allergic reactions.
Types of Pesticides:
A.On the basis of Environments: They are 2 types :
(i) Environmentally degradable or non persistent:
The pesticides that gradually decay after coming in contact with environmental components such as water, air, light, heat, etc are called Environmentally degradable or non persistent pesticides. For example: Dimethoate (Nugar, Roger, Dimet), Malathayan etc.

(ii) Environmentally non-degradable or
persistent: The Pesticides that do
not decay after coming in contact with environmental components such as water, air, light,
heat etc and remain in our body mixed with fat
through the food chain are called Environmentally
non-degradable or persistent Pesticides. Import, export,
sale and use of Pesticides of this group have been banned in most countries.For Example:DDT (Dichloro
diphenyl trichrolo ethane),BHC(Benzene Hexa chloride),Aldrine ,Dialdrine .
B.On the basis of target organisms :They are 5 types :
(ii) Fungicides :The Pesticides which are used to against various
types of fungal diseases in plants are called Fungicides such as: Dimethomorph,
Sectin, Mancozeb, Carbendazim etc.
(iii) Herbicides: The Pesticides which are used to kill various types of weeds that attack crops are called Herbicides .such as Butachlor, Isoproteron, Atrazine etc.
(iv) Rodenticides: The Pesticides which are used to kill
harmful animals such as rats and mice, rats, mice, rats, rabbits, etc are called Rodenticides. For example Kimateraline,
Phosphide .
(v) Miticides: The Pesticides which are used to kill mites are called Miticides. For example :Bifenazet, Phenazaquone, Proparzite, Fenpyroximate etc.
C.On the basis of nature and action: They are 4 types :
(i) Contact pesticide:The pesticides which are used to kill the Insects with soft bodies such as larvae, thrips,
whiteflies etc. come in direct contact with the outer covering are called contact pesticide .For example: Malathien, chloropyrifus etc.
(ii) Stomach pesticide:The pesticides which are used to kill the insect when the insects eat the leaves or fruits of the poisoned plants are called Stomach pesticides .Forexamle: malathion, cypermethrin, fenvalerate etc.
(iii) Systemic pesticide :The pesticides which are used to kill the insects such as Lahi, Thrips, White Binga, Leaf Miner, Gabaro by sucking the juice of poisonous plants, are called systemic pesticides etc. For control, Folithion, Biomultinim, Multinim etc. In this process the leaves or roots of the plant absorb the poison, as a result, the poison reaches the entire part and the plant itself becomes toxic.
(iv) Fumigants pesticide: The pesticides when come in contact
with the air, poisonous gases are released due to which
the insects die. These types of pesticides are called Fumigants pesticide. For example
: aluminum
phosphide, methyl bromide, etc.
Advantages of Pesticides :
i.It help to save the farmer by protecting
crops from insects and other pests .
i.Environmental Impact:
Pesticides can contaminate soil, water bodies,
and air, and also can harm non-target organisms, such as beneficial insects, birds, fish, and amphibians, disrupting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity.
The following precautions must be
taken when storing and using chemical pesticides:
(i) Pesticides should be imported,
produced, bought and used only as prescribed by the
Pesticides Management Act, 2076 and regulations.
(ii) Pesticides should be purchased
only according to the consultation of the agricultural technician.
(iii) The name should be clearly
identified on the container where the pesticide is kept.
(iv)
Storing pesticides should not be kept close to
children's access and food.
(v) Pesticides should be kept
tightly closed in airtight and leak-proof containers.
(vi) When using pesticides, the
instructions written on the label (indicator letter) of the pesticide should be
read carefully and used only.
(vii) Equipment used for spraying
pesticides should be cleaned immediately and kept in a safe place.
E.Chemical
pollution :The environmental degradation due to unscientific
and improper uses of chemical substances is called chemical pollution .
1.)Uses of
insecticides and chemical fertilizer :It causes of air
,water and soil pollution ,different diseases ,the death of fishes and other
aquatic life .
i)By scientific and proper uses of insecticides and fertilizer .
ii)By management of household wastages and plastics .
iii)By management of smoke produce
by vehicles and industries .
iv)By less uses of coloring materials in food stuff .
v)By management of uses of synthetic cleaner .








































.gif)




















































Comments
Post a Comment